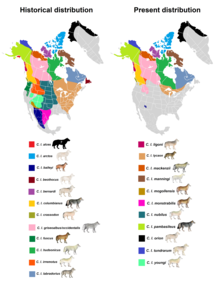
There are 38 subspecies of Canis lupus listed in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World. These subspecies were named over the past 250 years, and since their naming, a number of them have gone extinct. The nominate subspecies is the Eurasian wolf.

The moose or elk is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus Alces. It is also the tallest, and the second-largest, land animal in North America, falling short only of the American bison in body mass. Most adult male moose have broad, palmate antlers; other members of the deer family have pointed antlers with a dendritic ("twig-like") configuration. Moose inhabit the circumpolar boreal forests or temperate broadleaf and mixed forests of the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in cooler, temperate areas as well as subarctic climates.

The red wolf is a canine native to the southeastern United States. Its size is intermediate between the coyote and gray wolf.

The wolf, also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gray wolves, as popularly understood, only comprise naturally-occurring wild subspecies. The wolf is the largest extant member of the family Canidae, and is further distinguished from other Canis species by its less pointed ears and muzzle, as well as a shorter torso and a longer tail. The wolf is nonetheless related closely enough to smaller Canis species, such as the coyote and the golden jackal, to produce fertile hybrids with them. The wolf's fur is usually mottled white, brown, gray, and black, although subspecies in the arctic region may be nearly all white.

The eastern wolf, also known as the timber wolf, Algonquin wolf and eastern timber wolf, is a canine of debated taxonomy native to the Great Lakes region and southeastern Canada. It is considered to be either a unique subspecies of gray wolf or red wolf or a separate species from both. Many studies have found the eastern wolf to be the product of ancient and recent genetic admixture between the gray wolf and the coyote, while other studies have found some or all populations of the eastern wolf, as well as coyotes, originally separated from a common ancestor with the wolf over 1 million years ago and that these populations of the eastern wolf may be the same species as or a closely related species to the red wolf of the Southeastern United States. Regardless of its status, it is regarded as unique and therefore worthy of conservation with Canada citing the population in eastern Canada as being the eastern wolf population subject to protection.

The Arctic wolf, also known as the white wolf, polar wolf, and the Arctic grey wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to the High Arctic tundra of Canada's Queen Elizabeth Islands, from Melville Island to Ellesmere Island. Unlike some populations that move between tundra and forest regions, Arctic wolves spend their entire lives north of the northern treeline. Their distribution to south is limited to the northern fringes of the Middle Arctic tundra on the southern half of Prince of Wales and Somerset Islands. It is a medium-sized subspecies, distinguished from the northwestern wolf by its smaller size, its whiter colouration, its narrower braincase, and larger carnassials. Since 1930, there has been a progressive reduction in size in Arctic wolf skulls, which is likely the result of wolf-dog hybridization.

The Hokkaido wolf, also known as the Ezo wolf and in Russia as the Sakhalin wolf, is an extinct subspecies of gray wolf that once inhabited coastal northeast Asia. Its nearest relatives were the wolves of North America rather than Asia. It was exterminated in Hokkaido during the Meiji Restoration period, when American-style agricultural reforms incorporated the use of strychnine-laced baits to kill livestock predators. Some taxonomists believe that it survived up until 1945 on the island of Sakhalin. It was one of two subspecies that were once found in the Japanese archipelago, the other being the Japanese wolf.

The northwestern wolf, also known as the Mackenzie Valley wolf, Alaskan timber wolf, or Canadian timber wolf, is a subspecies of gray wolf in western North America. Arguably the largest gray wolf subspecies in the world, it ranges from Alaska, the upper Mackenzie River Valley; southward throughout the western Canadian provinces, aside from prairie landscapes in its southern portions, as well as the Northwestern United States.

The Great Plains wolf, also known as the buffalo wolf or loafer, is a subspecies of gray wolf that once extended throughout the Great Plains, from southern Manitoba and Saskatchewan in Canada southward to northern Texas in the United States. The subspecies was thought to be extinct in 1926, until studies declared that its descendants were found in Minnesota, Wisconsin and Michigan. They were described as a large, light-colored wolf but with black and white varying between individual wolves, with some all white or all black. The Native Americans of North Dakota told of how only three Great Plains wolves could bring down any sized bison.

The Vancouver Island wolf, also known as the coastal wolf or sea wolf is a subspecies of grey wolf, endemic to the coast of the Pacific Northwest. They are a unique species of wolf due to their semi-aquatic lifestyle, which includes a diet that is almost entirely marine-based.

The British Columbia wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf which lives in a narrow region that includes those parts of the mainland coast and near-shore islands that are covered with temperate rain-forest, which extends from Vancouver Island, British Columbia, to the Alexander Archipelago in south-east Alaska. This area is bounded by the Coast Mountains.
Gregory's wolf, also known as the Mississippi Valley wolf, was a subspecies of the red wolf. It was declared extinct in 1980. It once roamed the regions in and around the lower Mississippi River basin.

The Hudson Bay wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf native to the northern Kivalliq Region, including the northwestern coast of Hudson Bay in Canada. It was first classed as a distinct subspecies in 1941 by Edward Goldman, who described it as being a white colored, medium-sized subspecies similar to C. l. arctos, but with a flatter skull. This wolf is recognized as a subspecies of Canis lupus in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World (2005).

The Alexander Archipelago wolf, also known as the Islands wolf, is a subspecies of the gray wolf. The coastal wolves of southeast Alaska inhabit the area that includes the Alexander Archipelago, its islands, and a narrow strip of rugged coastline that is biologically isolated from the rest of North America by the Coast Mountains.

The Baffin Island wolf, also known as the Baffin Island tundra wolf, is a subspecies of grey wolf which resides exclusively on Baffin Island and several nearby islands. It was not formally recognized as a subspecies until 1943, when it was given its taxonomic classification by Anderson. This wolf is recognized as a subspecies of Canis lupus in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World (2005).

The Mogollon mountain wolf is an extinct subspecies of gray wolf whose range once included Arizona and New Mexico. It is darker than its more northern cousins, and has a highly arched frontal bone.

The Greenland wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf that is native to Greenland. Historically, it was heavily persecuted, but today it is fully protected and about 90% of the wolf's range falls within the boundaries of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

The Interior Alaskan wolf, also known as the Yukon wolf, is a subspecies of gray wolf native to parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, Interior Alaska and Yukon.

The southern Rocky Mountain wolf is an extinct subspecies of gray wolf which was once distributed over southeastern Idaho, southwestern Wyoming, northeastern Nevada, Utah, western and central Colorado, northwestern Arizona, and northwestern New Mexico. It was a light-colored, medium-sized subspecies closely resembling the Great Plains wolf, though larger, with more blackish-buff hairs on the back. This wolf went extinct by 1935. Wolves of the subspecies Canis lupus occidentalis have now been reestablished in Idaho and Wyoming.

The Mongolian wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf which is native to Mongolia, northern and central China, Korea, and the Ussuri region of Russia.