
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.

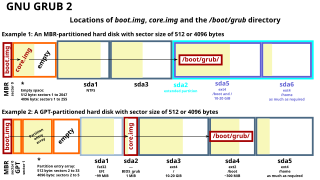
GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A Live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.

Ghost is a disk cloning and backup tool originally developed by Murray Haszard in 1995 for Binary Research. The technology was acquired in 1998 by Symantec.
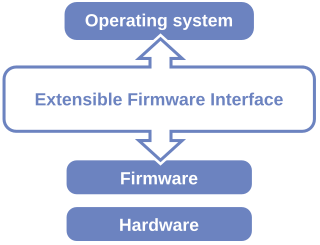
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.
In computing, data recovery is a process of salvaging (retrieving) inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).

BartPE(Bart's Preinstalled Environment) is a discontinued tool that customizes Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 into a lightweight environment, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which could be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive. A BartPE system image is created using PE Builder, a freeware program created by Bart Lagerweij.

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers, which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOS systems, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.

Windows Preinstallation Environment is a lightweight version of Windows used for the deployment of PCs, workstations, and servers, or troubleshooting an operating system while it is offline. It is intended to replace MS-DOS boot disks and can be booted via USB flash drive, PXE, iPXE, CD-ROM, or hard disk. Traditionally used by large corporations and OEMs, it is now widely available free of charge via Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK).

The terms Recovery disc, Rescue Disk/Disc and Emergency Disk all refer to a capability to boot from an external device, possibly a thumb drive, that includes a self-running operating system: the ability to be a boot disk/Disc that runs independent of an internal hard drive that may be failing, or for some other reason is not the operating system to be run.

TestDisk is a free and open-source data recovery utility. It is primarily designed to help recover lost data storage partitions and/or make non-booting disks bootable again when these symptoms are caused by faulty software, certain types of viruses or human error . TestDisk can be used to collect detailed information about a corrupted drive, which can then be sent to a technician for further analysis.

A live USB is a USB flash drive or external hard disk drive containing a full operating system that can be booted. They are the evolutionary next step after live CDs, but with the added benefit of writable storage, allowing customizations to the booted operating system. Live USBs can be used in embedded systems for system administration, data recovery, or test driving, and can persistently save settings and install software packages on the USB device.
The startup process of Windows NT 6 differ from the startup process part of previous versions of Windows.

WinBuilder is a free application designed to build and customize boot disks based on Microsoft Windows (WinPE).
Linux startup process is the multi-stage initialization process performed during booting a Linux installation. It is in many ways similar to the BSD and other Unix-style boot processes, from which it derives.

EasyBCD is a program developed by NeoSmart Technologies to configure and tweak the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), a boot database first introduced in Windows Vista and used in all subsequent Windows releases. EasyBCD can be used to set up multi-boot environments for computers on which some versions of Windows, Linux, BSD and Mac OS X can be simultaneously installed; EasyBCD can also be used for adding entries to bootable tools and utilities, as well as modifying and controlling the behavior of the Windows boot menu. EasyBCD 2.3 introduced additional support for creating and managing entries for UEFI-based Windows entries in the boot menu. As of June 20, 2011 with the release of EasyBCD 2.1, it is no longer free for use in commercial environments which require the purchase of a paid license, however it remains free for home and non-profit use without limitations.

Windows Setup is an installer that prepares a hard disk drive for a Microsoft Windows operating system installation by executing two processes: a) initializing the drive and b) copying system files to that drive in order for the operating system to be run locally .
The early versions of Windows required an existing compatible version of DOS operating system in order to be installed. The Windows NT family, from 3.1 through 6.0 featured text-based installation that prompted users to a GUI wizard in the final steps. The 9x family installer was similar to NT despite it being MS-DOS-based. Additionally, it did not need preinstalled DOS as a requirement. With the release of Windows NT 6.0 (Vista), Microsoft introduced a fully graphical setup environment and UEFI support after dropping MS-DOS backward compatibility from Windows.
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.














