
The Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx (1567–1647) and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was granted a charter for a trade monopoly in the Dutch West Indies by the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands and given jurisdiction over Dutch participation in the Atlantic slave trade, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America. The area where the company could operate consisted of West Africa and the Americas, which included the Pacific Ocean and the eastern part of New Guinea. The intended purpose of the charter was to eliminate competition, particularly Spanish or Portuguese, between the various trading posts established by the merchants. The company became instrumental in the largely ephemeral Dutch colonization of the Americas in the seventeenth century. From 1624 to 1654, in the context of the Dutch-Portuguese War, the GWC held Portuguese territory in northeast Brazil, but they were ousted from Dutch Brazil following fierce resistance.

1738 (MDCCXXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1738th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 738th year of the 2nd millennium, the 38th year of the 18th century, and the 9th year of the 1730s decade. As of the start of 1738, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of various enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans, or by half-European "merchant princes" to Western European slave traders, who brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade. The South Atlantic and Caribbean economies were particularly dependent on labour for the production of sugarcane and other commodities. This was viewed as crucial by those Western European states that, in the late 17th and 18th centuries, were vying with each other to create overseas empires.
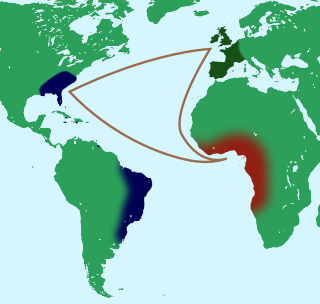
The Middle Passage was the stage of the triangular trade in which millions of Africans were forcibly transported to the New World as part of the Atlantic slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods, which were traded for purchased or kidnapped Africans, who were transported across the Atlantic as slaves; the enslaved Africans were then sold or traded for raw materials, which would be transported back to Europe to complete the voyage. The First Passage was the transportation of captives (slaves) to the African ports, such as Elmina, where they would be loaded onto ships. The Final Passage was the journey from the port of disembarkation, such as Charleston, to the plantation or other destination where they would be put to work. The Middle Passage across the Atlantic joined these two. Voyages on the Middle Passage were large financial undertakings, generally organized by companies or groups of investors rather than individuals.

The Asiento de Negros was a monopoly contract between the Spanish Crown and various merchants for the right to provide African slaves to colonies in the Spanish Americas. The Spanish Empire rarely engaged in the trans-Atlantic slave trade directly from Africa itself, choosing instead to contract out the importation to foreign merchants from nations more prominent in that part of the world; typically Portuguese and Genovese, but later the Dutch, French and British. The Asiento did not concern French or British Caribbean but Spanish America. The 1479 Treaty of Alcáçovas divided the Atlantic Ocean and other parts of the globe into two zones of influence, Spanish and Portuguese. The Spanish acquired the west side washing South America and the West Indies, whilst the Portuguese obtained the east side washing the west coast of Africa - and also the Indian Ocean beyond. The Spanish relied on African slave labour to make their American colonial project possible, but now lacked any trading or territorial foothold in West Africa, the principal source of slave labour. Thus the Spanish were reliant on Portuguese slave traders for all their requirements. The asiento specified the places of importation and the points of delivery, as well as navigation routes. The contract was usually obtained by foreign merchant banks who cooperated with local or foreign traders, specialized in shipping. Different organisations and individuals would bid for the right to hold the asiento.

A Baltimore Clipper is a fast sailing ship historically built on the mid-Atlantic seaboard of the United States of America, especially at the port of Baltimore, Maryland. An early form of clipper, the name is most commonly applied to two-masted schooners and brigantines. These vessels may also be referred to as Baltimore Flyers.

The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. The Dutch began trading in the area around 1598, joining the Portuguese which had a trading post there since the late 1400s. Eventually, the Dutch Gold Coast became the most important Dutch colony in West Africa after Fort Elmina was captured from the Portuguese in 1637, but fell into disarray after the abolition of the slave trade in the early 19th century. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–71, ceded to the United Kingdom.

The first European colonization wave began with Castilian Conquest of the Canary Islands, and primarily involved the European colonization of the Americas, though it also included the establishment of European colonies in India and in Maritime Southeast Asia. During this period, European interests in Africa primarily focused on the establishment of trading posts there, particularly for the African slave trade. The wave ended with British annexation of Kingdom of Kandy in 1815 and founding of colony of Singapore in 1819.

Loango-Angola is the name for the possessions of the Dutch West India Company in contemporary Angola and the Republic of the Congo. Notably, the name refers to the colony that was captured from the Portuguese between 1641 and 1648. Due to the distance between Luanda and Elmina, the capital of the Dutch Gold Coast, a separate administration for "Africa South" was established at Luanda during the period of the Dutch occupation.

Brooks was a British slave ship launched at Liverpool in 1781. She became infamous after prints of her were published in 1788. Between 1782 and 1804 when she was condemned as unseaworthy she made 11 slave–trading voyages. During this period she spent some years as a West Indiaman, and also captured a French merchantman.

Sunny South, an extreme clipper, was the only full-sized sailing ship built by George Steers, and resembled his famous sailing yacht America, with long sharp entrance lines and a slightly concave bow. Initially, she sailed in the California and Brazil trades. Sold in 1859 and renamed Emanuela, she was considered to be the fastest slaver sailing out of Havana. The British Royal Navy captured Emanuela off the coast of Africa in 1860 with over 800 slaves aboard. The Royal Navy purchased her as a prize and converted her into a Royal Navy store ship, Enchantress. She was wrecked in the Mozambique Channel in 1861.

African Slave Trade Patrol was part of the suppression of the Atlantic slave trade between 1819 and the beginning of the American Civil War in 1861. Due to the abolitionist movement in the United States, a squadron of U.S. Navy warships and Cutters were assigned to catch slave traders in and around Africa. In 42 years about 100 suspected slave ships were captured.

The Meermin slave mutiny took place in February 1766 and lasted for three weeks. Meermin was one of the Dutch East India Company's fleet of slave ships. Her final voyage was cut short by the mutiny of the Malagasy people onboard, who had been sold to Dutch East India Company officials on Madagascar to be enslaved by the company in its Cape Colony in southern Africa. During the mutiny half the ship's crew and almost 30 Malagasy lost their lives.

The Middelburgsche Commercie Compagnie (MCC) was a Dutch trading company established in 1720 in the Zeeland capital of Middelburg, Netherlands. It was initially called the Commercial Company of the city of Middelburg. However, after the archive industry was published in 1950, it became known as the Middelburg Commercial Company. After the monopoly of the Dutch West India Company for the Atlantic slave trade was abolished in 1730, the MCC became the principal Dutch slave trading company. The company was eventually liquidated in 1889.

Surinam was a Dutch plantation colony in the Guianas, neighboured by the equally Dutch colony of Berbice to the west, and the French colony of Cayenne to the east. Surinam was a Dutch colony from 26 February 1667, when Dutch forces captured Francis Willoughby's English colony during the Second Anglo-Dutch War, until 15 December 1954, when Surinam became a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The status quo of Dutch sovereignty over Surinam, and English sovereignty over New Netherland, which it had conquered in 1664, was kept in the Treaty of Breda of 31 July 1667, and again confirmed in the Treaty of Westminster of 1674.
The Anglo-Dutch Slave Trade Treaty was a treaty signed between the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of the Netherlands signed on 4 May 1818, aimed at preventing slave trade carried out through Dutch vessels. The treaty allowed both parties to search vessels of the other for on-board slaves. Among other things, the treaty established two Mixed Commission Courts, one with a seat in Freetown, Sierra Leone and another in Paramaribo, Suriname, which had the power to sentence slavers.
John and James was built in France in 1791 under another name and taken in prize in 1796. New owners renamed her and initially sailed her as a West Indiaman. She then made a voyage for the British East India Company (EIC). Next, she became a slave ship, making three voyages between West Africa and the West Indies. Finally, she became a whaler, but was lost in 1806 to a mutinous crew.
Wilding was launched at Liverpool in 1788 and spent much of her career as a West Indiaman, sailing between Liverpool and Jamaica. During this time, in November 1794, she participated in a single-ship action during which her opponent, a French privateer, blew up. In 1798 after a series of captures and recaptures she briefly became a transport for the French Navy, but a final recapture returned her to British hands. Later, she made one voyage to the South Pacific as a whaler, and one voyage to the Cape of Good Hope as a victualler for the 1795-1796 invasion of the Cape. She traded with the West Indies, Africa, the United States, and Russia. Her crew abandoned her in September 1824, dismasted and in a sinking state.

Ceres was launched in France in 1784. The British captured her circa 1800 and sold her as a prize. Once under British ownership she sailed to the Mediterranean, but in 1801 she started sailing in the slave trade. She made four voyages as a slave ship, gathering slaves in West Africa and delivering them to the West Indies. After the abolition of the British slave trade in 1807 she became a West Indiaman, and then an East Indiaman. She was last listed in 1822.

Willem Krul, was a vice-admiral in the Dutch Navy in the latter 18th century, and then commander of the Dutch frigate Mars, during the American Revolutionary War. He was also known as Adrianus Hendrik Willem Krul. After serving in various assignments about the European Atlantic coast Krul served in his final naval assignment at Saint Eustatius, a Dutch possession in the West Indies, during which time he lost his life while engaged in a naval battle with the British, making him a national hero in the Netherlands.














