Related Research Articles

The Gunboat War was a naval conflict between Denmark–Norway and Great Britain during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Navy. In Scandinavia it is seen as the later stage of the English Wars, whose commencement is accounted as the First Battle of Copenhagen in 1801.

The capture of HMS Frolic was a naval action fought in the Atlantic on 18 October 1812, between the sloop-of-war USS Wasp, commanded by Master Commandant Jacob Jones, and the Cruizer-class brig-sloopHM Brig Frolic, under Commander Thomas Whinyates. The Americans captured the British vessel, but both vessels shortly thereafter were captured by a British ship of the line which happened upon the scene of the battle.

The Aubrietia-class sloops were a class of twelve sloops built under the Emergency War Programme for the Royal Navy in World War I as part of the larger Flower class. They were also referred to as the "cabbage class", or "herbaceous borders". The Flowers were the first ships designed as minesweepers.

HMS Egeria was a Royal Navy 26-gun Cormorant-class ship-sloop launched at Bridport in 1807. During the Gunboat War she captured three privateers and several merchant vessels. After the Napoleonic Wars she continued on active service until 1825, after which she served as a receiving or accommodation ship. She was eventually broken up in 1865.
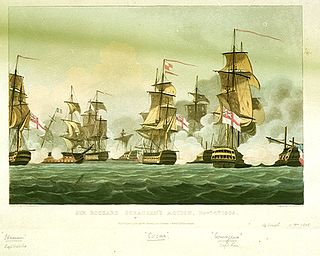
HMS Courageux was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 26 March 1800 at Deptford. She was designed by Sir John Henslow as one of the large class 74-gun ships, and was the only ship built to her draught. Unlike the middling and common class 74-gun ships, which carried 18-pounder long guns, as a large 74-gun ship, Courageux carried 24-pounders on her upper gun deck.

The Cruizer class was an 18-gun class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy. Brig-sloops were the same as ship-sloops except for their rigging. A ship-sloop was rigged with three masts whereas a brig-sloop was rigged as a brig with only a fore mast and a main mast.

The Battle of Delaware Bay, or the Battle of Cape May, was a naval engagement fought between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the United States during the American Revolutionary War. A British squadron of three vessels attacked three American privateers that were escorting a fleet of merchantmen. The ensuing combat in Delaware Bay near Cape May ended with an American victory over a superior British force.

Grinder was a gunboat serving as a tender, rather than a commissioned warship, to HMS Anholt, the British garrison on the island of Anholt during the Gunboat War. Grinder's origins are obscure, but the Danes captured her in 1810 and the British recaptured her in 1811. She was sold in 1832.

HMS Grasshopper was a Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1806, captured several vessels, and took part in two notable actions before the Dutch captured her in 1811. She then served The Netherlands navy until she was broken up in 1822.
Prince William was built in Newcastle in 1788. She then traded between England and the Baltic. The Royal Navy first hired her in 1797. His Majesty's hired armed ship Prince William served on two contracts, one during the French Revolutionary Wars and one during the Napoleonic Wars. The Admiralty returned her to her owners at the end of each contract.
HMS Vautour was 16-gun brig-sloop of the British Royal Navy. The navy captured her from the French on the stocks in 1809 and commissioned her in 1810. She foundered in October 1813.
Lord Eldon was launched at Sunderland in 1801. She was initially a London-based transport, but new owners contracted with the Admiralty. From certainly 1804 through approximately 1811 she served the British Royal Navy as a hired armed ship. During this period Spanish vessels captured her, but the Royal Navy recaptured her. Between 1812 and 1813 she underwent lengthening. In 1814 she returned to serving as a transport. She was driven ashore and damaged in 1817; she was no longer listed in 1819.

HMS Snake was a British Royal Navy ship launched in 1797 as the only member of her class of brig-sloops. She captured or destroyed two French privateers and one Danish privateer. She also captured numerous small merchantmen, but spent time escorting convoys to and from the West Indies. She was sold in 1816.
Lord Forbes was launched at Chester in 1803 as a West Indiaman. She soon became an "armed defense ship", but by 1805 had returned to being a West Indiaman. She made two voyages as an "extra" ship for the British East India Company (EIC). She continued trading with India until 1817 when she sustained damage on her way to Bengal. There she was surveyed, condemned and sold.
Archimedes was launched at Sunderland in 1796 or 1797. She traded between England and the Baltic until the British government chartered her as a transport c. 1809. She was lost in December 1811 while coming back from the Baltic.
Rosina was launched at Hull in 1803. She almost immediately became a hired armed ship for the British Royal Navy for about a year. After she returned to her owners she became a West Indiaman and then a transport. She was last listed in 1818.
HMS Nimble was the name vessel of a two-vessel class of cutters built at Cowes in 1811 for the Royal Navy. Lieutenant John Reynolds commissioned her in 1812.
HMS Attack was launched in 1804 as a later Archer-class gunbrig. Danish gunboats captured Attack in August 1812.
Rear Admiral John Toup Nicolas RN CB KH (1788–1851) was a Royal Navy commander.
Several ships have been named Centurion for the Roman military rank of Centurion.
References
- 1 2 Gentleman's Magazine (1812), p. 174.
- ↑ Marshall, John (1829). . Royal Naval Biography . Vol. supp part 3. London: Longman and company. pp. 13, 14.
- 1 2 3 4 LL 21 January 1812, №4632.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "SHIP NEWS", Hull Packet and Original Weekly Commercial, Literary and General Advertiser (Hull, England), Tuesday, January 28, 1812; Issue 1307.