
A Masonic lodge, often termed a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. It is also commonly used as a term for a building in which such a unit meets. Every new lodge must be warranted or chartered by a Grand Lodge, but is subject to its direction only in enforcing the published constitution of the jurisdiction. By exception the three surviving lodges that formed the world's first known grand lodge in London have the unique privilege to operate as time immemorial, i.e., without such warrant; only one other lodge operates without a warrant – the Grand Stewards' Lodge in London, although it is not also entitled to the "time immemorial" title. A Freemason is generally entitled to visit any lodge in any jurisdiction in amity with his own. In some jurisdictions this privilege is restricted to Master Masons. He is first usually required to check, and certify, the regularity of the relationship of the Lodge – and be able to satisfy that Lodge of his regularity of membership. Freemasons gather together as a Lodge to work the three basic Degrees of Entered Apprentice, Fellowcraft, and Master Mason.
The York Rite, sometimes referred to as the American Rite, is one of several Rites of Freemasonry. It is named for, but not practiced in, York, Yorkshire, England. A Rite is a series of progressive degrees that are conferred by various Masonic organizations or bodies, each of which operates under the control of its own central authority. The York Rite specifically is a collection of separate Masonic Bodies and associated Degrees that would otherwise operate independently. The three primary bodies in the York Rite are the Chapter of Royal Arch Masons, Council of Royal & Select Masters or Council of Cryptic Masons, and the Commandery of Knights Templar, each of which are governed independently but are all considered to be a part of the York Rite. There are also other organizations that are considered to be directly associated with the York Rite, or require York Rite membership to join such as the York Rite Sovereign College but in general the York Rite is considered to be made up of the aforementioned three. The Rite's name is derived from the city of York, where, according to one Masonic legend, the first meetings of Masons in England took place.

The George Washington Masonic National Memorial is a Masonic building and memorial located in Alexandria, Virginia, outside Washington, D.C. It is dedicated to the memory of George Washington, the first president of the United States and a Mason. The tower is fashioned after the ancient Lighthouse of Ostia in Ostia Antica. The 333-foot (101 m) tall memorial sits atop Shooter's Hill at 101 Callahan Drive. Construction began in 1922, the building was dedicated in 1932, and the interior finally completed in 1970. In July 2015, it was designated a National Historic Landmark for its architecture, and as one of the largest-scale private memorials to honor Washington.

The Order of Mark Master Masons is an appendant order of Freemasonry that exists in some Masonic jurisdictions, and confers the degrees of Mark Mason and Mark Master.

The Most Worshipful Grand Lodge of Ancient Free and Accepted Masons of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, commonly referred to as the Grand Lodge of Massachusetts and abbreviated GLMA, is the main governing body of Freemasonry within Massachusetts, and maintains Lodges in other jurisdictions overseas, namely Panama, Chile, the People's Republic of China, and Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, Cuba.

The Royal Order of Scotland is an appendant order within the structures of Freemasonry. Membership is an honour extended to Freemasons by invitation. The Grand Lodge of the Royal Order of Scotland is headquartered in Edinburgh, with a total of 88 subordinate Provincial Grand Lodges; of these, the greatest concentration is in the British Isles, with the rest located in countries around the world.

The Knights Templar, full name The United Religious, Military and Masonic Orders of the Temple and of St John of Jerusalem, Palestine, Rhodes and Malta, is a fraternal order affiliated with Freemasonry. Unlike the initial degrees conferred in a regular Masonic Lodge, which only require a belief in a Supreme Being regardless of religious affiliation, the Knights Templar is one of several additional Masonic Orders in which membership is open only to Freemasons who profess a belief in Christianity. One of the obligations entrants to the order are required to declare is to protect and defend the Christian faith. The word "United" in its full title indicates that more than one historical tradition and more than one actual order are jointly controlled within this system. The individual orders 'united' within this system are principally the Knights of the Temple, the Knights of Malta, the Knights of St Paul, and only within the York Rite, the Knights of the Red Cross.
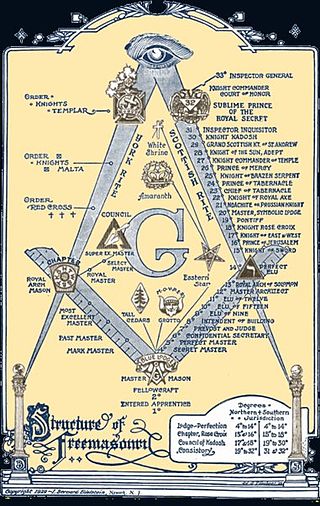
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.

The Royal Arch is a degree of Freemasonry. The Royal Arch is present in all main masonic systems, though in some it is worked as part of Craft ('mainstream') Freemasonry, and in others in an appendant ('additional') order. Royal Arch Masons meet as a Chapter; in the Supreme Order of the Royal Arch as practised in the British Isles, much of Europe and the Commonwealth, Chapters confer the single degree of Royal Arch Mason.
The Allied Masonic Degrees (AMD) are a series of Masonic degrees conferred by Councils of the Allied Masonic Degrees. The Allied Masonic Degrees form an appendant order of Freemasonry that exists in some Masonic jurisdictions; its degrees are conferred only by invitation. Councils of the Allied Masonic Degrees exist in Great Britain, the United States, Canada, France, Australia, India, Benin and Congo, and their members also educate one another by presenting research papers on Freemasonry.

Thomas Dunckerley was a prominent freemason, being appointed Provincial Grand Master of several provinces, promoting Royal Arch masonry, introducing Mark Masonry to England, and instituting a national body for Templar masonry. This was made possible by an annuity of £100, rising to £800, which he obtained from King George III by claiming to be his father's illegitimate half brother.

The current Indianapolis Masonic Temple, also known as Indiana Freemasons Hall, is a historic Masonic Temple located at Indianapolis, Indiana. Construction was begun in 1908, and the building was dedicated in May 1909. It is an eight-story, Classical Revival style cubic form building faced in Indiana limestone. The building features rows of engaged Ionic order columns. It was jointly financed by the Indianapolis Masonic Temple Association and the Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons of Indiana, and was designed by the distinguished Indianapolis architectural firm of Rubush and Hunter.

The Red Cross of Constantine, or more formally the Masonic and Military Order of the Red Cross of Constantine and the Appendant Orders of the Holy Sepulchre and of St John the Evangelist, is a Christian fraternal order of Freemasonry. Candidates for the order must already be members of Craft Freemasonry (lodge) and Royal Arch Freemasonry (chapter); they must also be members of the Christian religion, and proclaim their belief in the Christian doctrine of the Holy Trinity.

The Order of Knight Masons is a chivalric Masonic order, open to all Master Masons who are also members of a Mark Lodge and a Royal Arch Chapter Members of the order meet in Councils of Knight Masons which are governed by the Grand Council of Knight Masons based in Dublin, Ireland. A member of the group is a Knight Mason.
Freemasonry in Scotland in lodges chartered by the Grand Lodge of Scotland comprises the Scottish Masonic Constitution as regular Masonic jurisdiction for the majority of freemasons in Scotland. There are also lodges operating under the Scottish Masonic Constitution in countries outside of Scotland. Many of these are countries linked to Scotland and the United Kingdom through the Commonwealth of Nations and prior colonies and other settlements of the British Empire although there are several lodges in countries such as Lebanon, Belgium, Chile and Peru, which do not have such connections.

The Asheville Masonic Temple is a Masonic Temple located in Asheville, North Carolina. Designed by British American architect and Freemason Richard Sharp Smith, the building was opened in April 1915. It is listed in the United States National Register of Historic Places as a contributing building in the Downtown Asheville Historic District.
The Order of Royal and Select Masters is an appendant order of Freemasonry and frequently referred to as 'Cryptic Degrees'. In England and Wales, the degrees are practiced as a stand-alone organisation of Freemasonry while in some other Masonic Constitutions, they form part of the York Rite.

The Fort Worth Masonic Temple is a Masonic Temple located at 1100 Henderson Street, Fort Worth, Texas. Designed by Wiley G. Clarkson, the Neoclassical/early PWA Art Moderne structure was completed in 1931 and has largely remained unchanged. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2017 as Masonic Temple.
Isaac Newton University Lodge No 859 is a Masonic Lodge based at the University of Cambridge for matriculated members of the university. As of 2013 there were approximately 200 members. This is about half the 397 subscribing members in 1955. The lodge meets at Bateman Street Masonic Hall, with the lodge's badge or standard a combination of Isaac Newton's coat of arms and the University of Cambridge's coat of arms. The lodge is also a member of the Association of Medical, university, and Legal Lodges.
















