
The ancient history of Afghanistan, also referred to as the pre-Islamic period of Afghanistan, dates back to the Helmand Civilization around 3300–2350 BCE and the Oxus Civilization around 2400–1950 BCE. Archaeological exploration began in Afghanistan in earnest after World War II and proceeded until the late 1970s during the Soviet–Afghan War. Archaeologists and historians suggest that humans were living in Afghanistan at least 50,000 years ago, and that farming communities of the region were among the earliest in the world. Urbanized culture has existed in the land from between 3000 and 2000 BC. Artifacts typical of the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Bronze, and Iron ages have been found inside Afghanistan.
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the history of South Asia:

Shapur I was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III, he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty".

Atropatene, also known as Media Atropatene, was an ancient Iranian kingdom established in c. 323 BC by the Persian satrap Atropates. The kingdom, centered in present-day northern Iran, was ruled by Atropates' descendants until the early 1st-century AD, when the Parthian Arsacid dynasty supplanted them. It was conquered by the Sasanians in 226, and turned into a province governed by a marzban ("margrave"). Atropatene was the only Iranian region to remain under Zoroastrian authority from the Achaemenids to the Arab conquest without interruption, aside from being briefly ruled by the Macedonian king Alexander the Great.

Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of Nineveh and starting at least with the rule of Monobazos I, Gordyene became an Adiabenian dependency. It reached its zenith under Izates II, who was granted the district of Nisibis by the Parthian king Artabanus II as a reward for helping him regain his throne. Adiabene's eastern borders stopped at the Zagros Mountains, adjacent to the region of Media. Arbela served as the capital of Adiabene.

Sasanian music encompasses the music of the Sasanian Empire, which existed from 224 to 651 CE. Many Sasanian Shahanshahs were enthusiastic supporters of music, including the founder of the empire Ardashir I and Bahram V. In particular, Khosrow II was an outstanding patron, his reign being regarded as a golden age of Persian music.

Istakhr was an ancient city in Fars province, five kilometres north of Persepolis in southwestern Iran. It flourished as the capital of the Persian Frataraka governors and Kings of Persis from the third century BC to the early 3rd century AD. It reached its apex under the Sasanian Empire, and was the hometown of the Sasanian dynasty. Istakhr briefly served as the first capital of the Sasanian Empire from 224 to 226 AD and then as principal city, region, and religious centre of the Sasanian province of Pars.

Zoroastrianism is considered to be the oldest religion still practiced in Iran. It is an Iranian religion that emerged around the 2nd millennium BCE, spreading through the Iranian plateau and eventually gaining official status under the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BCE. It remained the Iranian state religion until the 7th century CE, when the Arab conquest of Persia resulted in the fall of the Sasanian Empire to the nascent Rashidun Caliphate. Over time, the persecution of Zoroastrians led to them becoming a religious minority amidst the Islamization of Iran, as many fled east to take refuge in India. Some of Zoroastrianism's holiest sites are located in Iran, such as Yazd.

Touraj Daryaee is an Iranian Iranologist and historian. He currently works as the Maseeh Chair in Persian Studies and Culture and the director of the Dr. Samuel M. Jordan Center for Persian Studies at the University of California, Irvine.

Juansher was the Mihranid prince of Caucasian Albania, ruling the principality from 637 to 669. He was the son and successor of Varaz Grigor.

The Sasanian Empire or Sassanid Empire, sometimes refered to Second Persian Empire or Neo-Persian Empire, officially known as Eranshahr, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th to 8th centuries. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651, making it the second longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty after the Arsacids of the Parthian Empire.
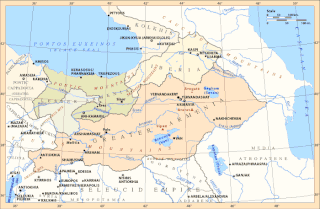
The Satrapy of Armenia, a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty, was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an independent kingdom. Its capitals were Tushpa and later Erebuni.

Sistān, also known as Sakastān and Sijistan, is a historical region in present-day south-eastern Iran, south-western Afghanistan and extending across the borders of south-western Pakistan. Mostly corresponding to the then Achaemenid region of Drangiana and extending southwards of the Helmand River not far off from the city of Alexandria in Arachosia. Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between Iran and Afghanistan.

The modern Persian name of Iran (ایران) derives from the 3rd-century Sasanian Middle Persian ērān, where it initially meant "of the Aryans," and acquired a geographical connotation in the sense of "(lands inhabited by) Aryans." In both geographic and demonymic senses, ērān is distinguished from its antonymic anērān, meaning "non-Iran(ian)".
The Mihranids were an Iranian family which ruled several regions of Caucasus from 330 to 821. They claimed to be of Sasanian Persian descent but were of Parthian origin.

The Kingdom of Hatra,also called Kingdom of Arabaya and Araba. was a 2nd-century Arab kingdom located between the Roman Empire and the Parthian Empire, mostly under Parthian suzerainty, in modern-day northern Iraq.
Zoroastrian Empire may refer to empires with Zoroastrianism as the state religion:

Adurbadagan was a Sasanian province located in northern Iran, almost corresponded to the present-day Iranian Azerbaijan. Governed by a marzban ("margrave"), it functioned as an important frontier region against the neighbouring country of Armenia.

The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Persian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
















