Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any delay, overshoot, or steady-state error and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality.
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring, and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related areas of metrology, automation, and control theory. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
A proportional–integral–derivative controller is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, hence the name.

A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants. In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators.
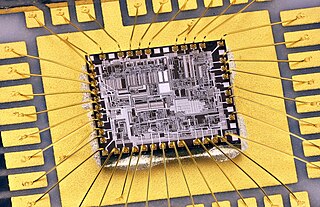
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board (PCB) to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz.
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerised control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localising control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision.

A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process.
An industrial process control or simply process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems and control theory to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. It is implemented widely in industries such as automotive, mining, dredging, oil refining, pulp and paper manufacturing, chemical processing and power generating plants.

Wave soldering is a bulk soldering process used for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. The circuit board is passed over a pan of molten solder in which a pump produces an upwelling of solder that looks like a standing wave. As the circuit board makes contact with this wave, the components become soldered to the board. Wave soldering is used for both through-hole printed circuit assemblies, and surface mount. In the latter case, the components are glued onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) by placement equipment, before being run through the molten solder wave. Wave soldering is mainly used in soldering of through hole components.

A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.
A process automation or automation system (PAS) is used to automatically control a process such as chemical, oil refineries, paper and pulp factories. The PAS often uses a network to interconnect sensors, controllers, operator terminals and actuators. A PAS is often based on open standards in contrast to a DCS, which is traditionally proprietary. However in recent times the PAS is considered to be more associated with SCADA systems.
Process optimization is the discipline of adjusting a process so as to optimize some specified set of parameters without violating some constraint. The most common goals are minimizing cost and maximizing throughput and/or efficiency. This is one of the major quantitative tools in industrial decision making.
In control theory, advanced process control (APC) refers to a broad range of techniques and technologies implemented within industrial process control systems. Advanced process controls are usually deployed optionally and in addition to basic process controls. Basic process controls are designed and built with the process itself, to facilitate basic operation, control and automation requirements. Advanced process controls are typically added subsequently, often over the course of many years, to address particular performance or economic improvement opportunities in the process.
An industrial control system (ICS) is an electronic control system and associated instrumentation used for industrial process control. Control systems can range in size from a few modular panel-mounted controllers to large interconnected and interactive distributed control systems (DCSs) with many thousands of field connections. Control systems receive data from remote sensors measuring process variables (PVs), compare the collected data with desired setpoints (SPs), and derive command functions that are used to control a process through the final control elements (FCEs), such as control valves.
Industrial technology is the use of engineering and manufacturing technology to make production faster, simpler, and more efficient. The industrial technology field employs creative and technically proficient individuals who can help a company achieve efficient and profitable productivity.
Oxygen plants are industrial systems designed to generate oxygen. They typically use air as a feedstock and separate it from other components of air using pressure swing adsorption or membrane separation techniques. Such plants are distinct from cryogenic separation plants which separate and capture all the components of air.

Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is different from fusion welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sheets together under high pressure.
Ultrapure water (UPW), high-purity water or highly purified water (HPW) is water that has been purified to uncommonly stringent specifications. Ultrapure water is a term commonly used in manufacturing to emphasize the fact that the water is treated to the highest levels of purity for all contaminant types, including: organic and inorganic compounds; dissolved and particulate matter; volatile and non-volatile; reactive, and inert; hydrophilic and hydrophobic; and dissolved gases.
Predictive engineering analytics (PEA) is a development approach for the manufacturing industry that helps with the design of complex products. It concerns the introduction of new software tools, the integration between those, and a refinement of simulation and testing processes to improve collaboration between analysis teams that handle different applications. This is combined with intelligent reporting and data analytics. The objective is to let simulation drive the design, to predict product behavior rather than to react on issues which may arise, and to install a process that lets design continue after product delivery.





