The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Incoterms define the responsibilities of exporters and importers in the arrangement of shipments and the transfer of liability involved at various stages of the transaction. They are widely used in international commercial transactions or procurement processes and their use is encouraged by trade councils, courts and international lawyers. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common contractual sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs, and risks associated with the global or international transportation and delivery of goods. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer, but they do not themselves conclude a contract, determine the price payable, currency or credit terms, govern contract law or define where title to goods transfers.

A customs officer is a law enforcement agent who enforces customs laws, on behalf of a government.

A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are used for military purposes.

The Australian Customs and Border Protection Service was an Australian federal government agency responsible for managing the security and integrity of the Australian border and facilitating the movement of legitimate international travelers and goods, whilst protecting the safety, security and commercial interests of Australians. It was headquartered in Canberra and employed over 5,800 people around Australia and overseas.

The Port of Hong Kong, located by the South China Sea, is a deepwater seaport dominated by trade in containerised manufactured products, and to a lesser extent raw materials and passengers. A key factor in the economic development of Hong Kong, the natural shelter and deep waters of Victoria Harbour provide ideal conditions for berthing and the handling of all types of vessels. It is one of the busiest ports in the world, in the three categories of shipping movements, cargo handled and passengers carried. This makes Hong Kong a Large-Port Metropolis.
A freight rate is a price at which a certain cargo is delivered from one point to another. The price depends on the form of the cargo, the mode of transport, the weight of the cargo, and the distance to the delivery destination. Many shipping services, especially air carriers, use dimensional weight for calculating the price, which takes into account both weight and volume of the cargo.

Sealift is a term used predominantly in military logistics and refers to the use of cargo ships for the deployment of military assets, such as weaponry, vehicles, military personnel, and supplies. It complements other means of transport, such as strategic airlifts, in order to enhance a state's ability to project power.

A freight forwarder, or forwarding agent, is a person or a company who, for a fee, organizes shipments for the shipper by liaising with carriers. A forwarder does not move the goods but acts as an agent in the logistics network.
A charterparty is a maritime contract between a shipowner and a "charterer" for the hire of either a ship for the carriage of passengers or cargo, or a yacht for pleasure purposes.
The Maritime Transportation Security Act of 2002 (MTSA) is an Act of Congress enacted by the 107th United States Congress to address port and waterway security. It was signed into law by President George W. Bush on November 25, 2002.

The National Cargo Bureau (NCB) a not-for-profit marine surveying organization charged with assisting the U.S. Coast Guard with carrying out the provisions of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea. The NCB was formed by a group of marine underwriters and the Coast Guard for the purpose of reducing losses of grain ships. Any ship loading grain in the US sailing for a foreign port must have a certificate issued by the NCB in order to sail( See U.S. Coast Guard Navigation and Vessel Inspection Circular No. 5-94 - NVIC 05-94 ). The NCB acts with and enforces the regulations of the Coast Guard in this area. Grain ships have unique stability issues and are prone to capsize if loaded improperly. Headquartered in New York City, the NCB has offices throughout United States.

The Standard Carrier Alpha Code (SCAC) is a privately controlled US code used to identify vessel operating common carriers (VOCC). It is typically two to four letters long. The National Motor Freight Traffic Association developed the SCAC code in the 1960s to help road transport companies computerize data and records.

An arrival card, also known as an incoming passenger card, landing card or disembarkation card, is a legal document used by immigration authorities of many countries to obtain information about incoming passenger not provided by the passenger's passport and to provide a record of a person's entry into the country. The card may also provide information on health and character requirements for non-citizens entering the country. Some countries require an arrival card for each incoming passenger, while others require one card per family unit, and some only require an arrival card for non-citizens only.

In shipping, break-bulk, breakbulk, or break bulk cargo, also called general cargo, refers to goods that are stowed on board ship in individually counted units. Traditionally, the large numbers of items are recorded on distinct bills of lading that list them by different commodities. This is in contrast to cargo stowed in modern intermodal containers as well as bulk cargo, which goes directly, unpackaged and in large quantities, into a ship's hold(s), measured by volume or weight.
Affreightment is a legal term relating to shipping.
The Importer Security Filing (ISF) also referred to as 10+2, is a customs import requirement of the United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) ; which requires containerized cargo information, for security purposes, to be transmitted to the agency at least 24 hours (19 CFR section 149.2 before goods are loaded onto an ocean vessel headed to the U.S. for shipment into the U.S. 10+2 is pursuant to section 203 of the SAFE Port Act, and requires importers to provide 10 data elements to CBP, as well as 2 more data documents from the carrier.

The doctrine of deviation is a particular aspect of contracts of carriage of goods by sea. A deviation is a departure from the "agreed route" or the "usual route", and it can amount to a serious breach of contract.
A shipping agency or shipping agent is the designated person or agency held responsible for handling shipments and cargo, and the general interests of its customers, at ports and harbors worldwide, on behalf of ship owners, managers, and charterers. In some parts of the world, these agents are referred to as port agents or cargo brokers. There are several categories of shipping agents such as: port agents, liner agents, and own agencies, each rendering specific services depending on the shipping company they represent.
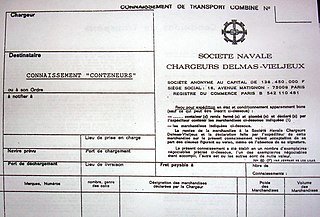
A bill of lading is a document issued by a carrier to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment. Although the term historically related only to carriage by sea, a bill of lading may today be used for any type of carriage of goods. Bills of lading are one of three crucial documents used in international trade to ensure that exporters receive payment and importers receive the merchandise. The other two documents are a policy of insurance and an invoice. Whereas a bill of lading is negotiable, both a policy and an invoice are assignable. In international trade outside the United States, bills of lading are distinct from waybills in that the latter are not transferable and do not confer title. Nevertheless, the UK Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1992 grants "all rights of suit under the contract of carriage" to the lawful holder of a bill of lading, or to the consignee under a sea waybill or a ship's delivery order.
Container port design process is a set of correlated practices considered during container port design, aiming to transfer general business mission into detailed design documents for future construction and operation.










