A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874 and developed in detail in 1893. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word zeppelin came to be commonly used to refer to all rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and as scouts, resulting in over 500 deaths in bombing raids in Britain.

LZ 129 Hindenburg was a German commercial passenger-carrying rigid airship, the lead ship of the Hindenburg class, the longest class of flying machine and the largest airship by envelope volume. It was designed and built by the Zeppelin Company on the shores of Lake Constance in Friedrichshafen, Germany, and was operated by the German Zeppelin Airline Company. It was named after Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, who was President of Germany from 1925 until his death in 1934.

Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin was a German general and later inventor of the Zeppelin rigid airships. His name soon became synonymous with airships and dominated long-distance flight until the 1930s. He founded the company Luftschiffbau Zeppelin.

LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin was a German passenger-carrying hydrogen-filled rigid airship that flew from 1928 to 1937. It offered the first commercial transatlantic passenger flight service. The ship was named after the German airship pioneer Ferdinand von Zeppelin, a count in the German nobility. It was conceived and operated by Hugo Eckener, the chairman of Luftschiffbau Zeppelin.

His Majesty's Airship R100 was a privately designed and built British rigid airship made as part of a two-ship competition to develop a commercial airship service for use on British Empire routes as part of the Imperial Airship Scheme. The other airship, the R101, was built by the British Air Ministry, but both airships were funded by the Government.
R.36 was a British airship designed during World War I, but not completed until after the war. When she first flew in 1921, it was not in her originally intended role as a patrol aircraft for the Royal Navy, but as an airliner, the first airship to carry a civil registration (G-FAAF).

The Graf Zeppelin was the last of the German rigid airships built by Zeppelin Luftschiffbau during the period between the World Wars, the second and final ship of the Hindenburg class, and the second zeppelin to carry the name "Graf Zeppelin" and thus often referred to as Graf Zeppelin II. Due to the United States refusal to export helium to Germany, the Graf Zeppelin II was filled with hydrogen and therefore never carried commercial passengers. It made 30 flights over 11 months in 1938–39, many being propaganda publicity flights; but staff of the Reich Air Ministry were aboard to conduct radio surveillance and measurements. The airship, along with its LZ 127 namesake were both scrapped in April 1940, and their duralumin framework salvaged to build aircraft for the Luftwaffe.
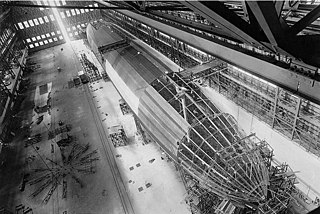
A rigid airship is a type of airship in which the envelope is supported by an internal framework rather than by being kept in shape by the pressure of the lifting gas within the envelope, as in blimps and semi-rigid airships. Rigid airships are often commonly called Zeppelins, though this technically refers only to airships built by the Luftschiffbau Zeppelin company.

The ZeppelinLZ 1 was the first successful experimental rigid airship. It was first flown from a floating hangar on Lake Constance, near Friedrichshafen in southern Germany, on 2 July 1900. "LZ" stood for Luftschiff Zeppelin, or "Airship Zeppelin".

The ZeppelinLZ 3 was a German experimental airship constructed in Friedrichshafen under the direction of Ferdinand von Zeppelin. It was first flown on 9 October 1906 and was later purchased by the German Army and operated as Z I until being retired in 1913. Before being purchased by the Army, LZ 3 made many flights and carried a number of influential passengers, including the German Crown Prince.
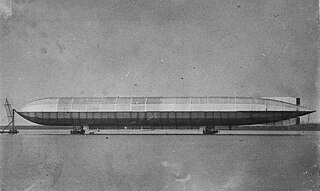
His Majesty's Airship No. 1 was designed and built by Vickers, Sons and Maxim at their works in Barrow-in-Furness, Lancashire, England, as an aerial scout airship for the Royal Navy. It was the first British rigid airship to be built, and was constructed in a direct attempt to compete with the German airship programme. Often referred to as "Mayfly", a nickname given to it by the lower deck, in public records it is designated 'HMA Hermione' because the naval contingent at Barrow were attached to HMS Hermione, a cruiser moored locally preparing to act as its tender.

The Dixmude was a Zeppelin airship built for the Imperial German Navy as L 72 and unfinished at the end of the First World War, when it was given to France as war reparations and recommissioned in French Navy service and renamed Dixmude. It was lost when it exploded in mid-air on 21 December 1923 off the coast of Sicily, killing all 52 on board. This was one of the first of the great airship disasters, preceded by the crash of the British R38 in 1921 and the US airship Roma in 1922, and followed by the destruction of the USS Shenandoah in 1925 the British R101 in 1930, the USS Akron in 1933 and the German Hindenburg in 1937.

LZ 10 Schwaben was a German rigid airship built by Luftschiffbau Zeppelin in 1911 and operated by DELAG for passenger service. It is regarded as the first commercially successful passenger-carrying aircraft.

LZ 18 was the second Zeppelin airship to be bought by the Imperial German Navy. It caught fire and crashed with the loss of all aboard on 17 October 1913 before entering service.

The Zeppelin P Class was the first Zeppelin airship type to be produced in quantity after the outbreak of the First World War. Twenty-two of the type were built as well as twelve of a lengthened version, the Q Class. They were used for many of the airship bombing raids on the United Kingdom in 1915-16, for naval patrol work over the North Sea and Baltic and were also deployed on the eastern and south-eastern fronts.

The Zeppelin R Class was a type of rigid airship developed by Zeppelin Luftschiffbau in 1916 for use by the Imperial German Navy and the German Army for bombing and naval patrol work. Introduced in July 1916 at a time when British air defences were becoming increasingly capable, several were lost in the first months of operation, leading the Germans to reconsider their technical requirements and eventually to develop airships capable of bombing from a greater height. Most surviving examples were modified to meet these requirements, by reducing weight at the expense of performance. A total of 17 were built.

The Imperial German Army Zeppelin LZ 47 was a P-class World War I zeppelin. Destroyed by enemy fire on 21 February 1916 in the Battle of Verdun, killing the crew of 15.

The Imperial German Navy Zeppelin LZ 53 was a P-class World War I zeppelin.

The Imperial German Army Zeppelin LZ 43 was a P-class World War I zeppelin. While taking part in a bombing raid of the United Kingdom the Airship was hit by AA fire and it crashed outside of Ostend, Belgium on 10 August 1915. While being towed into the harbour, it burst into fire.

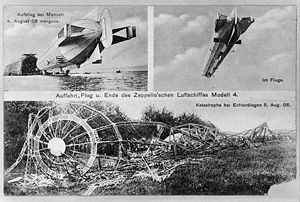
The Zeppelin LZ 5, tactical number Z II, was a German experimental military rigid airship constructed under the direction of Ferdinand von Zeppelin. After having made numerous successful trips, LZ 5 broke loose from its moorings in a storm and subsequentely crashed on 25 April 1910.