
Adult education, distinct from child education, is a practice in which adults engage in systematic and sustained self-educating activities in order to gain new forms of knowledge, skills, attitudes, or values. It can mean any form of learning adults engage in beyond traditional schooling, encompassing basic literacy to personal fulfillment as a lifelong learner. and to ensure the fulfillment of an individual.
The knowledge economy is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is based principally on knowledge-intensive activities that contribute to advancement in technical and scientific innovation. The key element of value is the greater dependence on human capital and intellectual property for the source of the innovative ideas, information and practices. Organisations are required to capitalise this "knowledge" into their production to stimulate and deepen the business development process. There is less reliance on physical input and natural resources. A knowledge-based economy relies on the crucial role of intangible assets within the organisations' settings in facilitating modern economic growth.
The National Innovation System is the flow of technology and information among people, enterprises and institutions which is key to the innovative process on the national level. According to innovation system theory, innovation and technology development are results of a complex set of relationships among actors in the system, which includes enterprises, universities and government research institutes.
The concept of the innovation system stresses that the flow of technology and information among people, enterprises, and institutions is key to an innovative process. It contains the interactions between the actors needed in order to turn an idea into a process, product, or service on the market.
Lifelong learning is the "ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated" pursuit of knowledge for either personal or professional reasons. It is important for an individual's competitiveness and employability, but also enhances social inclusion, active citizenship, and personal development.
M-learning or mobile learning is "learning across multiple contexts, through social and content interactions, using personal electronic devices". A form of distance education, m-learners use mobile device educational technology at their convenience time.
A learning management system (LMS) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, materials or learning and development programs. The learning management system concept emerged directly from e-Learning. Learning management systems make up the largest segment of the learning system market. The first introduction of the LMS was in the late 1990s. Learning management systems have faced a massive growth in usage due to the emphasis on remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
OpenLearn is an educational website. It is the UK's Open University's contribution to the open educational resources (OER) project and the home of free, open learning from The Open University. The original project was part-funded by the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation. OpenLearn is a member of the OpenCourseWare Consortium (OCWC).

Open education is an educational movement founded on openness, with connections to other educational movements such as critical pedagogy, and with an educational stance which favours widening participation and inclusiveness in society. Open education broadens access to the learning and training traditionally offered through formal education systems and is typically offered through online and distance education. The qualifier "open" refers to the elimination of barriers that can preclude both opportunities and recognition for participation in institution-based learning. One aspect of openness or "opening up" education is the development and adoption of open educational resources in support of open educational practices.
The IKE Group is a research group at the Department of Business Studies, Aalborg University, Denmark and is central part of the Danish Research Unit for Industrial Dynamics (DRUID) founded in 1995 by the IKE Group and scholars from the Department of Industrial Economics and Strategy, Copenhagen Business School. The coordination of this research group has been in the hands of Bengt-Åke Lundvall.
The technological innovation system is a concept developed within the scientific field of innovation studies which serves to explain the nature and rate of technological change. A Technological Innovation System can be defined as ‘a dynamic network of agents interacting in a specific economic/industrial area under a particular institutional infrastructure and involved in the generation, diffusion, and utilization of technology’.
The Institute for Development & Research in Banking Technology (IDRBT) is an engineering training institution exclusively focused on banking technology. Established by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1996, the institution works at the intersection of banking and technology. It is located in Hyderabad, India.
The Karachi School of Business and Leadership (KSBL) is a premier and HEC recognized independent degree awarding business school located in the heart of Karachi, Pakistan, established in 2009, under the charter of Sindh Government of Pakistan, 2012. KSBL is located on Stadium Road. The campus facilitates its students through modern teaching methodologies and latest technologies.
A virtual learning environment (VLE) in educational technology is a web-based platform for the digital aspects of courses of study, usually within educational institutions. They present resources, activities, and interactions within a course structure and provide for the different stages of assessment. VLEs also usually report on participation and have some level of integration with other institutional systems. In North America, VLE's are often referred to as Learning Management Systems (LMS).

Open educational practices (OEP) are part of the broader open education landscape, including the openness movement in general. It is a term with multiple layers and dimensions and is often used interchangeably with open pedagogy or open practices. OEP represent teaching and learning techniques that draw upon open and participatory technologies and high-quality open educational resources (OER) in order to facilitate collaborative and flexible learning. Because OEP emerged from the study of OER, there is a strong connection between the two concepts. OEP, for example, often, but not always, involve the application of OER to the teaching and learning process. Open educational practices aim to take the focus beyond building further access to OER and consider how in practice, such resources support education and promote quality and innovation in teaching and learning. The focus in OEP is on reproduction/understanding, connecting information, application, competence, and responsibility rather than the availability of good resources. OEP is a broad concept which can be characterised by a range of collaborative pedagogical practices that include the use, reuse, and creation of OER and that often employ social and participatory technologies for interaction, peer-learning, knowledge creation and sharing, empowerment of learners, and open sharing of teaching practices.
T-Labs, formerly known as "Telekom Innovation Laboratories", is the R&D unit of Deutsche Telekom. T-Labs current research areas are: Future Networks, Spatial Computing and Decentralized Systems.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The timestamp proves that the transaction data existed when the block was created. Since each block contains information about the previous block, they effectively form a chain, with each additional block linking to the ones before it. Consequently, blockchain transactions are irreversible in that, once they are recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.

The NITI Aayog serves as the apex public policy think tank of the Government of India, and the nodal agency tasked with catalyzing economic development, and fostering cooperative federalism through the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy-making process using a bottom-up approach. Its initiatives include "15-year road map", "7-year vision, strategy, and action plan", AMRUT, Digital India, Atal Innovation Mission, Medical Education Reform, agriculture reforms, Indices Measuring States’ Performance in Health, Education and Water Management, Sub-Group of Chief Ministers on Rationalization of Centrally Sponsored Schemes, Sub-Group of Chief Ministers on Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Sub-Group of Chief Ministers on Skill Development, Task Forces on Agriculture and up of Poverty, and Transforming India Lecture Series.
TVET refers to all forms and levels of education and training which provide knowledge and skills related to occupations in various sectors of economic and social life through formal, non-formal and informal learning methods in both school-based and work-based learning contexts. To achieve its aims and purposes, TVET focuses on the learning and mastery of specialized techniques and the scientific principles underlying those techniques, as well as general knowledge, skills and values.
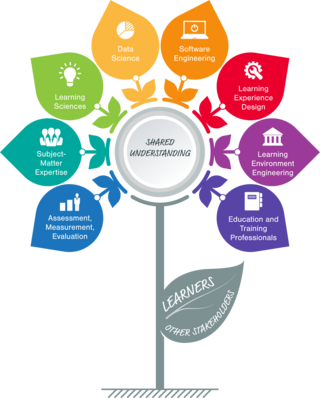
Learning Engineering is the systematic application of evidence-based principles and methods from educational technology and the learning sciences to create engaging and effective learning experiences, support the difficulties and challenges of learners as they learn, and come to better understand learners and learning. It emphasizes the use of a human-centered design approach in conjunction with analyses of rich data sets to iteratively develop and improve those designs to address specific learning needs, opportunities, and problems, often with the help of technology. Working with subject-matter and other experts, the Learning Engineer deftly combines knowledge, tools, and techniques from a variety of technical, pedagogical, empirical, and design-based disciplines to create effective and engaging learning experiences and environments and to evaluate the resulting outcomes. While doing so, the Learning Engineer strives to generate processes and theories that afford generalization of best practices, along with new tools and infrastructures that empower others to create their own learning designs based on those best practices.




