Related Research Articles

In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero. Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which microscopic quantum-mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. More generally, condensation refers to the appearance of macroscopic occupation of one or several states: for example, in BCS theory, a superconductor is a condensate of Cooper pairs. As such, condensation can be associated with phase transition, and the macroscopic occupation of the state is the order parameter.

In condensed matter physics, a supersolid is a spatially ordered material with superfluid properties. In the case of helium-4, it has been conjectured since the 1960s that it might be possible to create a supersolid. Starting from 2017, a definitive proof for the existence of this state was provided by several experiments using atomic Bose–Einstein condensates. The general conditions required for supersolidity to emerge in a certain substance are a topic of ongoing research.

Deborah Shiu-lan Jin was an American physicist and fellow with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST); Professor Adjunct, Department of Physics at the University of Colorado; and a fellow of the JILA, a NIST joint laboratory with the University of Colorado.

Wolfgang Ketterle is a German physicist and professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). His research has focused on experiments that trap and cool atoms to temperatures close to absolute zero, and he led one of the first groups to realize Bose–Einstein condensation in these systems in 1995. For this achievement, as well as early fundamental studies of condensates, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001, together with Eric Allin Cornell and Carl Wieman.

Lene Vestergaard Hau is a Danish physicist and educator. She is the Mallinckrodt Professor of Physics and of Applied Physics at Harvard University.
Hendricus Theodorus Christiaan "Henk" Stoof is a professor in theoretical physics at Utrecht University in the Netherlands. His main interests are atomic physics, condensed matter physics and many-body physics. He is a Fellow of the American Physical Society.

Rudolf Grimm is an experimental physicist from Austria. His work centres on ultracold atoms and quantum gases. He was the first scientist worldwide who, with his team, succeeded in realizing a Bose–Einstein condensation of molecules.

Theodor Wolfgang Hänsch is a German physicist. He received one-third of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics for "contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique", sharing the prize with John L. Hall and Roy J. Glauber.
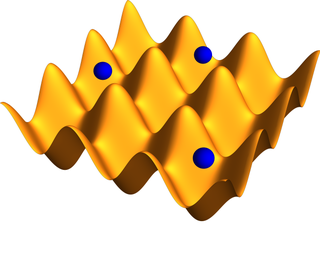
An optical lattice is formed by the interference of counter-propagating laser beams, creating a spatially periodic polarization pattern. The resulting periodic potential may trap neutral atoms via the Stark shift. Atoms are cooled and congregate at the potential extrema. The resulting arrangement of trapped atoms resembles a crystal lattice and can be used for quantum simulation.
The Bose–Hubbard model gives a description of the physics of interacting spinless bosons on a lattice. It is closely related to the Hubbard model that originated in solid-state physics as an approximate description of superconducting systems and the motion of electrons between the atoms of a crystalline solid. The model was introduced by Gersch and Knollman in 1963 in the context of granular superconductors. The model rose to prominence in the 1980s after it was found to capture the essence of the superfluid-insulator transition in a way that was much more mathematically tractable than fermionic metal-insulator models.
In condensed matter physics, an ultracold atom is an atom with a temperature near absolute zero. At such temperatures, an atom's quantum-mechanical properties become important.
Atomtronics is an emerging type of computing consisting of matter-wave circuits which coherently guide propagating ultra-cold atoms. The systems typically include components analogous to those found in electronic or optical systems, such as beam splitters and transistors. Applications range from studies of fundamental physics to the development of practical devices.

The Max-Planck-Institute of Quantum Optics is a part of the Max Planck Society which operates 87 research facilities in Germany.
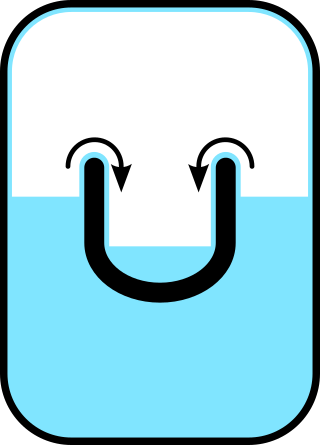
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two isotopes of helium when they are liquefied by cooling to cryogenic temperatures. It is also a property of various other exotic states of matter theorized to exist in astrophysics, high-energy physics, and theories of quantum gravity. The theory of superfluidity was developed by Soviet theoretical physicists Lev Landau and Isaak Khalatnikov.
Immanuel Bloch is a German experimental physicist. His research is focused on the investigation of quantum many-body systems using ultracold atomic and molecular quantum gases. Bloch is known for his work on atoms in artificial crystals of light, optical lattices, especially the first realization of a quantum phase transition from a weakly interacting superfluid to a strongly interacting Mott insulating state of matter.

Tilman Esslinger is a German experimental physicist. He is Professor at ETH Zurich, Switzerland, and works in the field of ultracold quantum gases and optical lattices.
Lev Petrovich Pitaevskii was a Russian theoretical physicist, who made contributions to the theory of quantum mechanics, electrodynamics, low-temperature physics, plasma physics, and condensed matter physics. Together with his PhD supervisor Evgeny Lifshitz and with Vladimir Berestetskii, he was also the co-author of a few volumes of the influential Landau–Lifschitz Course of Theoretical Physics series. His academic status was professor.
Monika Schleier-Smith is an American experimental physicist studying many-body quantum physics by precisely assembling systems of ultracold atoms. Her research helps connect the world of theoretical and experimental physics. These atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) engineered systems have applications in quantum sensing, coherent control, and quantum computing. Schleier-Smith is an associate professor of physics at Stanford University, a Sloan Research Fellow, and a National Science Foundation CAREER Award recipient. Schleier-Smith also serves on the board of directors for the Hertz Foundation. She also works to improve education through speaking and serving on panels.
The I. I. Rabi Prize in Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics is given by the American Physical Society to recognize outstanding work by mid-career researchers in the field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. The award was endowed in 1989 in honor of the physicist I. I. Rabi and has been awarded biannually since 1991.

Gretchen K. Campbell is an American atomic, molecular, and optical physicist associated with the National Institute of Standards and Technology. She works in the field of atomtronics and has received awards in recognition of her research contributions on Bose-Einstein condensates.
References
- ↑ Greiner, Markus; Mandel, Olaf; Esslinger, Tilman; Hänsch, Theodor W.; Bloch, Immanuel (January 2002). "Quantum phase transition from a superfluid to a Mott insulator in a gas of ultracold atoms". Nature. 415 (6867): 39–44. Bibcode:2002Natur.415...39G. doi:10.1038/415039a. PMID 11780110. S2CID 4411344.
- ↑ "Prize Recipient". www.aps.org. Retrieved November 16, 2015.
- ↑ "Winners of the McMillan Award | Department of Physics at the U of I". physics.illinois.edu. Retrieved November 16, 2015.
- ↑ "MacArthur Fellows Program: Meet the 2011 Fellows". September 20, 2011. John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation. Retrieved September 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Prize Recipient". www.aps.org. Retrieved November 16, 2015.
- ↑ "Greiner, Yelin are 2017 APS Fellows". Harvard University. Retrieved July 22, 2019.