
Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were Safinim for the country and Safineis for the people. The language of these endonyms and of the population was the Oscan language. However, not all the Samnites spoke Oscan, and not all the Oscan-speakers lived in Samnium.

Eynhallow is a small, presently uninhabited island, part of Orkney, off the north coast of mainland Scotland.

Hiyama is a district located in Hiyama Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.

Mogorjelo (Могорјело) is a Roman villa rustica which date back to the early 4th century AD. It is situated on a hill between the rivers Trebižat and Neretva, 5 km south of Čapljina, alongside the road to Gabela in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The area is currently protected by the state as the National Monument.
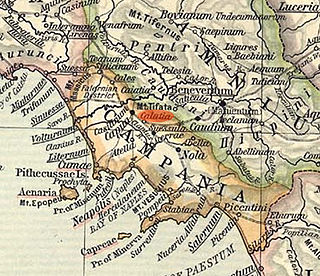
Cālātia was an ancient town of Campania, southern Italy, c. 10 km southeast of Capua, on the Via Appia, near the point where the Via Popillia branches off from it. It is represented by a locality known as Villa Galazia and by the church of San Giacomo alle Galazze, within the modern town of Maddaloni, very near the boundary with the neighboring town of San Nicola la Strada, and right on the Via Appia. The Via Appia here, as at Capua, abandons its former SE direction for a length of 2,000 Oscan feet (500 m), for which it runs due east and then resumes its course SE. Ruins include remains of the walls and the pre-Roman necropolis was partially excavated in 1882. The ten shafts lined with slabs of tuff which may have been the approaches to tombs or may have served as wells.
Bandora is a census town in Ponda Taluka in North Goa district in the state of Goa, India.

Torricella Peligna is a comune and town in the Province of Chieti in the Abruzzo region of Italy.

La Ribera is one of the areas of the quarter of Sant Pere, Santa Caterina i la Ribera of Ciutat Vella of Barcelona.
Villanueva de Carazo is a municipality located in the province of Burgos, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 30 inhabitants.

Adelsö Church is a church located on the Lake Mälaren island of Adelsö, in Ekerö Municipality in central eastern Sweden.
Karmrashen is a village in the Vayk Municipality of the Vayots Dzor Province of Armenia.

Koghb is a village and rural community in the Noyemberyan Municipality of the Tavush Province of Armenia, located near the town of Noyemberyan.
The Baths of Licinius Sura or Thermae Suranae were a private ancient Roman bath complex built by Lucius Licinius Sura on the Aventine Hill in Rome.
Bathonea is a long-lost ancient Greek city that was located on the European shore of the sea of Marmara, 20 km west from Istanbul, Turkey in Küçükçekmece.

Aphrodisias, sometimes called Aphrodisias of Cilicia to distinguish it from the town of the same name in Caria, was a port city of ancient Cilicia whose ruins now lie near Cape Tisan in Mersin Province, Turkey.

The Tirana Mosaic is a landmark in Tirana, Albania.
Metropolis was an ancient town in the north of Phrygia, and, as the name seems to indicate, a capital of the ancient kings of Phrygia, though Stephanus of Byzantium derives the name from the mother of the gods. It was situated to the north of Synnada, and must not be confounded with another town of the same name in the south of Phrygia. Its site is, in all probability, indicated by the ruins of Pismesh Kalasi, north of Doganlu, which show a very antique style of architecture, and mainly consist of tombs cut into the rocks; one of these tombs is that of king Midas. Although William Martin Leake is inclined to think that these ruins mark the site of Nicoleia; William Smith credits other travelers who identify them with Metropolis. From the extent of the ruins, it would seem that in the time of the Roman emperors Metropolis was an important town; but afterwards it declined, though it is still mentioned by Hierocles.
Delphin or Karandas was a town of ancient Thrace, inhabited during Roman times.
Rhegion, also called "Rhagion" or "Rhegium", was a town of ancient Thrace, inhabited during Byzantine times.

Toprak-Kala, in modern Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan, was an ancient palace city and the capital of in Chorasmia in the 2nd/3rd century CE, where wall paintings, coins and archives were discovered. Its history covers a period from the 1st to the 5th century CE. It is part of the "Fifty fortresses oasis" in modern-day Uzbekistan.
















