
The Cadillac V-16 was Cadillac's top-of-the-line model from its January 1930 launch until 1940. The V16 powered car was a first in the United States, both extremely expensive and exclusive, with every chassis being custom-finished to order. Only 4,076 were constructed in its 11-year run, with the majority built in its debut year before the Great Depression took strong hold. The onset of World War II reduced the sales, resulting in its demise. It was, however, at least thrice cheaper than Bugatti Royale.

Brasier was a French automobile manufacturer, based in the Paris conurbation, and active between 1905 and 1930. The firm began as Richard-Brasier in 1902, and became known as Chaigneau-Brasier in 1926.

Crossley Motors was an English motor vehicle manufacturer based in Manchester, England. It produced approximately 19,000 cars from 1904 until 1938, 5,500 buses from 1926 until 1958, and 21,000 goods and military vehicles from 1914 to 1945.

The Austin 7 is an economy car that was produced from 1923 until 1939 in the United Kingdom by Austin. It was nicknamed the "Baby Austin" and was at that time one of the most popular cars produced for the British market and sold well abroad. Its effect on the British market was similar to that of the Model T Ford in the US, replacing most other British economy cars and cyclecars of the early 1920s. It was also licensed and copied by companies all over the world. The first BMW car, the BMW Dixi, was a licensed Austin 7. In France they were made and sold as Rosengarts, and in the United States they were built by the American Austin Car Company. In Japan, Nissan also used the 7 design as the basis for their first cars, although not under licence. This eventually led to a 1952 agreement for Nissan to build and sell Austins in Japan under the Austin name.

Albion Motors was a Scottish automobile and commercial vehicle manufacturer.

Karrier was a British marque of motorised municipal appliances and light commercial vehicles and trolley buses manufactured at Karrier Works, Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, by Clayton and Co., Huddersfield, Limited. They began making Karrier motor vehicles in 1908 in Queen Street South, Huddersfield. In 1920, H.F. Clayton sold Clayton and Co's Huddersfield business into public listed company Karrier Motors while keeping their Penistone operation separate. Mechanical and electrical engineers Clayton & Co Penistone, remain active in 2020 as Clayton Penistone Group.
The Grose was an English automobile built between 1898 and 1901, Grose also built bodies for cars, buses, ambulances and commercial vehicles until the late 1950s.

The Lancia Appia is a passenger car introduced in 1953 by Italian car manufacturer Lancia as a replacement for the Ardea, and which remained in production for ten years. The Appia was the last in a long line of Lancia production cars dating back to the Lancia Lambda to use sliding pillar front suspension. All three series produced had a 1089cc Lancia V4 engine.

Richard Garrett & Sons was a manufacturer of agricultural machinery, steam engines and trolleybuses. Their factory was Leiston Works, in Leiston, Suffolk, England. The company was founded by Richard Garrett in 1778.

Rochet-Schneider was a French company, based in Lyons, that produced automobiles between 1894 and 1932. The Rochet-Schneider sales slogan was "strength, simplicity and silence".

The Alfa Romeo 6C name was used on road, race, and sports cars produced between 1927 and 1954 by Alfa Romeo; the "6C" name refers to the six cylinders of the car's straight-six engine. Bodies for these cars were made by coachbuilders such as James Young, Zagato, Touring Superleggera, Castagna, and Pinin Farina. Beginning in 1933 there was also a 6C version with an Alfa factory body, built in Portello. In the early 1920s Vittorio Jano received a commission to create a lightweight, high performance vehicle to replace the Giuseppe Merosi designed RL and RM models. The car was introduced in April 1925 at the Salone dell' Automobile di Milano as the 6C 1500. It was based on Alfa's P2 Grand Prix car, using a single overhead cam 1,487 cc in-line six-cylinder engine, producing 44 horsepower. In 1928 the 1500 Sport was presented, which was the first Alfa Romeo road car with double overhead camshafts.

The Lancia Artena is a passenger car produced by Italian car manufacturer Lancia from 1931 until 1936, and from 1940 until 1942 chiefly for army and government use. It was powered by a 2-litre Lancia V4 engine, while chassis and factory bodies were shared with the more luxurious 2.6-litre V8-engined Lancia Astura. Total production amounted to 5,567 examples.

The Lancia Augusta is a small passenger car produced by Italian car manufacturer Lancia between 1933 and 1936. It made its première at the 1932 Paris Motor Show. The car was powered by a 1,196 cc Lancia V4 engine.

The Lancia Dilambda is a passenger car produced by Lancia between 1928 and 1935. The car was officially presented in Paris Motor Show in 1929. The car has 4 litre V8 engine with 24 degree V angle.
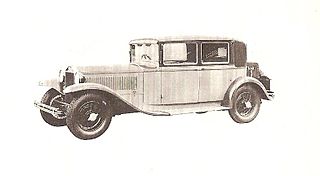
The Lancia Astura is a passenger car produced by Italian automobile manufacturer Lancia between 1931 and 1939. Lancia replaced the Lambda model with two models: the four-cylinder Artena and the larger, V8-powered Astura. Both of these models were introduced at the Paris Motor Show in 1931. The Astura chassis was used by various coachbuilders to create coupes, convertibles and sedans.

The Lancia Trikappa is an automobile produced by Lancia between 1922 and 1925. It was a luxury car, the flagship of Lancia's production. The Trikappa 4.5-litre V8 is notable as the first of Lancia's narrow V engines, a distinguishing feature the manufacturer only abandoned in the 1970s. The car was offered as a bare rolling chassis, as torpedo or 6-seater coupé de ville. In total 847 were manufactured.

The Peugeot Type 174, also known at the time and normally advertised simply according to its fiscal horse power as the Peugeot 18HP, was a large, powerful sedan made by Peugeot from 1923 to 1926. The Type 174 S was made until 1926. The engine displaced 3828 cc, large and low-revving for a four-cylinder engine, and produced a not inconsiderable 85 horsepower at 1900 rpm. The sport version sold 208 examples compared to 810 for the standard version.

The Alvis 12/50 is a car introduced by British business Alvis Car and Engineering Company Ltd in 1923. It went through a series of versions, with the last ones being made in 1932. A range of factory bodies could be specified in two- or four-seat form, with either open or closed bodies.

Rolland-Pilain was a French car maker formally established on 4 November 1905 at 95, rue Victor-Hugo in Tours by François Rolland and Émile Pilain.

The Bignan was a French automobile manufactured between 1918 and 1931 on the north side of central Paris, in Courbevoie. The business was created, and till the mid 1920s-headed up, by Jacques Bignan.
























