
Mandriva Linux is a discontinued Linux distribution developed by Mandriva S.A.

PCLinuxOS, often shortened to PCLOS, is a rolling release Linux distribution for x86-64 computers, with KDE Plasma, MATE, and XFCE as its default user interfaces. It is a primarily FOSS operating system for personal computers aimed at ease of use.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives are Linux distributions that are based on the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
WebSphere Application Server (WAS) is a software product that performs the role of a web application server. More specifically, it is a software framework and middleware that hosts Java-based web applications. It is the flagship product within IBM's WebSphere software suite. It was initially created by Donald F. Ferguson, who later became CTO of Software for Dell. The first version was launched in 1998. This project was an offshoot from IBM HTTP Server team starting with the Domino Go web server.

openSUSE is a free and open-source Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. It is offered in two main variations: Tumbleweed, an upstream rolling release distribution, and Leap, a stable release distribution which is sourced from SUSE Linux Enterprise.
Nitix was a retail Linux distribution, produced in Canada. The software is developed by Net Integration Technologies, Inc., which has been acquired by IBM as of January 2008 and currently operates as IBM Lotus Foundations.

SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE) is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is available in two editions, suffixed with Server (SLES) for servers and mainframes, and Desktop (SLED) for workstations and desktop computers.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator.
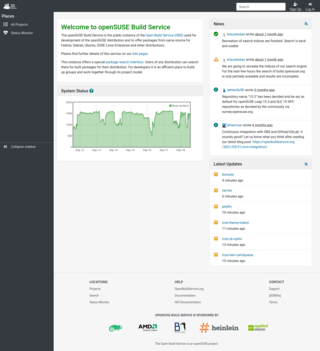
The Open Build Service is an open and complete distribution development platform designed to encourage developers to compile packages for multiple Linux distributions including SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, openSUSE, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Mandriva, Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and Arch Linux. It typically simplifies the packaging process, so developers can more easily package a single program for many distributions, and many openSUSE releases, making more packages available to users regardless of what distribution they use. Also, product and appliance building is supported by OBS.

Moblin, short for 'mobile Linux', is a discontinued open source operating system and application stack for Mobile Internet Devices (MIDs), netbooks, nettops and embedded devices.

RPM Package Manager (RPM) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the .rpm file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.
Mandriva S.A. was a public software company specializing in Linux and open-source software. Its corporate headquarters was in Paris, and it had development centers in Metz, France and Curitiba, Brazil. Mandriva, S.A. was the developer and maintainer of a Linux distribution called Mandriva Linux, as well as various enterprise software products. Mandriva was a founding member of the Desktop Linux Consortium.

Linoma Software was a developer of secure managed file transfer and IBM i software solutions. The company was acquired by HelpSystems in June 2016. Mid-sized companies, large enterprises and government entities use Linoma's software products to protect sensitive data and comply with data security regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA/HITECH, SOX, GLBA and state privacy laws. Linoma's software runs on a variety of platforms including Windows, Linux, UNIX, IBM i, AIX, Solaris, HP-UX and Mac OS X.

ClearOS is a Linux distribution by ClearFoundation, with network gateway, file, print, mail, and messaging services.
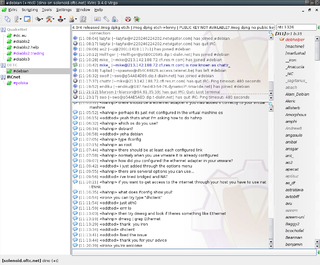
KVIrc is a graphical IRC client for Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows. The name is an acronym of K Visual IRC in which the K stands for a dependency to KDE, which became optional from version 2.0.0. The software is based on the Qt framework and its code is released under a modified GNU General Public License.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:

Endian Firewall is an open-source router, firewall and gateway security Linux distribution developed by the South Tyrolean company Endian. The product is available as either free software, commercial software with guaranteed support services, or as a hardware appliance.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL is not available to all Windows 10 users by default. It can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.













