Related Research Articles
GNU Image Manipulation Program, commonly known by its acronym GIMP, is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation (retouching) and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks. It is extensible by means of plugins, and scriptable. It is not designed to be used for drawing, though some artists and creators have used it in this way.

Git is a distributed version control system that tracks versions of files. It is often used to control source code by programmers collaboratively developing software.

OpenCV is a library of programming functions mainly for real-time computer vision. Originally developed by Intel, it was later supported by Willow Garage, then Itseez. The library is cross-platform and licensed as free and open-source software under Apache License 2. Starting in 2011, OpenCV features GPU acceleration for real-time operations.
LabelMe is a project created by the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) that provides a dataset of digital images with annotations. The dataset is dynamic, free to use, and open to public contribution. The most applicable use of LabelMe is in computer vision research. As of October 31, 2010, LabelMe has 187,240 images, 62,197 annotated images, and 658,992 labeled objects.
CellCognition is a free open-source computational framework for quantitative analysis of high-throughput fluorescence microscopy (time-lapse) images in the field of bioimage informatics and systems microscopy. The CellCognition framework uses image processing, computer vision and machine learning techniques for single-cell tracking and classification of cell morphologies. This enables measurements of temporal progression of cell phases, modeling of cellular dynamics and generation of phenotype map.
Eclipse Deeplearning4j is a programming library written in Java for the Java virtual machine (JVM). It is a framework with wide support for deep learning algorithms. Deeplearning4j includes implementations of the restricted Boltzmann machine, deep belief net, deep autoencoder, stacked denoising autoencoder and recursive neural tensor network, word2vec, doc2vec, and GloVe. These algorithms all include distributed parallel versions that integrate with Apache Hadoop and Spark.

Intel RealSense Technology, formerly known as Intel Perceptual Computing, is a product range of depth and tracking technologies designed to give machines and devices depth perception capabilities. The technologies, owned by Intel are used in autonomous drones, robots, AR/VR, smart home devices amongst many others broad market products.

The KDE Gear is a set of applications and supporting libraries that are developed by the KDE community, primarily used on Linux-based operating systems but mostly multiplatform, and released on a common release schedule.
JPEG XL is a royalty-free raster-graphics file format that supports both lossy and lossless compression. It is designed to outperform existing raster formats and thus become their universal replacement.

Project Jupyter is a project to develop open-source software, open standards, and services for interactive computing across multiple programming languages.
In computer vision, SqueezeNet is the name of a deep neural network for image classification that was released in 2016. SqueezeNet was developed by researchers at DeepScale, University of California, Berkeley, and Stanford University. In designing SqueezeNet, the authors' goal was to create a smaller neural network with fewer parameters while achieving competitive accuracy.
Microsoft, a technology company historically known for its opposition to the open source software paradigm, turned to embrace the approach in the 2010s. From the 1970s through 2000s under CEOs Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft viewed the community creation and sharing of communal code, later to be known as free and open source software, as a threat to its business, and both executives spoke negatively against it. In the 2010s, as the industry turned towards cloud, embedded, and mobile computing—technologies powered by open source advances—CEO Satya Nadella led Microsoft towards open source adoption although Microsoft's traditional Windows business continued to grow throughout this period generating revenues of 26.8 billion in the third quarter of 2018, while Microsoft's Azure cloud revenues nearly doubled.
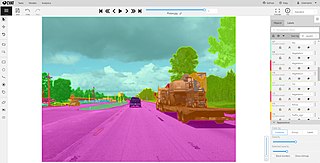
Computer Vision Annotation Tool (CVAT) is a free, open source, web-based image and video annotation tool used for labeling data for computer vision algorithms. Originally developed by Intel, CVAT is designed for use by a professional data annotation team, with a user interface optimized for computer vision annotation tasks.
AirSim is an open-source, cross platform simulator for drones, ground vehicles such as cars and various other objects, built on Epic Games’ proprietary Unreal Engine 4 as a platform for AI research. It is developed by Microsoft and can be used to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles. This allows testing of autonomous solutions without worrying about real-world damage.
Foliate is a free e-book reading application for desktop Linux systems. The name refers to leaves, meaning "(getting) leafy" or "…-leaved".
VoTT is a free and open source Electron app for image annotation and labeling developed by Microsoft. The software is written in the TypeScript programming language and used for building end-to-end object detection models from image and videos assets for computer vision algorithms.
Medical open network for AI (MONAI) is an open-source, community-supported framework for Deep learning (DL) in healthcare imaging. MONAI provides a collection of domain-optimized implementations of various DL algorithms and utilities specifically designed for medical imaging tasks. MONAI is used in research and industry, aiding the development of various medical imaging applications, including image segmentation, image classification, image registration, and image generation.
References
- ↑ "Intel open-sources CVAT, a toolkit for data labeling". VentureBeat. 2019-03-05. Retrieved 2019-03-09.
- ↑ "Computer Vision Annotation Tool: A Universal Approach to Data Annotation". software.intel.com. 2019-03-01. Retrieved 2019-03-09.
- ↑ "Computer Vision Annotation Tool (CVAT) source code on github". GitHub . Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ "LabelMe Source". GitHub . Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ "Encord Source". Documentation . Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ "TagLab Source". GitHub . Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- ↑ Pavoni, Gaia; Corsini, Massimiliano; Ponchio, Federico; Muntoni, Alessandro; Edwards, Clinton; Pedersen, Nicole; Sandin, Stuart; Cignoni, Paolo (2022). "TagLab: AI-assisted annotation for the fast and accurate semantic segmentation of coral reef orthoimages". Journal of Field Robotics. 39 (3): 246–262. doi:10.1002/rob.22049. S2CID 244648241.
- ↑ Costa, Bryan; Sweeney, Edward; Mendez, Arnold (October 2022). "Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Annotate Marine Benthic Species and Habitats". Noaa Technical Memorandum Nos Nccos. 306. doi:10.25923/7kgv-ba52.
- ↑ Tung, Liam. "Free AI developer app: IBM's new tool can label objects in videos for you". ZDNet.
- ↑ Bornstein, Aaron (Ari) (February 4, 2019). "Using Object Detection for Complex Image Classification Scenarios Part 4". Medium.
- ↑ Solawetz, Jacob (July 27, 2020). "Getting Started with VoTT Annotation Tool for Computer Vision". Roboflow Blog.
- ↑ "Best Open Source Annotation Tools for Computer Vision". www.sicara.ai.
- ↑ "Beyond Sentiment Analysis: Object Detection with ML.NET". September 20, 2020.
- ↑ "GitHub - microsoft/VoTT: Visual Object Tagging Tool: An electron app for building end to end Object Detection Models from Images and Videos". November 15, 2020 – via GitHub.