
The Cordillera Central or Cordillera Range is a massive mountain range 320 km long north-south and 118 km east-west. The Cordillera mountain range is situated in the north-central part of the island of Luzon, in the Philippines. The mountain range encompasses all provinces of the Cordillera Administrative Region, as well as portions of eastern Ilocos Norte, eastern Ilocos Sur, eastern La Union, northeastern Pangasinan, western Nueva Vizcaya, and western Cagayan.

Mount Pulag is Luzon's highest peak at 2,928 metres (9,606 ft) above sea level, third-highest mountain in the Philippines, and the 26th-highest peak of an island on Earth. It is second-most prominent mountain in the Philippines, it is a dormant volcano. Located on the triple border of the provinces of Benguet, Ifugao, and Nueva Vizcaya, the borders meet at the mountain's peak. Mount Pulag is third highest next to Mount Apo and Mount Dulang-dulang.
The Philippine archipelago is one of the world's great reservoirs of biodiversity and endemism. The archipelago includes over 7000 islands, and a total land area of 300,780 km².

The Nicobar Islands rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Nicobar Islands. The Nicobar Islands are in the Indian Ocean, lying north of Sumatra and south of the Andaman Islands. The islands are politically part of India, although physically closer to Southeast Asia. Millions of years of isolation from the mainland has given rise to a distinct flora and fauna, including many endemic species.

The Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of Northeastern India and southern Bhutan.

The Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a forest and savanna ecoregion of central Africa. It extends east and west across central Africa, covering parts of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and Uganda. It is part of the belt of transitional forest-savanna mosaic that lie between Africa's moist equatorial Guineo-Congolian forests and the tropical dry forests, savannas, and grasslands to the north and south.

The shrewlike rats, genus Rhynchomys, also known as the tweezer-beaked rats are a group of unusual Old World rats found only on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. They look a great deal like shrews and are an example of convergent evolution. Shrewlike rats evolved to be vermivores (worm-eaters) and insectivores feeding on soft-bodied invertebrates associated with leaf litter.

The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya 16,024 ft (4,884 m), the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home to many intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities. The highlands run generally east-west the length of the island, which is divided politically between Indonesia in the west and Papua New Guinea in the east.
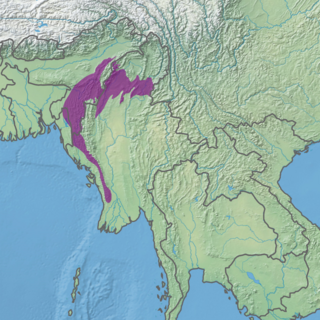
The Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion which occupies the lower hillsides of the mountainous border region joining India, Bangladesh, and Burma (Myanmar). The ecoregion covers an area of 135,600 square kilometres (52,400 sq mi). Located where the biotas of the Indian Subcontinent and Indochina meet, and in the transition between subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, the Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests are home to great biodiversity. The WWF rates the ecoregion as "Globally Outstanding" in biological distinctiveness.

The Borneo montane rain forests are an ecoregion, of cloud forest, within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia.

Balbalasang–Balbalan National Park is a protected area of the Philippines located in the municipality of Balbalan, Kalinga in the Cordillera Administrative Region. The park covers an area of 1,338 hectares and is centered on Mount Balbalasang in the barangay of the same name near the provincial border with Abra. Dubbed the "green heart of the Cordillera", the park is representative of the rich biodiversity and landscape of this mountain region with some of the most intact pine forests and richly endemic flora and fauna. It was declared a national park in 1972 by virtue of Republic Act No. 6463.

The Luzon rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Luzon. Luzon is the largest island in the Philippines, and the Luzon rain forests is the most extensive rainforest ecoregion of the country. The ecoregion includes the lowlands of Luzon and neighboring islands below 1000 meters elevation. Very little of the original rainforest remains, and the status of this area is critical/endangered.

The Luzon montane rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The ecoregion is located on several volcanic and non-volcanic mountains of the island. Luzon is the largest and northernmost major island of the Philippines, located in the western Pacific Ocean.

The Sulawesi lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Indonesia. The ecoregion includes the lowlands of Sulawesi and neighboring islands.

The Mindanao montane rain forests ecoregion covers the montane forests - the zone between the lowland forest and the treeline - in the mountains on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. Because the ecoregion covers only elevations above 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), it exists in seven discontinuous patches surrounded by lowland rainforest. Biodiversity is high, both because of the isolation of separate mountain ranges that have led to species variation within the island, and because of the altitude zonation. Because most of the surrounding lowland forest has been cleared for human use, the montane regions have become an important refuge for rare and endemic species.

The Greater Negros–Panay rain forests ecoregion covers the central Visayan Islands in the Philippines, including the islands of Panay, Negros, Cebu, Masbate, Sibuyan, Ticao, Guimaras, Romblon, Tablas, Siquijor, and Bohol, but excludes Leyte and Samar. During the last ice age, these were all on the same island. The lack of a land bridge to Asia during the ice age kept most Asian megafauna, including elephants and tigers, from reaching the Philippines and the Visayan Islands, which hosts many unique and endemic species with some exclusive only to an island.

The Upper Agno River Basin Resource Reserve is a protected area located on the southeast flank of the Cordillera Central in the Philippine province of Benguet along its border with Ifugao and Nueva Vizcaya. It is a resource reserve located high in the Central and Polis ranges protecting the headwaters of the Agno River. According to section 4 of the National Integrated Protected Areas System Act, a resource reserve is an extensive and relatively isolated area designated as such to preserve the natural resources of the area. The reserve comprises 77,561 hectares of the catchment area that feeds the Ambuklao and Binga dams, two of the country's oldest hydroelectric plants that supply power to the city of Baguio and entire Benguet province. Upper Agno is north of and contiguous with the Lower Agno Watershed Forest Reserve that preserves the immediate downstream of the Binga Dam where the Agno River is impounded by a third dam, the San Roque Dam, the largest in the Philippines and the main source of water, electric energy and irrigation for surrounding regions in Luzon.

The Lower Agno Watershed Forest Reserve is a Philippine protected area that straddles the Cordillera and Ilocos regions encompassing land from the provinces of Benguet and Pangasinan. Operated by the Lower Agno WFR Protected Area Management Board under the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Lower Agno follows the Agno River corridor from the northern villages of Itogon to just north of the municipalities of San Manuel and San Nicolas. The reserve also known as the San Roque Watershed protects the mid-Agno River basin with its meandering river and short tributaries in a pine-forested mountainous terrain at the southern end of the Cordillera Central, around 30 kilometres (19 mi) southeast of Baguio. It is located in an important mining district and includes the reservoir of the San Roque Dam, the largest dam in the country and the prime source of water, hydropower and irrigation for surrounding regions in Luzon.




















