
Vigna mungo, also known as black gram, urad bean, urid bean, matimah, matikolai, mash kalai, maas/kalo daal, uzhunnu parippu, ulundu parippu, minapa pappu, uddu, or black matpe, is a bean grown in South Asia. Like its relative, the mung bean, it has been reclassified from the Phaseolus to the Vigna genus. The product sold as black lentil is usually the whole urad bean, whereas the split bean is called white lentil. It should not be confused with the much smaller true black lentil.

Vigna umbellata, previously Phaseolus calcaratus, is a warm-season annual vine legume with yellow flowers and small edible beans. It is commonly called ricebean or rice bean. To date, it is little known, little researched and little exploited. It is regarded as a minor food and fodder crop and is often grown as intercrop or mixed crop with maize, sorghum or cowpea, as well as a sole crop in the uplands, on a very limited area. Like the other Asiatic Vigna species, ricebean is a fairly short-lived warm-season annual. Grown mainly as a dried pulse, it is also important as a fodder, a green manure and a vegetable. Ricebean is most widely grown as an intercrop, particularly of maize, throughout Indo-China and extending into southern China, India, Nepal and Bangladesh. In the past it was widely grown as lowland crop on residual soil water after the harvest of long-season rice, but it has been displaced to a great extent where shorter duration rice varieties are grown. Ricebean grows well on a range of soils. It establishes rapidly and has the potential to produce large amounts of nutritious animal fodder and high quality grain.

Rewari district is one of the 22 districts in the state of Haryana, India. It was carved out of Gurgaon district by the Government of Haryana on 1 November 1989. It is also part of the National Capital Region. The administrative headquarter of the district is the city of Rewari, which is also the biggest city in the district. In medieval times, it was an important market town. It is located in southern Haryana. As of 2011, it is the second least populous district of Haryana after Panchkula.

Lucknow district is a district located in the state of Uttar Pradesh in northern India. The city of Lucknow is the district headquarters and the district is part of Lucknow Division. It is also the capital city of Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow is bounded on the east by Barabanki district, on the west by Unnao and Hardoi districts, on the south by Raebareli district and in the north by Sitapur district.

Raebareli district is a district of Uttar Pradesh state in northern India. The city of Raebareli is the district headquarters. This district is a part of Lucknow Division in Uttar Pradesh state. The total area of Raebareli district is 3,371 Sq. km.

Alwar is a district in the state of Rajasthan in northern India, whose district headquarters is Alwar city. The district covers 8,380 km2. It is bound on the north by Rewari district of Haryana, on the east by Bharatpur district of Rajasthan and Nuh district of Haryana, on the south by Dausa district, and on the west by Jaipur district.

Drought has resulted in millions of deaths in India over the years. Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the country's climate: a favorable monsoon is critical to securing water for irrigating India's crops. In parts of India, failure of the monsoons causes water shortages, resulting in poor yields. This is particularly true of major drought-prone regions southeastern Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, and Rajasthan.

A western disturbance is an extratropical storm originating in the Mediterranean region that brings sudden winter rain to the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent, which extends as east as up to northern parts of Bangladesh and South eastern Nepal. It is a non-monsoonal precipitation pattern driven by the westerlies. The moisture in these storms usually originates over the Mediterranean Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea. Extratropical storms are a global phenomena with moisture usually carried in the upper atmosphere, unlike their tropical counterparts where the moisture is carried in the lower atmosphere. In the case of the Indian subcontinent, moisture is sometimes shed as rain when the storm system encounters the Himalayas. Western disturbances are more frequent and stronger in the winter season.

Rabi crops or the rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. Complementary to the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after the rabi and zaid crops are harvested one after another respectively.

Agriculture accounts for 22 percent of Cambodia’s GDP, and employs about 3 million people.

Rice production in Bangladesh commands vast economic significance across multiple sectors and socioeconomic factors. Rice is Bangladesh's primary crop and staple food, dominating agricultural production, employment, nutritional intake, and contributing substantially to national income. Bangladesh ranks as the third-largest producer of rice globally, reaching about 39.1 million tonnes in 2023.
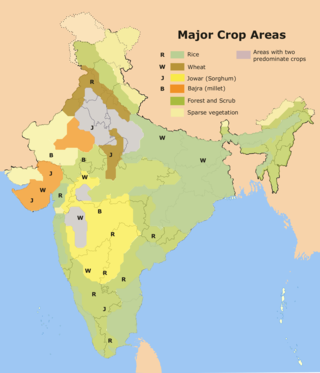
Rice production in India is an important part of the national economy.
Datta is a village in Hansi Tehsil, Hisar district, in Haryana, India. It is situated 36 km from Hisar city and 20 km from Hansi city on the road which also leads to Barwala. At Data there is another road that leads to Narnaund. It is 15 km from Narnaund Tehsil and only 16 km from Barwala town. Datta comes under Roghi Khap Panchayat. There is an oil depot of HPCL situated on Bianakhera road.
Madha is a village of Jats located in Hissar district in Haryana, India.

Farming systems in India are strategically utilized, according to the locations where they are most suitable. The farming systems that significantly contribute to the agriculture of India are subsistence farming, organic farming, industrial farming. Regions throughout India differ in types of farming they use; some are based on horticulture, ley farming, agroforestry, and many more. Due to India's geographical location, certain parts experience different climates, thus affecting each region's agricultural productivity differently. India is very dependent on its monsoon cycle for large crop yields. India's agriculture has an extensive background which goes back to at least 9 thousand years. In India, in the alluvial plains of the Indus River in Pakistan, the old cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa experienced an apparent establishment of an organized farming urban culture. That society, known as the Harappan or Indus civilization, flourished until shortly after 4000 BP; it was much more comprehensive than those of Egypt or Babylonia and appeared earlier than analogous societies in northern China. Currently, the country holds the second position in agricultural production in the world. In 2007, agriculture and other industries made up more than 16% of India's GDP. Despite the steady decline in agriculture's contribution to the country's GDP, agriculture is the biggest industry in the country and plays a key role in the socio-economic growth of the country. India is the second-largest producer of wheat, rice, cotton, sugarcane, silk, groundnuts, and dozens more. It is also the second biggest harvester of vegetables and fruit, representing 8.6% and 10.9% of overall production, respectively. The major fruits produced by India are mangoes, papayas, sapota, and bananas. India also has the biggest number of livestock in the world, holding 281 million. In 2008, the country housed the second largest number of cattle in the world with 175 million.
Zaid crops are summer season crops. They grow for a short time period between Rabi and Kharif crops, mainly from March to June. These crops are mainly grown in the summer season during a period called the Zaid crop season. They require warm dry weather as major growth period and longer day length for flowering. Some summer months and rainy season is required. These crops also mature early.
Khanpur Ahir or Khanpur Aheer is a village in Mundawar Mandal in Alwar district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Khanpur Ahir is 40 km (25 mi) from its district headquarters, Alwar. It is 140 km (87 mi) from its state capital, Jaipur.
Bihar lies in the river plains of the basin of the river Ganga. As a result, its land contains fertile alluvial soil and groundwater resources. This makes the agriculture of Bihar rich and diverse. Rice, wheat, and maize are the major cereal crops. Arhar, urad, moong, gram, pea, lentils, and khesaria are some of the pulses cultivated in Bihar. Bihar is the fourth largest producer of vegetables, which is dominated by potato, onion, eggplant, and cauliflower. In fruit cultivation, it is the largest producer of lychee and the third largest producer of pineapple, as well as a major producer of mango, banana, and guava. Sugar cane and jute are two other major cash crops of Bihar.
Amarsar is a village in Jaipur district, Rajasthan, India.

The Pradhan Mantri fasal bima yojana (PMFBY) launched on 18 February 2016 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi is an insurance service for farmers for their yields. It was formulated in line with One Nation–One Scheme theme by replacing earlier two schemes Agricultural insurance in India#National Agriculture Insurance Scheme and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme by incorporating their best features and removing their inherent drawbacks (shortcomings). It aims to reduce the premium burden on farmers and ensure early settlement of crop assurance claim for the full insured sum.













