
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. It was fought between the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which controlled Kosovo before the war, and the Kosovo Albanian rebel group known as the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA). The conflict ended when the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) intervened by beginning air strikes in March 1999 which resulted in Yugoslav forces withdrawing from Kosovo.

Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a country in Southeast Europe with partial diplomatic recognition. Kosovo lies landlocked in the centre of the Balkans, bordered by Serbia to the north and east, North Macedonia to the southeast, Albania to the southwest, and Montenegro to the west. Most of central Kosovo is dominated by the vast plains and fields of Metohija and the Kosovo field. The Accursed Mountains and Šar Mountains rise in the southwest and southeast, respectively. Its capital and largest city is Pristina.
Music of Kosovo is music that originates from Kosovo, a country in the Balkans. Kosovo's population is mainly Kosovo Albanians, also known as Kosovars, and there are various minority ethnic groups as well. Kosovan music is closely related to that of neighbouring Albania, as well as to that of countries in the former Yugoslavia.

The Medieval Monuments in Kosovo are a World Heritage Site consisting of four Serbian Orthodox Christian churches and monasteries which represent the fusion of the eastern Orthodox Byzantine and the western Romanesque ecclesiastical architecture to form the Palaiologian Renaissance style. The construction was founded by members of Nemanjić dynasty, the most important dynasty of Serbia in the Middle Ages. The sites are located in Kosovo.

Radio Television of Kosovo is the public service broadcaster in Kosovo. RTK operates two radio services broadcasting a diverse programming of news and entertainment and four 24-hour television services broadcasting on terrestrial and satellite networks.

Islam in Kosovo has a long-standing tradition dating back to the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans. Before the Battle of Kosovo in 1389, the entire Balkan region had been Christianized by both the Western and Eastern Roman Empire. From 1389 until 1912, Kosovo was officially governed by the Muslim Ottoman Empire and a high level of Islamization occurred among Catholic and Orthodox Albanians, mainly due to Sufi orders and socio-political opportunism. Both Christian and Muslim Albanians intermarried and some lived as "Laramans", also known as Crypto-Christians. During the time period after World War II, Kosovo was ruled by secular socialist authorities in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). During that period, Kosovars became increasingly secularized. After the end of Communist period religion had a revival in Kosovo. Today, 95.6% of Kosovo's population are Muslims, most of whom are ethnic Albanians. There are also non-Albanian speaking Muslims, who define themselves as Bosniaks, Gorani and Turks.

The Albanian National Army, is an Albanian paramilitary organization which operates in North Macedonia, Serbia and Kosovo. The group opposes the Ohrid Framework Agreement which ended the 2001 insurgency in Macedonia between members of the National Liberation Army and Macedonian security forces.
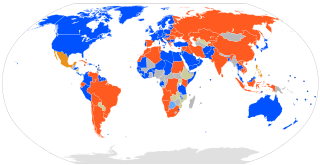
International governments are divided on the issue of recognition of the independence of Kosovo from Serbia, which was declared in 2008. The Government of Serbia does not diplomatically recognise Kosovo as a sovereign state, although the two countries have enjoyed normalised economic relations since 2020 and have agreed not to try to interfere with the other's accession to the European Union.

The Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija, commonly known as Kosovo and abbreviated to Kosmet or KiM, is an autonomous province defined by the Constitution of Serbia that occupies the southernmost part of Serbia. The territory is the subject of an ongoing political and territorial dispute between Republic of Serbia and the partially recognised Republic of Kosovo, the latter of which has control over the territory. Its claimed administrative capital and largest city is Pristina.
Television in Kosovo was first introduced in 1974. The Radio Television of Pristina was the first Albanian-speaking broadcaster in Kosovo, founded in 1974 following Radio Pristina's founding in 1945. It was forcefully shut down in 1990 by the Yugoslavian government, forbidding the flow of information through Kosovan airwaves during the Kosovo War. In wartime, the information blackout was covered by Radio 21 and Koha Ditore, while television was under the sole ownership of the Radio Television of Serbia.

Klokot or Kllokot is a town and municipality in the District of Gjilan in southeastern Kosovo. The municipality was established on 8 January 2010, the settlements having been part of the municipality of Viti. The seat of the municipality is in the town of Klokot.

The Kosovo Security Force (KSF) is the military of Kosovo. The KSF is tasked with defending the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Kosovo, military support for civilian authorities, and participation in international peacekeeping missions and operations. Since 2018, it is in the process of transforming into the Kosovo Armed Forces.

Numerous war crimes were committed by all sides during the Kosovo War, which lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. According to Human Rights Watch, the vast majority of abuses were attributable to the government of Slobodan Milošević, mainly perpetrated by the Serbian police, the Yugoslav army, and Serb paramilitary units. During the war, regime forces killed between 7,000–9,000 Kosovar Albanians, engaged in countless acts of rape, destroyed entire villages, and displaced nearly one million people. The Kosovo Liberation Army has also been implicated in atrocities, such as kidnappings and summary executions of civilians. Moreover, the NATO bombing campaign has been harshly criticized by human rights organizations and the Serbian government for causing roughly 500 civilian casualties.
Classical music in Kosovo refers to the art music cultivated in Kosovo. The roots of classical music in Kosovo are found in the 1940s and include the time period from the times when Kosovo was part of Yugoslavia to this day. It can be said that there is a tradition of classical music in Kosovo, however, compared to other Balkan countries and especially European countries this tradition is younger. Classical music in Kosovo reaches back about 70 years. Even though in a short period of time, this music has evolved, passing through generations of composers and artists. In his book Albanian: Zhvillimi i stileve në veprat e kompozitorëve shqiptarë të Kosovës, Engjëll Berisha comments:
"The diversity of styles in Albanian music [of Kosovo], its national patterns with sound idea-aesthetic foundations are a characteristic of the European musical reality, so many many works are of interest abroad, too, because during this relatively short period Albanian classical music in Kosovo has compensated for the delay in its development."
In March and April 1981, a student protest in Pristina, the capital of the then Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo, led to widespread protests by Kosovo Albanians demanding more autonomy within the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The Presidency of Yugoslavia declared a state of emergency in Pristina and Kosovska Mitrovica, which led to rioting. The unrest was suppressed by a large police intervention that caused numerous casualties, and a period of political repression followed.

This is a list of Kosovo national football team results from 1993 to 2019.

Kosovo participated at the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil from 5 to 21 August 2016. It was represented by the Olympic Committee of Kosovo (KOK/OKK) with a delegation of eight people, including three men and five women. Most of them were awarded places in their respective sporting events through wild card entries and Tripartite Commission invitations. Two Kosovar athletes, on the other hand, qualified directly for the Olympics on merit: judoka Nora Gjakova and Majlinda Kelmendi, the lone returning Olympian on the team after representing Albania four years earlier in London. The world's top-ranked judoka in her weight category and the frontrunner for the country's first Olympic medal, Kelmendi was selected to become Kosovo's flag bearer in the opening ceremony.
The Serb List is a Serb minority political party in Kosovo. It was the dominant Serb party in Kosovo politics, claiming all ten of Assembly seats reserved for the community, from 2014 until all its members resigned and withdrew in 2022. The party retains close links to the Government of Serbia, led by the Serbian Progressive Party and President Aleksandar Vučić.
The Albanians in the Nordic countries refers to the Albanian migrants in Nordic countries such as Denmark, Faroe Islands, Finland, Norway and Sweden and their descendants.
 (107.7 KB)(in Albanian)
(107.7 KB)(in Albanian)










