
Adoptionism, also called dynamic monarchianism, is an early Christian nontrinitarian theological doctrine, subsequently revived in various forms, which holds that Jesus was adopted as the Son of God at his baptism, his resurrection, or his ascension. How common adoptionist views were among early Christians is debated, but it appears to have been most popular in the first, second, and third centuries. Some scholars see adoptionism as the belief of the earliest followers of Jesus, based on the epistles of Paul and other early literature. However, adoptionist views sharply declined in prominence in the fourth and fifth centuries, as Church leaders condemned it as a heresy.

Christ, used by Christians as both a name and a title, unambiguously refers to Jesus. It is also used as a title, in the reciprocal use "Christ Jesus", meaning "the Messiah Jesus", and independently as "the Christ". The Pauline epistles, the earliest texts of the New Testament, often refer to Jesus as "Christ Jesus" or "Christ".

In Christianity, Christology, translated from Greek as 'the study of Christ', is a branch of theology that concerns Jesus. Different denominations have different opinions on questions such as whether Jesus was human, divine, or both, and as a messiah what his role would be in the freeing of the Jewish people from foreign rulers or in the prophesied Kingdom of God, and in the salvation from what would otherwise be the consequences of sin.

The resurrection of Jesus is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lord. According to the New Testament writing, Jesus was firstborn from the dead, ushering in the Kingdom of God. He appeared to his disciples, calling the apostles to the Great Commission of forgiving sin and baptizing repenters, and ascended to Heaven.
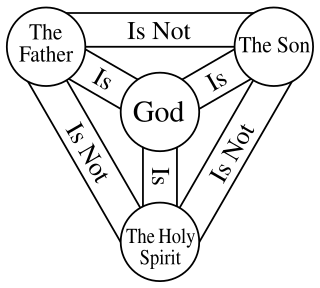
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity is the central doctrine concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son and God the Holy Spirit, three distinct persons (hypostases) sharing one essence/substance/nature (homoousion) As the Fourth Lateran Council declared, it is the Father who begets, the Son who is begotten, and the Holy Spirit who proceeds. In this context, one essence/nature defines what God is, while the three persons define who God is. This expresses at once their distinction and their indissoluble unity. Thus, the entire process of creation and grace is viewed as a single shared action of the three divine persons, in which each person manifests the attributes unique to them in the Trinity, thereby proving that everything comes "from the Father," "through the Son," and "in the Holy Spirit."

Lamb of God is a title for Jesus that appears in the Gospel of John. It appears at John 1:29, where John the Baptist sees Jesus and exclaims, "Behold the Lamb of God who takes away the sin of the world." It appears again in John 1:36.

In Christian theology, the Harrowing of Hell is an Old English and Middle English term referring to the period of time between the Crucifixion of Jesus and his resurrection. In triumphant descent, Christ brought salvation to the souls held captive there since the beginning of the world.

In Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God as written in the Bible's New Testament, and in mainstream Christian denominations he is God the Son, the second Person in the Trinity. He is believed to be the Jewish messiah who is prophesied in the Hebrew Bible, which is called the Old Testament in Christianity. Through his crucifixion and subsequent resurrection, God offered humans salvation and eternal life, that Jesus died to atone for sin to make humanity right with God.
In Christian theology, kenosis is the "self-emptying" of Jesus. The word ἐκένωσεν is used in the Epistle to the Philippians: "[Jesus] made himself nothing" (NIV), or "[he] emptied himself" (NRSV), using the verb form κενόω, meaning "to empty".

Two names and a variety of titles are used to refer to Jesus in the New Testament. In Christianity, the two names Jesus and Emmanuel that refer to Jesus in the New Testament have salvific attributes. After the crucifixion of Jesus the early Church did not simply repeat his messages, but focused on him, proclaimed him, and tried to understand and explain his message. One element of the process of understanding and proclaiming Jesus was the attribution of titles to him. Some of the titles that were gradually used in the early Church and then appeared in the New Testament were adopted from the Jewish context of the age, while others were selected to refer to, and underscore the message, mission and teachings of Jesus. In time, some of these titles gathered significant Christological significance.
In Christian theology, the beatific vision is the ultimate direct self-communication of God to the individual person. A person possessing the beatific vision reaches, as a member of redeemed humanity in the communion of saints, perfect salvation in its entirety, i.e., heaven. The notion of vision stresses the intellectual component of salvation, though it encompasses the whole of human experience of joy, happiness coming from seeing God finally face to face and not imperfectly through faith..

Hans Urs von Balthasar was a Swiss theologian and Catholic priest who is considered an important Catholic theologian of the 20th century. Pope John Paul II announced his choice of Balthasar to become a cardinal, but he died shortly before the consistory. Cardinal Joseph Ratzinger said in his funeral oration for Balthasar that "he is right in what he teaches of the faith" and that he "points the way to the sources of living water".

Christian meditation is a form of prayer in which a structured attempt is made to become aware of and reflect upon the revelations of God. The word meditation comes from the Latin word meditārī, which has a range of meanings including to reflect on, to study, and to practice. Christian meditation is the process of deliberately focusing on specific thoughts and reflecting on their meaning in the context of the love of God.

In Christian theology, the imitation of Christ is the practice of following the example of Jesus. In Eastern Christianity, the term life in Christ is sometimes used for the same concept.
Theopoetics in its modern context is an interdisciplinary field of study that combines elements of poetic analysis, process theology, narrative theology, and postmodern philosophy. Originally developed by Stanley Hopper and David Leroy Miller in the 1960s and furthered significantly by Amos Wilder with his 1976 text, Theopoetic: Theology and the Religious Imagination.
Christian theology is the theology of Christian belief and practice. Such study concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theologians use biblical exegesis, rational analysis and argument. Theologians may undertake the study of Christian theology for a variety of reasons, such as in order to:
The perfection of Christ is a principle in Christology which asserts that Christ's human attributes exemplified perfection in every possible sense. Another perspective characterizes Christ's perfection as purely spiritual and moral, while his humanistic traits are subject to flaw, potential, and improvement as part of the current human condition.

The love of Christ is a central element of Christian belief and theology. It refers to the love of Jesus Christ for humanity, the love of Christians for Christ, and the love of Christians for others. These aspects are distinct in Christian teachings—the love for Christ is a reflection of his love for all people.

Philippians 3 is the third chapter of the Epistle to the Philippians in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It is authored by Paul the Apostle, probably in the mid-50s or early 60s CE and addressed to the Christians in Philippi. This chapter contains Paul's comments and exhortations centering on a narrative about his life.
In Christianity, the title Son of God refers to the status of Jesus as the divine son of God the Father. In Trinitarian Christianity, it also refers to his status as God the Son, the second Person of the Trinity or hypostasis of the Trinity.















