
In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term convolution refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function.

In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency. The interval at which the DTFT is sampled is the reciprocal of the duration of the input sequence. An inverse DFT (IDFT) is a Fourier series, using the DTFT samples as coefficients of complex sinusoids at the corresponding DTFT frequencies. It has the same sample-values as the original input sequence. The DFT is therefore said to be a frequency domain representation of the original input sequence. If the original sequence spans all the non-zero values of a function, its DTFT is continuous, and the DFT provides discrete samples of one cycle. If the original sequence is one cycle of a periodic function, the DFT provides all the non-zero values of one DTFT cycle.
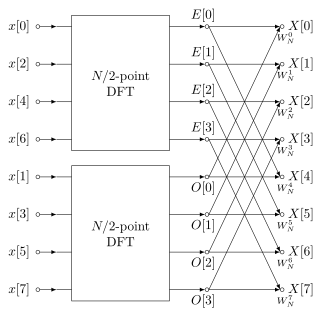
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from , which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to , where n is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where n may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorithms are much more accurate than evaluating the DFT definition directly or indirectly. There are many different FFT algorithms based on a wide range of published theories, from simple complex-number arithmetic to group theory and number theory.
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fourier, who showed that representing a function as a sum of trigonometric functions greatly simplifies the study of heat transfer.
Harmonic analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with investigating the connections between a function and its representation in frequency. The frequency representation is found by using the Fourier transform for functions on the real line or by Fourier series for periodic functions. Generalizing these transforms to other domains is generally called Fourier analysis, although the term is sometimes used interchangeably with harmonic analysis. Harmonic Analysis has become a vast subject with applications in areas as diverse as number theory, representation theory, signal processing, quantum mechanics, tidal analysis and neuroscience.

In physics, engineering and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that converts a function into a form that describes the frequencies present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made the Fourier transform is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.
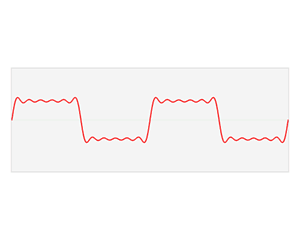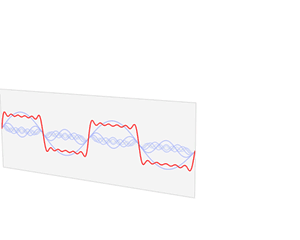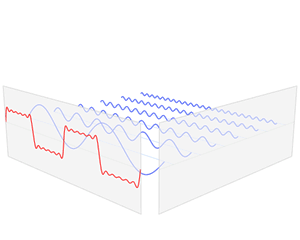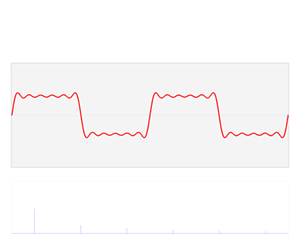
A Fourier series is an expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series, but not all trigonometric series are Fourier series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always converge. Well-behaved functions, for example smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric functions, described in Common forms of the Fourier series below.
Fourier may refer to:
In mathematics, a unitary representation of a group G is a linear representation π of G on a complex Hilbert space V such that π(g) is a unitary operator for every g ∈ G. The general theory is well-developed in the case that G is a locally compact (Hausdorff) topological group and the representations are strongly continuous.
In mathematics and signal processing, the Hilbert transform is a specific singular integral that takes a function, u(t) of a real variable and produces another function of a real variable H(u)(t). The Hilbert transform is given by the Cauchy principal value of the convolution with the function (see § Definition). The Hilbert transform has a particularly simple representation in the frequency domain: It imparts a phase shift of ±90° (π/2 radians) to every frequency component of a function, the sign of the shift depending on the sign of the frequency (see § Relationship with the Fourier transform). The Hilbert transform is important in signal processing, where it is a component of the analytic representation of a real-valued signal u(t). The Hilbert transform was first introduced by David Hilbert in this setting, to solve a special case of the Riemann–Hilbert problem for analytic functions.
In mathematics, the question of whether the Fourier series of a periodic function converges to a given function is researched by a field known as classical harmonic analysis, a branch of pure mathematics. Convergence is not necessarily given in the general case, and certain criteria must be met for convergence to occur.

In mathematics, Hilbert spaces allow the methods of linear algebra and calculus to be generalized from (finite-dimensional) Euclidean vector spaces to spaces that may be infinite-dimensional. Hilbert spaces arise naturally and frequently in mathematics and physics, typically as function spaces. Formally, a Hilbert space is a vector space equipped with an inner product that induces a distance function for which the space is a complete metric space.
In mathematics, noncommutative harmonic analysis is the field in which results from Fourier analysis are extended to topological groups that are not commutative. Since locally compact abelian groups have a well-understood theory, Pontryagin duality, which includes the basic structures of Fourier series and Fourier transforms, the major business of non-commutative harmonic analysis is usually taken to be the extension of the theory to all groups G that are locally compact. The case of compact groups is understood, qualitatively and after the Peter–Weyl theorem from the 1920s, as being generally analogous to that of finite groups and their character theory.
Isidore Isaac Hirschman Jr. (1922–1990) was an American mathematician, and professor at Washington University in St. Louis working on analysis.