The history of Guam starts with the early arrival around 2000 BC of Austronesian people known today as the Chamorro Peoples. The Chamorus then developed a "pre-contact" society, that was colonized by the Spanish in the 17th century. The present American rule of the island began with the 1898 Spanish–American War. Guam's history of colonialism is the longest among the Pacific islands.

Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.

The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, is an unincorporated territory and commonwealth of the United States consisting of 14 islands in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The CNMI includes the 14 northernmost islands in the Mariana Archipelago; the southernmost island, Guam, is a separate U.S. territory. The Northern Mariana Islands were listed by the United Nations as a non-self governing territory until 1990.
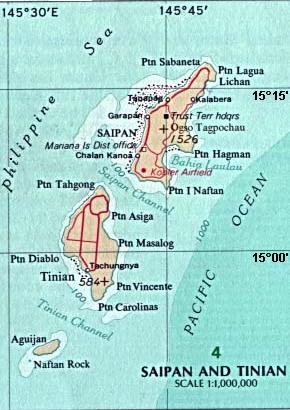
Tinian is one of the three principal islands of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI). Together with uninhabited neighboring Aguiguan, it forms Tinian Municipality, one of the four constituent municipalities of the Northern Marianas. Tinian's largest village is San Jose. Tinian is just south of the most inhabited island Saipan, but north of the populated Rota to the south. The island is home to many WW2 historical sites, cattle ranches, and beaches. There was a 5-star casino that operated from 1998 to 2015; remaining are other hotels/resorts and a golf course. The main access to Saipan is by a short airplane ride from the international airport, or by a charter boat.

The Mariana Islands, also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fourteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east. They lie south-southeast of Japan, west-southwest of Hawaii, north of New Guinea and east of the Philippines, demarcating the Philippine Sea's eastern limit. They are found in the northern part of the western Oceanic sub-region of Micronesia, and are politically divided into two jurisdictions of the United States: the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and, at the southern end of the chain, the territory of Guam. The islands were named after the influential Spanish queen Mariana of Austria following their colonization in the 17th century.

The Chamorro people are the Indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia, a commonwealth of the US. Today, significant Chamorro populations also exist in several U.S. states, including Hawaii, California, Washington, Texas, Tennessee, Oregon, and Nevada, all of which together are designated as Pacific Islander Americans according to the U.S. Census. According to the 2000 Census, about 64,590 people of Chamorro ancestry live in Guam and another 19,000 live in the Northern Marianas.

Rota, also known as the "Friendly Island", is the southernmost island of the United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) and the third southernmost of the Marianas Archipelago. In early Spanish records it is called "Zarpana"; the name Rota may have come from the Spaniards possibly naming the island after the municipality of Rota, Spain. It lies approximately 40 nautical miles (74 km) north-northeast of the United States territory of Guam. Sinapalo village is the largest and most populated, followed by Songsong village (Songsong). Rota also functions as one of the four municipalities of the CNMI.
Micronesian mythology comprises the traditional belief systems of the people of Micronesia. There is no single belief system in the islands of Micronesia, as each island region has its own mythological beings.
Chalan Piao is a village on the southwestern area of Saipan. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. It is bordered on the north by Chalan Kanoa, on the east by As Perdido village and on the south by San Antonio village. To the west is the Pacific Ocean.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.

The Refaluwasch people are a Micronesian ethnic group who originated in Oceania, in the Caroline Islands, with a total population of over 8,500 people in the Northern Mariana Islands. They are also known as Remathau in the Yap's outer islands. The Carolinian word means "People of the Deep Sea." It is thought that their ancestors may have originally immigrated from Asia and Melanesia to Micronesia around 2,000 years ago. Their primary language is Carolinian, called Refaluwasch by native speakers, which has a total of about 5,700 speakers. The Refaluwasch have a matriarchal society in which respect is a very important factor in their daily lives, especially toward the matriarchs. Most Refaluwasch are of the Roman Catholic faith.

Rota Latte Stone Quarry, also known as the As Nieves quarry, is located near the Chamorro village of Sinapalo, on the island of Rota in the Marianas Archipelago. The prehistoric megaliths found there are believed to have been used as foundation pillars for houses, with some of them weighing up to 35 tons. Their exact age, origin, methods of quarrying and means of transportation have not been determined.

The House of Taga is an archeological site located near San Jose Village, on the island of Tinian, United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, in the Marianas Archipelago. The site is the location of a series of prehistoric latte stone pillars which were quarried about 4,000 feet (1,200 m) south of the site, only one of which is left standing erect due to past earthquakes. The name is derived from a mythological chief named Taga, who is said to have erected the pillars as a foundation for his own house.

The Laulau Kattan Latte Site is a prehistoric archaeological site on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. Located near the shore of Laulau Bay, it is a small village site containing the remains of four latte stone house foundations, and an extensive scattering of pottery artifacts. When first reported by the pioneering archaeologist Alexander Spoehr in the 1940s, the latte stones were described as mostly fallen over and extremely weathered.
The Unai Obyan Latte Site is a prehistoric archaeological site on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. Located near Obyan Beach on the south coast of the island, it is the site of what was once a fairly extensive village, which was significantly disturbed by Japanese defensive preparations during World War II. The site includes the fragmentary remains of a single latte stone house site and a wide scattering of surface-level remains. Excavation of the latte house site in the 1940s by the pioneering archeologist Alexander Spoehr yielded evidence of a length period of occupation. The village at Obyan was documented in early Spanish accounts of the island, and was probably abandoned when the Spanish forcibly relocated the entire island population to Guam in 1698.

Star Marianas Air, Inc. is a U.S. commuter airline headquartered at Tinian International Airport in Tinian Municipality, Northern Mariana Islands. It operates scheduled and charter passenger service in the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and Guam, both U.S. territories in the Pacific Ocean.
Don Allen Farrell is an educator, local historian and author based on the island of Tinian in the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI). He is known for his research and publications on the history of the Mariana Islands with an emphasis on World War II.

The Marianas tropical dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion on the Marianas Islands in the western Pacific Ocean.
The Spanish–Chamorro Wars, also known as the Chamorro Wars and the Spanish–Chamorro War, refer to the late seventeenth century unrest among the Chamorros of the Mariana Islands in the western Pacific Ocean against the colonial effort of Habsburg Spain. Anger at proselytizing by the first permanent mission to Guam, which was led by Diego Luis de San Vitores, and a series of cultural misunderstandings led to increasing unrest on Guam and a Chamorro siege of the Hagåtña presidio incited by maga'låhi (Chief) Hurao in 1670. Maga'låhi Matå'pang killed San Vitores in 1672, resulting in a campaign of Spanish reprisal burnings of villages through 1676. Local anger at the attacks against villages resulted in another open rebellion led by Agualin and a second siege of Hagåtña. Governor Juan Antonio de Salas conducted a counter-insurgency campaign that successfully created a system of collaboration in which Guamanians turned in rebels and murderers and transferred most of the people from about 180 villages to seven towns, a policy known as reducción. By the early 1680s, Guam was largely "reduced," or pacified.

Varanus tsukamotoi, the Mariana monitor or Saipan monitor, is a species of lizard of the Varanidae family. It is endemic to the Northern Mariana Islands and Guam, and has been introduced to Japtan in the Marshall Islands.

















