
Lists of shapes cover different types of geometric shape and related topics. They include mathematics topics and other lists of shapes, such as shapes used by drawing or teaching tools.

Lists of shapes cover different types of geometric shape and related topics. They include mathematics topics and other lists of shapes, such as shapes used by drawing or teaching tools.
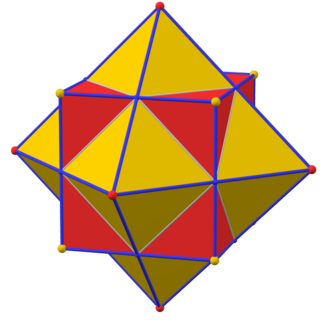
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual figure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. Such dual figures remain combinatorial or abstract polyhedra, but not all are also geometric polyhedra. Starting with any given polyhedron, the dual of its dual is the original polyhedron.

In geometry, a polyhedron is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. The word polyhedron comes from the Classical Greek πολύεδρον, as poly- + -hedron.
In elementary geometry, a polytope is a geometric object with flat sides (faces). It is a generalization in any number of dimensions of the three-dimensional polyhedron. Polytopes may exist in any general number of dimensions n as an n-dimensional polytope or n-polytope. In this context, "flat sides" means that the sides of a (k+1)-polytope consist of k-polytopes that may have (k−1)-polytopes in common. For example, a two-dimensional polygon is a 2-polytope and a three-dimensional polyhedron is a 3-polytope.
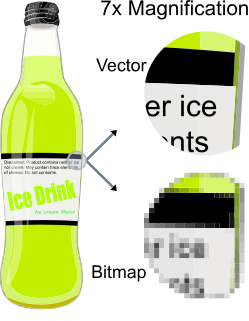
Vector graphics, as a form of computer graphics, is the set of mechanisms for creating visual images directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves, and polygons. These mechanisms may include vector display and printing hardware, vector data models and file formats, and software based on these data models. Vector graphics is an alternative to raster graphics, each having advantages and disadvantages in general and in specific situations.

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) is also used.
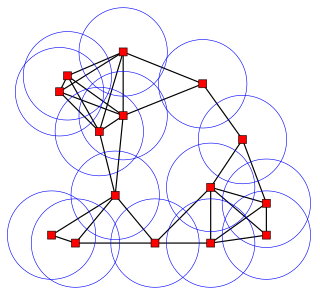
Discrete geometry and combinatorial geometry are branches of geometry that study combinatorial properties and constructive methods of discrete geometric objects. Most questions in discrete geometry involve finite or discrete sets of basic geometric objects, such as points, lines, planes, circles, spheres, polygons, and so forth. The subject focuses on the combinatorial properties of these objects, such as how they intersect one another, or how they may be arranged to cover a larger object.

In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n.

Lists of mathematics topics cover a variety of topics related to mathematics. Some of these lists link to hundreds of articles; some link only to a few. The template to the right includes links to alphabetical lists of all mathematical articles. This article brings together the same content organized in a manner better suited for browsing. Lists cover aspects of basic and advanced mathematics, methodology, mathematical statements, integrals, general concepts, mathematical objects, and reference tables. They also cover equations named after people, societies, mathematicians, journals, and meta-lists.

Mathematics encompasses a growing variety and depth of subjects over its history, and comprehension of it requires a system to categorize and organize these various subjects into more general areas of mathematics or fields of mathematics. A number of different classification schemes have arisen, and though they share some similarities, there are differences due in part to the different purposes they serve.
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels.

Alicia Boole Stott was an Irish mathematician. Despite never holding an academic position, she made a number of valuable contributions to the field, receiving an honorary doctorate from the University of Groningen. She is best known for introducing the term "polytope" for a convex solid in four dimensions, and having an impressive grasp of four-dimensional geometry from a very early age.
Geometric modeling is a branch of applied mathematics and computational geometry that studies methods and algorithms for the mathematical description of shapes.
In geometry, a facet is a feature of a polyhedron, polytope, or related geometric structure, generally of dimension one less than the structure itself. More specifically:

Regular Polytopes is a geometry book on regular polytopes written by Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter. It was originally published by Methuen in 1947 and by Pitman Publishing in 1948, with a second edition published by Macmillan in 1963 and a third edition by Dover Publications in 1973. The Basic Library List Committee of the Mathematical Association of America has recommended that it be included in undergraduate mathematics libraries.
In geometry, an edge is a particular type of line segment joining two vertices in a polygon, polyhedron, or higher-dimensional polytope. In a polygon, an edge is a line segment on the boundary, and is often called a polygon side. In a polyhedron or more generally a polytope, an edge is a line segment where two faces meet. A segment joining two vertices while passing through the interior or exterior is not an edge but instead is called a diagonal.

Geometry is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space that are related with distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a geometer.
In polyhedral combinatorics, a branch of mathematics, Steinitz's theorem is a characterization of the undirected graphs formed by the edges and vertices of three-dimensional convex polyhedra: they are exactly the 3-vertex-connected planar graphs. That is, every convex polyhedron forms a 3-connected planar graph, and every 3-connected planar graph can be represented as the graph of a convex polyhedron. For this reason, the 3-connected planar graphs are also known as polyhedral graphs.

Geometrical design (GD) is a branch of computational geometry. It deals with the construction and representation of free-form curves, surfaces, or volumes and is closely related to geometric modeling. Core problems are curve and surface modelling and representation. GD studies especially the construction and manipulation of curves and surfaces given by a set of points using polynomial, rational, piecewise polynomial, or piecewise rational methods. The most important instruments here are parametric curves and parametric surfaces, such as Bézier curves, spline curves and surfaces. An important non-parametric approach is the level-set method.
In mathematics, a sequence of n real numbers can be understood as a location in n-dimensional space. When n = 7, the set of all such locations is called 7-dimensional space. Often such a space is studied as a vector space, without any notion of distance. Seven-dimensional Euclidean space is seven-dimensional space equipped with a Euclidean metric, which is defined by the dot product.
The Symmetries of Things is a book on mathematical symmetry and the symmetries of geometric objects, aimed at audiences of multiple levels. It was written over the course of many years by John Horton Conway, Heidi Burgiel, and Chaim Goodman-Strauss, and published in 2008 by A K Peters. Its critical reception was mixed, with some reviewers praising it for its accessible and thorough approach to its material and for its many inspiring illustrations, and others complaining about its inconsistent level of difficulty, overuse of neologisms, failure to adequately cite prior work, and technical errors.