
The New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) is a public development corporation which provides public housing in New York City, and is the largest public housing authority in North America. Created in 1934 as the first agency of its kind in the United States, it aims to provide decent, affordable housing for low- and moderate-income New Yorkers throughout the five boroughs of New York City. NYCHA also administers a citywide Section 8 Leased Housing Program in rental apartments. NYCHA developments include single and double family houses, apartment units, singular floors, and shared small building units, and commonly have large income disparities with their respective surrounding neighborhood or community. These developments, particularly those including large-scale apartment buildings, are often referred to in popular culture as "projects."

Manhattanville is a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Manhattan bordered on the north by 135th Street; on the south by 122nd and 125th Streets; on the west by Hudson River; and on the east by Adam Clayton Powell Jr. Boulevard and the campus of City College.

Senator Robert F. Wagner Houses, also known as Triborough Houses, is a public housing development in the East Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan, in New York City and is administered by the New York City Housing Authority. It is located east of Second Avenue in the northeast corner of Manhattan, consists of fourteen 16-story buildings and eight 7-story buildings, a total of 22 buildings. It has 5,290 residents who live in 2,162 apartments. The complex occupies 26.91 acres (10.89 ha). It cost $30,926,000 to construct.

The Robert Fulton Houses is a housing project located in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan in New York City, owned and operated by the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA). The 6.27-acre (2.54 ha) site is located between West 16th and 19th Streets and bounded by Ninth and Tenth Avenues. The project consists of 945 apartments in eleven buildings; three of the developments are 25 stories, while the others are 6 stories high.

The Lester Patterson Houses or Patterson Houses is a public housing development in the Mott Haven neighborhood of the Bronx, New York City. It was named after Bronx assemblyman and judge Lester W. Patterson. It is one of the largest New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) complexes in the city with fifteen buildings 6 and 13-stories tall and 1,790 apartments. It spans an area of 17.18 acres (6.95 ha), which is located between East 138th and 145th Street and covers two main avenues, Third Avenue and Morris Avenue.

The New York City Housing Authority Police Department was a law enforcement agency in New York City that existed from 1952 to 1995, which was then merged into the NYPD. The roots of this organization go back to 1934 and the creation of the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA). New York City Mayor Fiorello H. La Guardia authorized the hiring of security guards to patrol the city's public housing buildings. These guards eventually were trained and became the first officers of the Housing Police, which was officially created in 1952. The Housing Police, along with the New York City Transit Police, was merged into the New York City Police Department in 1995 by New York City Mayor Rudy Giuliani and continues today as the Housing Bureau.

St. Nicholas Houses or "Saint Nick," is a public housing project in Central Harlem, in the borough of Manhattan, New York City and are managed by the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA). The project is located between Adam Clayton Powell Jr. Boulevard and Frederick Douglass Boulevard, spanning a superblock from 127th Street to 131st Street. The project consists of thirteen 14-story buildings containing 1,523 apartment units.

General Ulysses S. Grant Houses or Grant Houses is a public housing project at the northern boundary of Morningside Heights in the borough of Manhattan, New York City. The complex consists of 10 buildings with over 1,940 apartment units on 15.05-acres and is located between Broadway and Morningside Avenue, spanning oddly shaped superblocks from 123rd Street and La Salle Street to 125th Street. The development was named after Ulysses S. Grant (1822-1885), a Civil War Union army general and the 18th President of the United States.

The John Haynes Holmes Towers is a public housing project for low income residents of the Yorkville section of the Upper East Side located just south of the neighborhood's northern limit at 96th Street, in New York City, New York, United States. The neighboring Isaacs Houses and the Holmes Towers border East Harlem, which has the second highest concentration of public housing in the United States. The two public housing buildings, designed by Architects Eggers and Higgins, were completed in 1969, are 25 stories tall and contain 537 apartments. The project is located between 92nd and 93rd Streets from 1st Avenue to York Avenue and the FDR Drive.

The Stanley M. Isaacs Houses is a public housing project for those of low-to-moderate incomes located just south of 96th Street in the Yorkville neighborhood of Manhattan in New York City. The Isaacs Houses and the Holmes Towers border East Harlem, which has the second highest concentration of public housing in New York City. The three public housing buildings are 24 stories tall and contain 635 apartments. The project is located between 93rd and 95th Streets with playground & ball courts from 95th-97th street, stretching from 1st Avenue to the FDR Drive.

Bernard M. Baruch Houses, or Baruch Houses, is a public housing development built by the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) on the Lower East Side of Manhattan. Baruch Houses is bounded by Franklin D. Roosevelt East River Drive to the east, E. Houston Street to the north, Columbia Street to the west, and Delancey Street to the south. The complex, the largest NYCHA development in Manhattan, occupies 27.64 acres (111,900 m2), of which buildings cover 13.4%, a percentage similar to that of most "tower in the park" project designs. It has 2,194 apartments, which house an estimated 5,397 people. These apartments are distributed throughout 17 buildings. Baruch Houses I is seven stories tall, Baruch Houses XI, XIII, and XV are thirteen stories tall, and the rest are fourteen stories tall. Combined, these buildings have 2.9 million square feet (270,000 m2).

Vladeck Houses is a public housing development built and maintained by the New York City Housing Authority on the Lower East Side of Manhattan.

Carver Houses, or George Washington Carver Houses, is a public housing development built and maintained by the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) in Spanish Harlem, a neighborhood of Manhattan.
Governor DeWitt Clinton Houses, also known as DeWitt Clinton Houses or Clinton Houses, is a public housing development built and maintained by the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) in the Spanish Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan. Clinton Houses is composed of six buildings, resting on a non-continuous campus with an area of 5.6 acres (23,000 m2). Five of those (I-V) are 18 stories high, and another (VI) is nine stories high. The six buildings have a total of 749 apartments, which house 1,823 people. Clinton Houses occupies the two blocks that are bordered by East 110th Street to the north, Lexington Avenue to the east, Park Avenue to the west, and East 108th Street to the south. It also occupies the western half of the two blocks that are bordered by East 106th Street to the north, Lexington Avenue to the east, Park Avenue to the west, and East 104th Street to the south, with the exception of a small part along East 106th Street.

The Elliott-Chelsea Houses is a combined housing project of the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA), located between West 25th and 27th Streets and Ninth and Tenth Avenues in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It consists of two contiguous projects which were originally separate but have been combined for administrative purposes: the John Lovejoy Elliott Houses, named after the founder of the Hudson Guild, has four 11- and 12-story buildings which accommodate over 1400 residents in 589 apartments. The Chelsea Houses has over 1,000 residents in 426 apartments within two 21-story buildings.
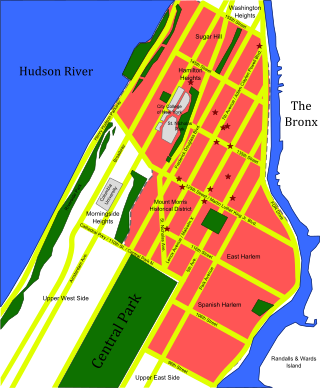
Greater Harlem, in the northern section of the New York City borough of Manhattan, has historically had high poverty and crime rates. Crime in Harlem is primarily related to illicit activities such as theft, robbery, drug trafficking and prostitution. Criminal organizations such as street gangs are responsible for a significant portion of crime, particularly violent crime. The leading cause of death among young black males in Harlem is homicide. According to a survey published in 2013 by Union Settlement Association, residents of East Harlem perceive crime as their biggest single concern. Greater Harlem has one of the highest violent crime rates in New York City despite significant declines from historic highs.

The Farragut Houses is a public housing project located in the downtown neighborhood of northwestern Brooklyn, New York City, bordering the Brooklyn Navy Yard. Farragut Houses is a property of New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA). The houses contain 3,272 residents who reside in ten buildings that are each 13 to 14 stories high.
The Louis Heaton Pink Houses or Pink Houses are a housing project in New York City that were established in the East New York neighborhood in Brooklyn in 1959. It consists of 22 eight-storey buildings with 1,500 apartment units over a 31.1-acre expanse, bordered by Crescent Street, Linden Boulevard, Elderts Lane and Stanley Avenue. It is owned and managed by New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA).

Edenwald Houses are a housing project in the Eastchester and Laconia neighborhoods of the Bronx, New York City. Established on October 30, 1953, the project consists of forty buildings, 3 and 14 stories tall with 2,039 apartment units. It covers a 48.88-acre development is bordered by Grenada Place, East 225th Street, Baychester Avenue, Schieffelin Avenue and Laconia Avenues. It is owned and managed by New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) and is the largest development in the Bronx.


















