Related Research Articles
PL/I is a procedural, imperative computer programming language initially developed by IBM. The PL/1 ANSI standard, X3.53-1976, was published in 1976. It is designed for scientific, engineering, business and system programming. It has been in continuous use by academic, commercial and industrial organizations since it was introduced in the 1960s.
TECO, short for Text Editor & Corrector, is both a character-oriented text editor and a programming language, that was developed in 1962 for use on Digital Equipment Corporation computers, and has since become available on PCs and Unix. Dan Murphy developed TECO while a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).

VAX is a series of computers featuring a 32-bit instruction set architecture (ISA) and virtual memory that was developed and sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in the late 20th century. The VAX-11/780, introduced October 25, 1977, was the first of a range of popular and influential computers implementing the VAX ISA. The VAX family was a huge success for DEC, with the last members arriving in the early 1990s. The VAX was succeeded by the DEC Alpha, which included several features from VAX machines to make porting from the VAX easier.

OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide.
OS/8 is the primary operating system used on the Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-8 minicomputer.
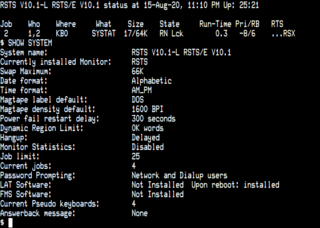
RSTS is a multi-user time-sharing operating system developed by Digital Equipment Corporation for the PDP-11 series of 16-bit minicomputers. The first version of RSTS was implemented in 1970 by DEC software engineers that developed the TSS-8 time-sharing operating system for the PDP-8. The last version of RSTS was released in September 1992. RSTS-11 and RSTS/E are usually referred to just as "RSTS" and this article will generally use the shorter form. RSTS-11 supports the BASIC programming language, an extended version called BASIC-PLUS, developed under contract by Evans Griffiths & Hart of Boston. Starting with RSTS/E version 5B, DEC added support for additional programming languages by emulating the execution environment of the RT-11 and RSX-11 operating systems.
BLISS is a system programming language developed at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) by W. A. Wulf, D. B. Russell, and A. N. Habermann around 1970. It was perhaps the best known system language until C debuted a few years later. Since then, C became popular and common, and BLISS faded into obscurity. When C was in its infancy, a few projects within Bell Labs debated the merits of BLISS vs. C.
The DEC Text Processing Utility is a dedicated programming language developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) to easily create multi-functional text editors.
IDL, short for Interactive Data Language, is a programming language used for data analysis. It is popular in particular areas of science, such as astronomy, atmospheric physics and medical imaging. IDL shares a common syntax with PV-Wave and originated from the same codebase, though the languages have subsequently diverged in detail. There are also free or costless implementations, such as GNU Data Language (GDL) and Fawlty Language (FL).
TOPS-10 System is a discontinued operating system from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) for the PDP-10 mainframe computer family. Launched in 1967, TOPS-10 evolved from the earlier "Monitor" software for the PDP-6 and PDP-10 computers; this was renamed to TOPS-10 in 1970.
DIBOL or Digital's Business Oriented Language is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that was designed for use in Management Information Systems (MIS) software development. It was developed from 1970 to 1993.
VSI BASIC for OpenVMS is the latest name for a dialect of the BASIC programming language created by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) and now owned by VMS Software Incorporated (VSI). It was originally developed as BASIC-PLUS in the 1970s for the RSTS-11 operating system on the PDP-11 minicomputer. It was later ported to OpenVMS, first on VAX, then Alpha, and most recently Integrity.

PRIMOS is a discontinued operating system developed during the 1970s by Prime Computer for its minicomputer systems. It rapidly gained popularity and by the mid-1980s was a serious contender as a mainline minicomputer operating system.
DATATRIEVE is a database query and report writer tool originally from Digital Equipment Corporation. It runs on the OpenVMS operating system, as well as several PDP-11 operating systems. DATATRIEVE's command structure is nearly plain English, and it is an early example of a Fourth Generation Language (4GL).
VAXELN is a discontinued real-time operating system for the VAX family of computers produced by the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) of Maynard, Massachusetts.
Programming languages are used for controlling the behavior of a machine. Like natural languages, programming languages follow rules for syntax and semantics.
VAX MACRO is the computer assembly language implementing the VAX instruction set architecture for the OpenVMS operating system, originally released by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1977.
Embedded SQL is a method of combining the computing power of a programming language and the database manipulation capabilities of SQL. Embedded SQL statements are SQL statements written inline with the program source code, of the host language. The embedded SQL statements are parsed by an embedded SQL preprocessor and replaced by host-language calls to a code library. The output from the preprocessor is then compiled by the host compiler. This allows programmers to embed SQL statements in programs written in any number of languages such as C/C++, COBOL and Fortran. This differs from SQL-derived programming languages that don't go through discrete preprocessors, such as PL/SQL and T-SQL.
References
- 1 2 Compaq (August 1999). DECset Release 12.2A for OpenVMS VAX Systems. Archived from the original on March 28, 2017. Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ↑ Stevens, Mark. "Language Sensitive Editor: LSE". VMS Users Guide. Retrieved August 31, 2016.
- ↑ "Kednos PL/I for OpenVMS Systems User Manual". Kednos.com. Retrieved August 31, 2016.