Related Research Articles

The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats, with Turtle currently being the most widely used notation.
The Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies. Ontologies are a formal way to describe taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects.
XML Linking Language, or XLink, is an XML markup language and W3C specification that provides methods for creating internal and external links within XML documents, and associating metadata with those links.
In computer hypertext, a URI fragment is a string of characters that refers to a resource that is subordinate to another, primary resource. The primary resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), and the fragment identifier points to the subordinate resource.
RDF Schema (Resource Description Framework Schema, variously abbreviated as RDFS, RDF(S), RDF-S, or RDF/S) is a set of classes with certain properties using the RDF extensible knowledge representation data model, providing basic elements for the description of ontologies. It uses various forms of RDF vocabularies, intended to structure RDF resources. RDF and RDFS can be saved in a triplestore, then one can extract some knowledge from them using a query language, like SPARQL.
RDFa or Resource Description Framework in Attributes is a W3C Recommendation that adds a set of attribute-level extensions to HTML, XHTML and various XML-based document types for embedding rich metadata within Web documents. The Resource Description Framework (RDF) data-model mapping enables its use for embedding RDF subject-predicate-object expressions within XHTML documents. It also enables the extraction of RDF model triples by compliant user agents.
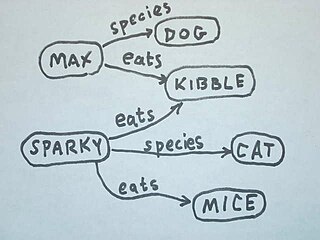
The ultimate goal of semantic technology is to help machines understand data. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, well-known technologies are RDF and OWL. These technologies formally represent the meaning involved in information. For example, ontology can describe concepts, relationships between things, and categories of things. These embedded semantics with the data offer significant advantages such as reasoning over data and dealing with heterogeneous data sources.
Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS) is a W3C recommendation designed for representation of thesauri, classification schemes, taxonomies, subject-heading systems, or any other type of structured controlled vocabulary. SKOS is part of the Semantic Web family of standards built upon RDF and RDFS, and its main objective is to enable easy publication and use of such vocabularies as linked data.
AGROVOC is a multilingual controlled vocabulary covering all areas of interest of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), including food, nutrition, agriculture, fisheries, forestry and the environment. By November 2021, the vocabulary consisted of over 39,600 concepts with up to 924,000 terms in up to 41 different languages. It is a collaborative effort, edited by a community of experts and coordinated by FAO. AGROVOC is made available by FAO as an RDF/SKOS-XL concept scheme and published as a linked data set aligned to 20 other vocabularies.
Agricultural Information Management Standards (AIMS) is a web site managed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) for accessing and discussing agricultural information management standards, tools and methodologies connecting information workers worldwide to build a global community of practice. Information management standards, tools and good practices can be found on AIMS:
The International Society for Knowledge Organization, or ISKO, is a professional association for scholars of knowledge organization, knowledge structures, classification studies, and information organization and structure.
Metadata Authority Description Schema (MADS) is an XML schema developed by the United States Library of Congress' Network Development and Standards Office that provides an authority element set to complement the Metadata Object Description Schema (MODS).

ISO 25964 is the international standard for thesauri, published in two parts as follows:
ISO 25964 Information and documentation - Thesauri and interoperability with other vocabulariesPart 1: Thesauri for information retrieval [published August 2011] Part 2: Interoperability with other vocabularies [published March 2013]
In library and information science documents are classified and searched by subject – as well as by other attributes such as author, genre and document type. This makes "subject" a fundamental term in this field. Library and information specialists assign subject labels to documents to make them findable. There are many ways to do this and in general there is not always consensus about which subject should be assigned to a given document. To optimize subject indexing and searching, we need to have a deeper understanding of what a subject is. The question: "what is to be understood by the statement 'document A belongs to subject category X'?" has been debated in the field for more than 100 years
JSON-LD is a method of encoding linked data using JSON. One goal for JSON-LD was to require as little effort as possible from developers to transform their existing JSON to JSON-LD. JSON-LD allows data to be serialized in a way that is similar to traditional JSON. It was initially developed by the JSON for Linking Data Community Group before being transferred to the RDF Working Group for review, improvement, and standardization, and is currently maintained by the JSON-LD Working Group. JSON-LD is a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation.
Birger Hjørland is a professor of knowledge organization at the Royal School of Library and Information Science (RSLIS) in Copenhagen. His main areas of study pertain to theory of library and information science and of knowledge organization. Hjørland has contributed important developments to domain analysis and concept theory. He has been cited as an anchor of North American knowledge organization studies, as well as an information science pioneer.

Ingetraut Dahlberg was a German information scientist and philosopher who developed the universal Information Coding Classification covering some 6,500 subject fields. Her career spanned various roles in research, teaching, editing, and publishing. Dahlberg founded the journal International Classification as well as both the scientific Society for Classification and International Society for Knowledge Organization.
The Information Coding Classification (ICC) is a classification system covering almost all extant 6500 knowledge fields. Its conceptualization goes beyond the scope of the well known library classification systems, such as Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC), Universal Decimal Classification (UDC), and Library of Congress Classification (LCC), by extending also to knowledge systems that so far have not afforded to classify literature. ICC actually presents a flexible universal ordering system for both literature and other kinds of information, set out as knowledge fields. From a methodological point of view, ICC differs from the above-mentioned systems along the following three lines:
- Its main classes are not based on disciplines but on nine live stages of development, so-called ontical levels.
- It breaks them roughly down into hierarchical steps by further nine categories which makes decimal number coding possible.
- The contents of a knowledge field is earmarked via a digital position scheme, which makes the first hierarchical step refer to the nine ontical levels, and the second hierarchical step refer to nine functionally ordered form categories.
The AtoM is a project originated by the International Council on Archives (ICA) that aimed to provide free license software that allows institutions to disseminate their archival holdings on the web. Its last version in collaboration with the ICA was Release 1.3.2. As of October 2013, with version 2.0, the AToM project remained in the hands of the company Artefactual Systems without the ICA.
References
- ↑ Hjørland, Birger. 2016. Knowledge organization. Knowledge Organization 43, no. 6: 475-84. Also available in Hjørland, Birger, ed. ISKO Encyclopedia of Knowledge Organization, https://www.isko.org/cyclo/knowledge_organization.
- ↑ Alistair, Miles; Bechhofer, Sean (18 August 2009). "SKOS Simple Knowledge Organization System, W3C Recommendation".
- Hodge, G. (2000). Systems of Knowledge Organization for Digital libraries. Beyond traditional authority files. Washington, DC: the Council on Library and Information Resources. http://www.clir.org/pubs/reports/pub91/contents.html
- Tudhope, D. & Lykke Nielsen, M. (2006). Introduction to special issue: Knowledge Organization Systems and Services. New Review of Hypermedia and Multimedia, 12(1), 3-9. http://www.journalsonline.tandf.co.uk/media/m35eac0c7l6wvk510nr7/contributions/r/0/7/7/r077564631920800.pdf
- Zeng, M. L. & Chan, L. M. (2004). Trends and issues in establishing interoperability among knowledge organization systems. Journal for the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 55(5), 377-395.
- Networked Knowledge Organization Systems/Services NKOS: http://nkos.slis.kent.edu/