
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, marking the end of the Napoleonic Wars. A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two armies of the Seventh Coalition. One of these was a British-led force with units from the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Hanover, Brunswick, and Nassau, under the command of the Duke of Wellington. The other comprised three corps of the Prussian army under Field Marshal Blücher; a fourth corps of this army fought at the Battle of Wavre on the same day. The battle was known contemporarily as the Battle of Mont Saint-Jean in France and La Belle Alliance in Prussia.

The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of conflicts fought between the First French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte (1804–1815) and a fluctuating array of European coalitions. The wars originated in political forces arising from the French Revolution (1789–1799) and from the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802), and produced a period of French domination over Continental Europe. The wars are categorised as seven conflicts, five named after the coalitions that fought Napoleon, plus two named for their respective theatres; the War of the Third Coalition, War of the Fourth Coalition, War of the Fifth Coalition, War of the Sixth Coalition, War of the Seventh Coalition, the Peninsular War, and the French invasion of Russia.

The Battle of Borodino took place near the village of Borodino on 7 September [O.S. 26 August] 1812 during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. The Grande Armée won the battle against the Imperial Russian Army, but failed to gain a decisive victory and suffered tremendous losses. Napoleon fought against General Mikhail Kutuzov, whom the Emperor Alexander I of Russia had appointed to replace Barclay de Tolly on 29 August [O.S. 17 August] 1812 after the Battle of Smolensk. After the Battle of Borodino, Napoleon remained on the battlefield with his army; the Imperial Russian forces retreated in an orderly fashion southwards. Because the Imperial Russian army had severely weakened the Grande Armée, they allowed the French occupation of Moscow, using the city as bait to trap Napoleon and his men. The failure of the Grande Armée to completely destroy the Imperial Russian army, in particular Napoleon's reluctance to deploy his Imperial Guard, has been widely criticised by historians as a huge blunder, as it allowed the Imperial Russian army to continue its retreat into territory increasingly hostile to the French. Approximately a quarter of a million soldiers were involved in the battle, and it was the bloodiest single day of the Napoleonic Wars.

Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Fürst von Wahlstatt, Graf (count), later elevated to Fürst von Wahlstatt, was a Prussian Generalfeldmarschall. He earned his greatest recognition after leading his army against Napoleon I at the Battle of the Nations at Leipzig in 1813 and the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.

The Hundred Days, also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on 20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII on 8 July 1815. This period saw the War of the Seventh Coalition, and includes the Waterloo Campaign and the Neapolitan War as well as several other minor campaigns. The phrase les Cent Jours was first used by the prefect of Paris, Gaspard, comte de Chabrol, in his speech welcoming the king back to Paris on 8 July.

In the War of the Sixth Coalition, sometimes known in Germany as the Wars of Liberation, a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, Great Britain, Portugal, Sweden, Sardinia, and a number of German States defeated France and drove Napoleon into exile on Elba. After the disastrous French invasion of Russia of 1812 in which they had been forced to support France, Prussia and Austria joined Russia, the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Portugal, and the rebels in Spain who were already at war with France.

The War of the Fifth Coalition was a European conflict in 1809 that was part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars. The main conflict took place in Central Europe between the Austrian Empire of Francis I and Napoleon's French Empire. The French were supported by their client states—the Kingdom of Italy, the Confederation of the Rhine and the Duchy of Warsaw. Austria was supported by the Fifth Coalition which included the United Kingdom, Portugal, Spain, and the Kingdoms of Sardinia and Sicily, although the latter two took no part in the fighting. By the start of 1809 much of the French army was committed to the Peninsular War against Britain, Spain and Portugal. After France withdrew 108,000 soldiers from Germany, Austria attacked France to seek the recovery of territories lost in the 1803–1806 War of the Third Coalition. The Austrians hoped Prussia would support them, having recently been defeated by France, but Prussia chose to remain neutral.

The Battle of Krasnoi unfolded from 15 to 18 November 1812 marking a critical episode in Napoleon's arduous retreat from Moscow. Over the course of six skirmishes the Russian forces under field marshal Kutuzov inflicted significant blows upon the remnants of the Grande Armée, already severely weakened by attrition warfare. These confrontations, though not escalated into full-scale battles, led to substantial losses for the French due to their depleted weapons and horses.

The Battle of La Suffel was a French victory over Austrian forces of the Seventh Coalition and the last French pitched battle victory in the Napoleonic Wars. It was fought on 28 June 1815 at Souffelweyersheim and Hoenheim, near Strasbourg.
The I Corps of the Grande Armée was a French military unit that existed during the Napoleonic Wars. Though disbanded in 1814, following the Treaty of Fontainebleau, it was reformed in April 1815 following the return of Napoléon during the Hundred Days. During the Hundred Days, the corps formed part of the quickly re-formed Army of the North.
The IV Corps of the Grande Armée was a French military unit that existed during the Napoleonic Wars. It consisted of several different units and commanders.
The Battle of the Göhrde took place during the War of the Sixth Coalition on 16 September 1813 between French and Coalition troops at Göhrde, Germany. The French troops were defeated and withdrew to Hamburg.
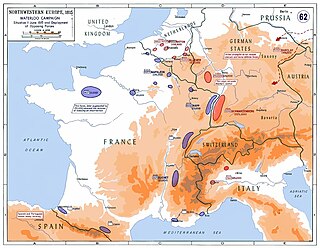
On 1 March 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte escaped from his imprisonment on the isle of Elba, and launched a bid to recover his empire. A confederation of European powers pledged to stop him. During the period known as the Hundred Days Napoleon chose to confront the armies of Prince Blücher and the Duke of Wellington in what has become known as the Waterloo Campaign. He was decisively defeated by the two allied armies at the Battle of Waterloo, which then marched on Paris forcing Napoleon to abdicate for the second time. However Russia, Austria and some of the minor German states also fielded armies against him and all of them also invaded France. Of these other armies the ones engaged in the largest campaigns and saw the most fighting were two Austrian armies: The Army of the Upper Rhine and the Army of Italy.

The Royal Prussian Army was the principal armed force of the Kingdom of Prussia during its participation in the Napoleonic Wars.

During the Hundred Days of 1815, both the Coalition nations and the First French Empire of Napoleon Bonaparte mobilised for war. This article describes the deployment of forces in early June 1815 just before the start of the Waterloo Campaign and the minor campaigns of 1815.

The 1814 campaign in north-east France was Napoleon's final campaign of the War of the Sixth Coalition. Following their victory at Leipzig in 1813, the Austrian, Prussian, Russian, and other German armies of the Sixth Coalition invaded France. Despite the disproportionate forces in favour of the Coalition, Napoleon managed to inflict several defeats, the Six Days' Campaign being the most well-known. However, the campaign ended in total defeat for Napoleon as the Coalition kept advancing towards Paris as Napoleon was out of position to defend the capital, which capitulated in late March 1814. When Napoleon proposed the army march on Paris, his Marshals decided to unanimously overrule Napoleon in order to save the city from further destruction. As a result, the victorious Coalition negotiated the Treaty of Paris, under which Napoleon was exiled to the island of Elba and the borders of France were returned to where they had been in 1792.

The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire after 1809 and also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 3 May 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena.

The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign and in Russia as the Patriotic War of 1812, was initiated by Napoleon with the aim of compelling the Russian Empire to comply with the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Widely studied, Napoleon's incursion into Russia stands as a focal point in military history, recognized as among the most devastating military endeavors globally. In a span of fewer than six months, the campaign exacted a staggering toll, claiming the lives of nearly a million soldiers and civilians.













