Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Nigeria face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. LGBT rights are generally infringed upon; both male and female expressions of homosexuality are illegal in Nigeria and punishable by up to 16 years of prison in the conventional court system. There is no legal protection for LGBT rights in Nigeria—a largely conservative country of more than 225 million people, split between a mainly Muslim north and a largely Christian south. Very few LGBT persons are open about their sexual orientation, as violence against them is frequent. According to PinkNews, Nigerian authorities generally target the LGBT community. Many LGBT Nigerians are fleeing to countries with progressive law to seek protection.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in the British Crown dependency of the Isle of Man have evolved substantially since the early 2000s. Private and consensual acts of male homosexuality on the island were decriminalised in 1992. LGBT rights have been extended and recognised in law since then, such as an equal age of consent (2006), employment protection from discrimination (2006), gender identity recognition (2009), the right to enter into a civil partnership (2011), the right to adopt children (2011) and the right to enter into a civil marriage (2016).

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBT citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Trinidad and Tobago face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as that of opposite-sex couples.
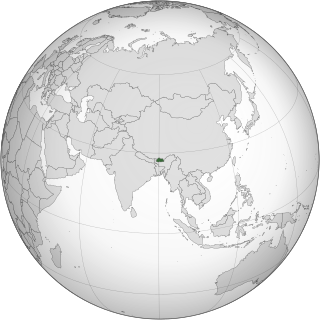
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Bhutan face legal challenges that are not faced by non-LGBT people. Same-sex sexual activity was decriminalised in Bhutan on 17 February 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Dominica face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Sodomy, also known as "buggery", is illegal for both heterosexuals and homosexuals. Dominica provides no recognition to same-sex unions, whether in the form of marriage or civil unions, and no law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Guyana face legal and societal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Guyana is the only country in South America, and the only mainland country in the Americas, where homosexual acts, including anal sex and oral sex, are illegal. Cross-dressing was illegal until November 2018, when the statute was struck down by the Caribbean Court of Justice, the court of last resort of Guyana.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Malawi face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are illegal within the nation. The Penal Code prohibits "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", attempts to commit "carnal knowledge against the order of nature", and acts of "gross indecency".
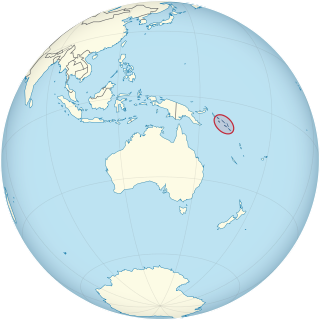
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Solomon Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Scotland are generally in line with the rest of the United Kingdom, which have evolved extensively over time and are now regarded as some of the most progressive in Europe. In both 2015 and 2016, Scotland was recognised as the "best country in Europe for LGBTI legal equality".

Oceania is, like other regions, quite diverse in its laws regarding LGBT rights. This ranges from significant rights, including same-sex marriage – granted to the LGBT+ community in New Zealand, Australia, Guam, Hawaii, Easter Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Wallis and Futuna, New Caledonia, French Polynesia and the Pitcairn Islands – to remaining criminal penalties for homosexual activity in six countries and one territory. Although acceptance is growing across the Pacific, violence and social stigma remain issues for LGBT+ communities. This also leads to problems with healthcare, including access to HIV treatment in countries such as Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands where homosexuality is criminalised.

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are deemed to be "illegal", "illicit", "unlawful", "unnatural" and/or "immoral". Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Antigua and Barbuda may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT citizens.
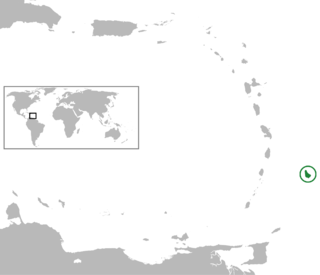
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Barbados do not possess the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. In December 2022, the courts ruled Barbados' laws against buggery and "gross indecency" were unconstitutional and struck them from the Sexual Offences Act. However, there is no recognition of same-sex relationships and only limited legal protections against discrimination.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Niue face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Niue, although there is no recent instance of it being actively prosecuted. Same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Grenada may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. The penal code makes same-sex acts on Grenada proper illegal with a punishment up to 10 years in prison, it also does not address discrimination or harassment on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor does it recognize same sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Household headed by same-sex couples are also not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples.

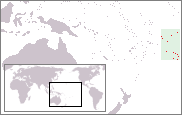
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Samoa face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBT residents. Sexual contact between men is illegal; punishable by up to seven years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Tonga face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male homosexuality is illegal in Tonga, with a maximum penalty of 10 years imprisonment, but the law is not enforced.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Nauru may face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since May 2016, but there are no legal recognition of same-sex unions, or protections against discrimination in the workplace or the provision of goods and services.