Related Research Articles
Effendi is a title of nobility.
Mersin İdmanyurdu Sports Club; located in Mersin, east Mediterranean coast of Turkey in 1973–74. The 1973–74 season was the sixth season of Mersin İdmanyurdu (MİY) football team in Turkish First Football League, the first level division in Turkey. They have relegated to second division at the end of the season.
Hacı is the Turkish spelling of the title and epithet Hajji. It may refer to:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Ottoman Empire:
The Ottoman Military College or Imperial Military Staff College or Ottoman Army War College, was a two-year military staff college of the Ottoman Empire. It was located in Constantinople. Its mission was to educate staff officers for the Ottoman Army.

Yahya Efendi or Molla Shaykhzadeh ul Yahya, Ottoman Islamic scholar, sufi sheikh, and poet buried in Beshiktash, Istanbul.

Mevlevi Tekke Museum is a tekke in Nicosia, Cyprus, currently in North Nicosia. It has historically been used by the Mevlevi Order and now serves as a museum. It is one of the most important historical and religious buildings on the island. It is located next to the Kyrenia Gate, on Girne Avenue, in the İbrahimpaşa quarter.
List of historical tekkes, zawiyas, and dergahs in Istanbul, Turkey:
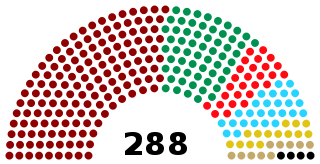
The Third Chamber of Deputies of the Ottoman Empire was elected in the 1908 Ottoman general election, which was called following the Young Turk Revolution. The new parliament consisted of 147 Turks, 60 Arabs, 27 Albanians, 26 Greeks (Rum), 14 Armenians, 10 Slavs, and four Jews. Including the amount of deputies elected in by-elections, the total amount of seats included 288 deputies. On 17 January 1912, through an imperial decree, the Sultan Mehmed V dissolved the Chamber of Deputies and called for new elections within three months.

The Taşköprü family is a Turkish family that rose to prominence in the Ottoman Empire for the important scholars, judges and artists it produced.

The Çapanoğlu dynasty, also Cebbarzâdeler, Çaparzâdeler and Çaparoğulları, is Turkish dynasty that originates in the 17th-century Ottoman Empire and was once one of the most prominent Ottoman families. They became one of the most powerful dynasties in the empire in the 18th century.
References
- ↑ Yurdakul, İlhami."Şeyhülislam (shaykhulislam)". Gábor Ágoston and Bruce Alan Masters, eds. Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire , pp. 524–25. Facts on File, 2009.
- ↑ Yakut 2005, p38
- ↑ For a list of şeyḫülislāmları, see Yakut 2005, pp. 242–247