
The Amiot 143 was a late 1930s French 5-seat Multiplace de Combat (M.5) designed to meet 1928 specifications for a monoplane capable of day and night bombing, long-range reconnaissance and bomber escort.

The PZL.37 Łoś (moose) was a Polish twin-engined medium bomber designed and manufactured by national aircraft company PZL. It is also known as "PZL P-37" or "PZL P.37", but the letter "P" was generally reserved for fighters of Zygmunt Puławski's design.

The Bloch MB.130 and its derivatives were a series of French monoplane reconnaissance-bombers developed during the 1930s. They saw some limited action at the beginning of World War II but were obsolete by that time and suffered badly against the Luftwaffe. After the fall of France, a few were pressed into Luftwaffe service.

The Bloch MB.210 and MB.211 were the successors of the French Bloch MB.200 bomber developed by Société des Avions Marcel Bloch in the 1930s and differed primarily in being low wing monoplanes rather than high wing monoplanes.

The Savoia-Marchetti SM.81 Pipistrello was the first three-engine bomber/transport aircraft serving in the Italian Regia Aeronautica. When it appeared in 1935, it represented a real step ahead in Italian military aviation: it was fast, well armed and had a long range. It proved effective during the war with Ethiopia and the Spanish Civil War. Despite being too slow to remain competitive as a bomber in the later years of World War II, it was one of the most flexible, reliable and important aircraft of the Regia Aeronautica from 1935 to 1944, and adapted to second-line duties in a wide range of tasks.

The Farman F.220 and its derivatives were thick-sectioned, high-winged, four engined monoplanes from Farman Aviation Works. Based on the push-pull configuration proven by the F.211, design started in August 1925 and the first flight of the prototype was on 26 May 1932. The largest bomber to serve in France between the two world wars was the final F.222 variant. One variation was intended to be an airliner.

The Dewoitine 37 was the first of a family of 1930s French-built monoplane fighter aircraft.

Lioré-et-Olivier LeO 45 was a French medium bomber that was used during and after the Second World War. It had been designed for the new Armée de l'air as a modern medium bomber capable of performing independent strategic operations, unlike the majority of previous French bombers.

The Avro 549 Aldershot was a British single-engined heavy bomber aircraft built by Avro.

The Bristol T.B.8, or Bristol-Coanda T.B.8 was an early British biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and designed by the Romanian Henri Coandă. Fifty four Bristol T.B.8s were built, being mainly used as a trainer. A small number of Bristol T.B.8s were briefly used as bombers at the start of the World War I by the Royal Naval Air Service.

The Gourdou-Leseurre GL.30 was a racing aircraft built in France in 1920 which formed the basis for a highly successful family of fighter aircraft based on the same design.

The SNCASE SE.100 was a French two-seat, twin-engined fighter that first flew in 1939. Mass production was planned to begin late in 1940 but the Fall of France prevented this.

The Potez 32 and its military version the Potez 33 was a single-engine French monoplane transport built by Potez and based on the Potez 29 biplane.

The Lioré et Olivier LeO 20 was a French night-bomber aircraft built by Lioré et Olivier.
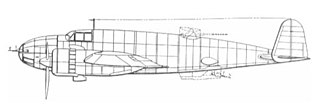
The PZL.49 Miś was a Polish twin-engined medium bomber design that remained only a project due to the outbreak of World War II. The PZL.49 was based on the contemporary PZL.37 Łoś and was to replace it at production lines at the PZL works.

The Loire-Nieuport 10 was a 1930s French prototype long-range maritime reconnaissance and combat floatplane produced by Loire-Nieuport, a joint venture between Loire Aviation and Nieuport-Delage. It was an attempt to answer the requirements for the Navy's programme Hydravion éclaireur de combat for a large floatplane capable of acting as a torpedo bomber or reconnaissance aircraft.
The Farman F.270 was a prototype French bomber/torpedo-bomber designed and built by the Farman Aviation Works for the French Air Force.

The SNCAO CAO.600 was a French prototype twin-engined torpedo-bomber of the Second World War. It was intended to operate from two new aircraft carriers of the French Navy, but only a single example had been completed and flown when the surrender of France in June 1940 ended development of the aircraft.
The Farman F.420 was a twin engine monoplane, built in France in the mid-1930s to compete in a government contest for an aircraft capable of fulfilling bomber, fighter and reconnaissance roles. Two prototypes were constructed but no production followed.
The Stampe et Vertongen RSV.22 was a training biplane produced in Belgium in the 1920s.

















