
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

Pelomedusidae is a family of freshwater turtles endemic to sub-Saharan Africa, including Madagascar, São Tomé, and the Seychelles. They range in size from 12 to 45 cm in carapace length, and are generally roundish in shape. They are unable to fully withdraw their heads into their shells, instead drawing them to the side and folding them beneath the upper edge of their shells, hence are called African side-necked turtles.

Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

The Arrau turtle, also known as the South American river turtle, giant South American turtle, giant Amazon River turtle, Arrau sideneck turtle, Amazon River turtle or simply the Arrau, is the largest of the side-neck turtles (Pleurodira) and the largest freshwater turtle in Latin America. The species primarily feeds on plant material and typically nests in large groups on beaches. Due to hunting of adults, collecting of their eggs, pollution, habitat loss, and dams, the Arrau turtle is seriously threatened.

Podocnemis is a genus of aquatic turtles, commonly known as South American river turtles, in the family Podocnemididae. The genus consists of six extant species occurring in tropical South America. Four additional species are known only from fossils.

The yellow-spotted Amazon river turtle, also known commonly as the yellow-headed sideneck turtle and the yellow-spotted river turtle, and locally as the taricaya, is one of the largest South American river turtles.

Stupendemys is an extinct genus of freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. It is the largest freshwater turtle known to have existed, with a carapace over 2 meters long. Its fossils have been found in northern South America, in rocks dating from the Middle Miocene to the very start of the Pliocene, about 13 to 5 million years ago. Male specimens are known to have possessed bony horns growing from the front edges of the shell and the discovery of the fossil of a young adult shows that the carapace of these turtles flattens with age. A fossil skull described in 2021 indicates that Stupendemys was a generalist feeder.

The Pleurodira are one of the two living suborders of turtles, the other being the Cryptodira. The division between these two suborders represents a very deep evolutionary divide between two very different types of turtles. The physical differences between them, although anatomical and largely internal, are nonetheless significant, and the zoogeographic implications of them are substantial. The Pleurodira are known more commonly as the side-necked turtles and the name Pleurodira quite literally translates to side neck, whereas the Cryptodira are known as hidden-necked turtles. The Pleurodira turtles are currently restricted to freshwater habitats in the Southern Hemisphere, largely to Australia, South America, and Africa. Within the Pleurodira, three living families are represented: Chelidae, also known as the Austro-South American side-necked turtles, the Pelomedusidae, also known as the African mud terrapins, and the Podocnemididae, also known as the American side-neck river turtles. However, they were cosmopolitan clade during the Cretaceous and most of the Cenozoic, and even occurred in marine environments around the world.

Elseya is a genus of large side-necked turtles, commonly known as Australian snapping turtles, in the family Chelidae. Species in the genus Elseya are found in river systems in northern and northeastern Australia and throughout the river systems of New Guinea. They are identified by the presence of alveolar ridges on the triturating surfaces of the mouth and the presence of a complex bridge strut.

The Big-headed Amazon River turtle, also known as the big-headed sideneck, is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae.

The red-headed Amazon side-necked turtle, red-headed river turtle or red-headed sideneck is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae. It is found in the Amazon basin in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. The red-headed river turtle is considered a small turtle with a size of less than 32 cm, making it easily distinguishable from other species in the area. Identifying factors of this turtle include colors ranging from dark brown to black, barbels under the chin, and a bright red strip that goes from behind its head to the tympanum.

The Magdalena River turtle or Rio Magdalena river turtle is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae, which diverged from other turtles in the Cretaceous Period, 100 million years ago. It is endemic to northern Colombia, where its home range consists of the Sinú, San Jorge, Cauca, and Magdalena river basins.

The six-tubercled Amazon River turtle or six-tubercled river turtle is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae.

Mesoclemmys is a genus of South American turtles in the family Chelidae.

Carbonemys cofrinii is an extinct giant podocnemidid turtle known from the Middle Paleocene Cerrejón Formation of the Cesar-Ranchería Basin in northeastern Colombia. The formation is dated at around 60 to 57 million years ago, starting at about five million years after the KT extinction event.
Richard Carl "Dick" Vogt was an American herpetologist based in Brazil. He was the director of the Centro de Estudos de Quelônios da Amazônia at the National Institute of Amazonian Research (INPA).
Bairdemys is an extinct genus of side-necked turtles in the family Podocnemididae. The genus existed from the Late Oligocene to Late Miocene and its fossils have been found in South Carolina, Puerto Rico, Panama and Venezuela. The genus was described in 2002 by Gaffney & Wood and the type species is B. hartsteini.
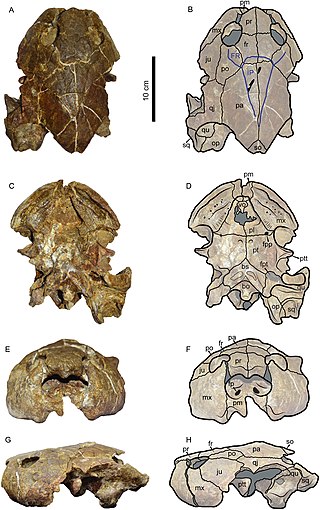
Caninemys is an extinct genus of large freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. Its fossils have been found in Brazil and Colombia, in rocks dating back from the middle to late Miocene.

Amabilis uchoensis is a species of prehistoric pleurodiran turtle from the Late Cretaceous of South America. It is the only species in the genus Amabilis.
Peltocephalus maturin is an extinct species of podocnemidid river turtle closely related to the big-headed Amazon River turtle that lived during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene in what is now Brazil. P. maturin is known from a singular lower jaw of enormous size, with estimates suggesting its carapace may have reached lengths of around 1.70 m. This would make it one of the largest freshwater turtles in history, comparable in size to the Paleocene podocnemidid Carbonemys and only exceeded by the Miocene podocnemidid Stupendemys. Like its closest relative, it was likely an omnivore, the narrow cutting surface of its lower jaw unsuited for strict herbivory or durophagy.


















