
The governor general of Canada is the federal representative of the Canadian monarch, currently King Charles III. The person who serves as king or queen of Canada is also monarch and head of state of 14 other Commonwealth realms and residence in the oldest and most populous realm, the United Kingdom. The monarch, on the advice of his or her Canadian prime minister, appoints a governor general to administer the government of Canada in the monarch's name. The commission is for an indefinite period—known as serving at His Majesty's pleasure—though, five years is the usual length of time. Since 1959, it has also been traditional to alternate between francophone and anglophone officeholders. The 30th and current governor general is Mary Simon, who was sworn in on 26 July 2021. An Inuk leader from Nunavik in Quebec, Simon is the first Indigenous person to hold the office.

The monarchy of Canada is Canada's form of government embodied by the Canadian sovereign and head of state. It is one of the key components of Canadian sovereignty and sits at the core of Canada's constitutional federal structure and Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. The monarchy is the foundation of the executive (King-in-Council), legislative (King-in-Parliament), and judicial (King-on-the-Bench) branches of both federal and provincial jurisdictions. The current monarch is King Charles III, who has reigned since 8 September 2022.
In political science, a reactionary or a reactionist is a person who holds political views that favor a return to the status quo ante—the previous political state of society—which the person believes possessed positive characteristics that are absent from contemporary society. As a descriptor term, reactionary derives from the ideological context of the left–right political spectrum. As an adjective, the word reactionary describes points of view and policies meant to restore a status quo ante.

Erik Maria Ritter von Kuehnelt-Leddihn was an Austrian-American nobleman and polymath, whose areas of interest included philosophy, history, political science, economics, linguistics, art and theology. He opposed the ideas of the French Revolution, as well as those of communism and Nazism. Describing himself as a "conservative arch-liberal" or "extreme liberal", Kuehnelt-Leddihn often argued that majority rule in democracies is a threat to individual liberties. He declared himself a monarchist and an enemy of all forms of totalitarianism, although he also supported what he defined as "non-democratic republics", such as Switzerland and the early United States. Kuehnelt-Leddihn cited the U.S. Founding Fathers, Tocqueville, Burckhardt, and Montalembert as the primary influences for his skepticism towards democracy.

The lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is the representative in Nova Scotia of the Canadian monarch, King Charles III, who operates distinctly within the province but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada, as well as the other Commonwealth realms and any subdivisions thereof, and resides predominantly in his oldest realm, the United Kingdom. The lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. The present, and 33rd lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is Arthur Joseph LeBlanc, who has served in the role since 28 June 2017.

Alexander Murray, was a Scottish geologist. Murray is best known for his career with the Geological Survey of Canada and the Geological Survey of Newfoundland.
The Commemorative Medal for the Centennial of Saskatchewan, also called the Saskatchewan Centennial Medal, is a commemorative medal struck to celebrate the first 100 years since Saskatchewan's entrance into Canadian Confederation.

Arlette Cousture, is a Canadian writer. She writes historical fiction, often depicting the lives of women in Quebec. Many of her novels have become best-sellers in the French language.

Canadian monarchism is a movement for raising awareness of Canada's constitutional monarchy among the Canadian public, and advocating for its retention, countering republican and anti-monarchical reform as being generally revisionist, idealistic, and ultimately impracticable. Generally, Canadian monarchism runs counter to anti-monarchist republicanism, but not necessarily to the classical form of republicanism itself, as most monarchists in Canada support the constitutional variety of monarchy, sometimes referred to as a crowned republic. These beliefs can be expressed either individually—generally in academic circles—or through what are known as loyal societies, which include the Monarchist League of Canada, legions, historical groups, ethnic organizations, and sometimes police and scout bodies. Though there may be overlap, this concept should not be confused with royalism, the support of a particular monarch or dynasty; Canadian monarchists may appreciate the monarchy without thinking highly of the monarch. There have also been, from time to time, suggestions in favour of a uniquely Canadian monarch, either one headed by a descendant of the present monarch and resident in Canada or one based on a First Nations royal house.

Bernard Keble Sandwell, or BK as he was more commonly known, was a Canadian author, and a magazine and newspaper editor, best known as the editor of Saturday Night (1932-1951).

Over the course of centuries, a multitude of national symbols and material items have arisen as uniquely Canadian or possessing uniquely Canadian characteristics. These symbols and items represent the culture of Canada—protectionism of that culture, identity, values, nationalism, and the heritage of its inhabitants.

James Miller Williams was a Canadian-American businessman and politician. Williams is best known for establishing the first commercially successful oil well in 1858 and igniting the first oil boom in North America. Williams is commonly viewed as the father of the petroleum industry in Canada.

Louis-Athanase David was a Canadian lawyer, politician, and businessman. He was a cabinet minister in the Provincial Parliament of Quebec, representing the riding of Terrebonne and serving as Provincial Secretary. He was later a member of the Canadian Senate.

By the arrangements of the Canadian federation, Canada's monarchy operates in Quebec as the core of the province's Westminster-style parliamentary democracy and constitution. As such, the Crown within Quebec's jurisdiction is referred to as the Crown in Right of Quebec, His Majesty in Right of Quebec, or the King in Right of Quebec. The Constitution Act, 1867, however, leaves many royal duties in the province specifically assigned to the sovereign's viceroy, the lieutenant governor of Quebec, whose direct participation in governance is limited by the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy.

The monarchy of Canada forms the core of each Canadian provincial jurisdiction's Westminster-style parliamentary democracy, being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government in each province. The monarchy has been headed since September 8, 2022 by King Charles III who as sovereign is shared equally with both the Commonwealth realms and the Canadian federal entity. He, his consort, and other members of the Canadian royal family undertake various public and private functions across the country. He is the only member of the royal family with any constitutional role.

John Henry Fairbank was variously a surveyor, oilman, inventor, banker, politician and fire chief in Lambton County, Ontario. Fairbank is best known for his invention of the jerker-line pumping system, which quickly spread across the world its introduction in the mid-1860s. Fairbank Oil, established by Fairbank in 1861, is the oldest continually operating petroleum company, and the company's property, known as the "First Commercial Oil Field", is included in the List of National Historic Sites of Canada in Ontario.
This is a bibliography of works on the military history of Canada.
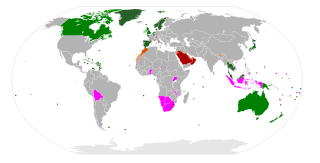
Monarchism is the advocacy of the system of monarchy or monarchical rule. A monarchist is an individual who supports this form of government independently of any specific monarch, whereas one who supports a particular monarch is a royalist. Conversely, the opposition to monarchical rule is referred to as republicanism.

William Henry McGarvey was a Canadian business magnate, entrepreneur and politician. McGarvey is best known for his exploits in Galicia, where he operated a highly successful petroleum company. McGarvey was one of the most successful "foreign drillers" of Petrolia, becoming a multimillionaire before the outbreak of the First World War destroyed his business.
Monarchism in the United States is the advocacy of a monarchical form of government in the United States of America. During the American Revolution a significant element of the population remained loyal to the British crown. However, aside from a few considerations in the 1780s, since independence there has not been any serious movement for an American monarchy.














