Related Research Articles

Alappuzha district, is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala. It was formed as Alleppey district on 17 August 1957, the name of the district being changed to Alappuzha in 1990. Alappuzha is the smallest district of Kerala. Alleppey town, the district headquarters, was renamed Alappuzha in 2012, even though the anglicised name is still commonly used to describe the town as well as the district.

Kollam, also known by its former name Quilon, is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is 71 km (44 mi) north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The city is on the banks of Ashtamudi Lake and the Kallada river. Kollam is the fourth largest city in Kerala and is known for cashew processing and coir manufacturing. It is the southern gateway to the Backwaters of Kerala and is a prominent tourist destination. Kollam is one of the most historic cities with continuous settlements in India. Geographically, Quilon formation seen around coastal cliffs of Ashtamudi Lake, represent sediments laid down in the Kerala basin that existed during Mio-Pliocene times.

Oommen Chandy was the 10th chief minister of Kerala, serving from 2004 to 2006 and 2011 to 2016. He served also as the leader of the opposition in the Kerala Legislative Assembly from 2006 to 2011.

Vallam kali, also known as snake boat race, is a traditional boat race in Kerala, India. It is a form of canoe racing, and uses paddled war canoes. It is mainly conducted during the season of the harvest festival Onam in spring. Vallam kali includes races of many kinds of paddled longboats and 'snake boats'. Each team spends about ₹6 lakhs for the Nehru Trophy Boat Race.

The Kerala backwaters are a network of brackish lagoons and canals lying parallel to the Arabian Sea of the Malabar coast of Kerala state in south-western India. It also includes interconnected lakes, rivers, and inlets, a labyrinthine system formed by more than 900 km (560 mi) of waterways, and sometimes compared to bayous. The network includes five large lakes linked by canals, both man made and natural, fed by 38 rivers, and extending virtually half the length of Kerala state. The backwaters were formed by the action of waves and shore currents creating low barrier islands across the mouths of the many rivers flowing down from the Western Ghats range. In the midst of this landscape there are a number of towns and cities, which serve as the starting and end points of backwater cruises. There are 34 backwaters in Kerala. Out of it, 27 are located either closer to Arabian Sea or parallel to the sea. The remaining 7 are inland navigation routes.
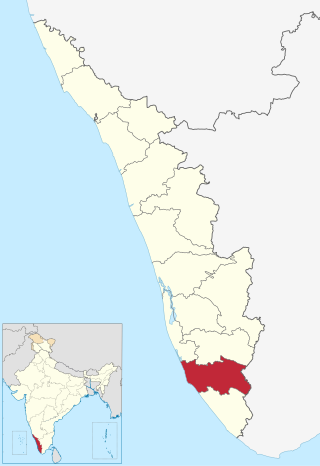
Kollam district, is one of 14 districts of the state of Kerala, India. The district has a cross-section of Kerala's natural attributes; it is endowed with a long coastline, a major Laccadive Sea seaport and an inland lake. The district has many water bodies. Kallada River is one among them, and land on the east bank of the river is East Kallada and that on the west bank is West Kallada.

Bekal is a small town in the Kasaragod district on the West coast of the state of Kerala, India.

Alappuzha or Alleppey is the administrative headquarters of Alappuzha district in the state of Kerala, India. The Backwaters of Alappuzha are one of the most popular tourist attractions in India which attracts millions of domestic and international tourists.

Kerala, a state situated on the tropical Malabar Coast of southwestern India, is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the country. Named as one of the ten paradises of the world by National Geographic Traveler, Kerala is famous especially for its ecotourism initiatives and beautiful backwaters. Its unique culture and traditions, coupled with its varied demography, have made Kerala one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world. Several international agencies ranging from UNESCO to National Geographic have recognised the state's tourism potential. Kerala was named by TIME magazine in 2022 among the 50 extraordinary destinations to explore in its list of the World's Greatest Places. In 2023, Kerala was listed at the 13th spot in The New York Times' annual list of places to visit and was the only tourist destination listed from India.

Kerala State Water Transport Department (SWTD) is a governmental department that regulates the inland navigation systems in the Indian state of Kerala and provides inland water transport facilities. It stands for catering to the traffic needs of the inhabitants of the waterlogged areas of the Districts of Alappuzha, Kottayam, Kollam, Ernakulam, Kannur and Kasaragod. The department is headed by the State Minister in charge of transportation.
Karunagappally is a municipality in the Kollam district of Kerala, India. It is 24 km north of Kollam and 60 km (37 mi) south of Alappuzha. Karunagappally taluk consists of Alappad, Ochira, Adinad, Karunagappally, Thazhava, Pavumba, Thodiyoor, Kallalibhagom, Thevalakkara, Chavara, Neendakara, Clappana, Kulasekharapuram, Thekkumbhagam, Ayanivelikulangara, Panmana, Ponmana and Vadakumthala. The taluk is bound on the north by Kayamkulam, on the east by Kunnathur taluk, on the south by Kollam and on the west by the Arabian Sea. It is one of the fastest developing towns in Kerala and is part of Kollam metropolitan area.

The West Coast Canal or National Waterway No 3 is a 205 km (127 mi) long inland navigational route located in Kerala, India, which runs from Kollam to Kottapuram. It was declared a National Waterway in 1993. In addition to the main stretch, Champakara and Udyogmandal canals are navigable and connect the industrial centers of Kochi to Kochi port Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) under the Ministry of Shipping is coordinating the task for developing, monitoring and administering national waterways. It is the first National Waterway in the country with 24-hour navigation facilities along the entire stretch. It has been extended to Kozhikode by the National Waterways Act, 2016. The National Waterway 3 mainly passes through the previous Thiruvananthapuram–Shoranur canal.

The United Democratic Front government led by Oommen Chandy sworn in on 18 May 2011. Seven of the total 20 members of the Cabinet took office on 18 May and the rest sworn in on 23 May after completing discussion with member parties of the UDF.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Kerala:

Kollam Port is one of the historic ports situated 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) away from Downtown Kollam It is the second largest port in Kerala by volume of cargo handled and facilities. Located on the south-west coast of India, under the name of Quilon Port it became one of the country's most important trade hubs from the ninth to the seventeenth centuries. Kollam was one of the five Indian ports visited by Ibn Battuta.

Kollam Bypass is a part of NH 66 that bypasses CBD of Kollam city in Kerala, India. The busy 13.141 km long bypass starts at Mevaram in the south to Kavanad in the north, via Ayathil, Kallumthazham, Kadavoor and Kureepuzha in Kollam city. It is a joint venture between the central and state government. It was inaugurated on 15 January 2019 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.

Transport in Kollam includes various modes of road, rail and water transportation in the city and its suburbs. State-owned Kerala State Road Transport Corporation buses, private buses, Indian Railways, state-owned Kerala State Water Transport Department boats & ferry, taxis and auto rickshaws are serving the city of Kollam. The city had a strong commercial reputation since the days of the Phoenicians and Romans. Ibn Battuta mentioned Kollam Port as one of the five Indian ports he had seen during the course of his twenty-four year travels.

Kollam KSWTD Boat Jetty or Kollam KSWTD Ferry Station is an transport hub in the city of Kollam in Kerala, India, one of 14 ferry stations owned by the Kerala State Water Transport Department.

City of Kollam or Quilon is a Port city in South India and was the commercial capital of erstwhile Kingdom of Travancore. It is situated on the Laccadive Sea coast of South Kerala. The city is known as the "Gateway to the backwaters of Kerala". The city lies on the banks of Ashtamudi Lake, Kerala's second largest lake, on the Arabian sea coast. Major parts of Kollam city are covered by Ashtamudi Lake.
Waterways have always been an important mode of transport in Kerala. The total length of navigable route in Kerala was 1,900 kilometres and the navigable rivers constitute about 54 per cent of the waterways. The 41 West-flowing rivers together with the backwaters are an integrated part of the inland navigation system in Kerala. In Kerala water transportation through these channels are mainly small distant passenger services, informal country boats, freight transportation to PSU's such as Fertilisers and Chemicals Travancore, Kochi etc.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Special Correspondent (2 June 2013). "Tourism to take wings with seaplane's take-off". The Hindu Delhi edition. p. 7.
- 1 2 "Despite brouhaha, seaplane project fails to take off". The New Indian Express . 24 August 2013. Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ↑ "Kerala Government keen to re-start sea plane service as early as possible". Daily News and Analysis . 25 February 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ↑ "Seaplane project fastest in Kerala". Times News Network. Kochin, India: The Times of India. 1 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- 1 2 IANS (2 June 2013). "Kerala launches India's first seaplane service". Hindustan Times . Kollam, India. Archived from the original on 3 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Kerala CM Oommen Chandy launches India's first seaplane service". IANS. IBNLive.com. 3 June 2013. Archived from the original on 29 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- 1 2 "Kerala launches country's first tourist seaplane service". The Times of India . Kollam, India. 2 June 2013. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ↑ "Kerala CM inaugurates seaplane Service". newskerala.com. Kollam, India. 2 June 2013. Archived from the original on 6 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ↑ "Hopes sink for seaplane service". IANS. IBNLive.com. 5 December 2013. Retrieved 11 August 2014.