
The mackerel, tuna, and bonito family, Scombridae, includes many of the most important and familiar food fishes. The family consists of 51 species in 15 genera and two subfamilies. All species are in the subfamily Scombrinae, except the butterfly kingfish, which is the sole member of subfamily Gasterochismatinae.

The swordfish, also known as the broadbill in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfish are elongated, round-bodied, and lose all teeth and scales by adulthood. These fish are found widely in tropical and temperate parts of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, and can typically be found from near the surface to a depth of 550 m (1,800 ft), and exceptionally up to depths of 2,234 m. They commonly reach 3 m (10 ft) in length, and the maximum reported is 4.55 m in length and 650 kg (1,430 lb) in weight.

A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through convergent evolution they have independently evolved external superficial fish-like body plans adapted to their marine environments, including most numerously fish, but also mammals such as cetaceans, and even extinct ancient marine reptiles such as various known species of ichthyosaurs. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three.

Coryphaena is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes known as the dolphinfishes, and is currently the only known genus in the family Coryphaenidae. The generic name is from Greek κορυφή and -αινα. Species in this genus have compressed heads and single dorsal fins that run the entire length of the fishes' bodies.

The Atlantic sailfish is a species of marine fish in the family Istiophoridae of the order Istiophoriformes. It is found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, except for large areas of the central North Atlantic and the central South Atlantic, from the surface to depths of 200 m (656 ft). The Atlantic sailfish is related to the marlin.

The Atlantic blue marlin is a species of marlin endemic to the Atlantic Ocean. It is closely related to, and usually considered conspecific with, the Indo-Pacific blue marlin, then simply called blue marlin. Some authorities consider both species distinct.

The sailfish is one of two species of marine fish in the genus Istiophorus, which belong to the family Istiophoridae (marlins). They are predominantly blue to gray in colour and have a characteristically large dorsal fin known as the sail, which often stretches the entire length of the back. Another notable characteristic is the elongated rostrum (bill) consistent with that of other marlins and the swordfish, which together constitute what are known as billfish in sport fishing circles. Sailfish live in colder pelagic waters of all Earth's oceans, and hold the record for the highest speed of any marine animal.

The billfish are a group of saltwater predatory fish characterised by prominent pointed bills (rostra), and by their large size; some are longer than 4 m (13 ft). Extant billfish include sailfish and marlin, which make up the family Istiophoridae; and swordfish, sole member of the family Xiphiidae. They are often apex predators which feed on a wide variety of smaller fish, crustaceans and cephalopods. These two families are sometimes classified as belonging to the order Istiophoriformes, a group which originated around 71 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous, with the two families diverging around 15 million years ago in the Late Miocene. However, they are also classified as being closely related to the mackerels and tuna within the suborder Scombroidei of the order Perciformes. However, the 5th edition of the Fishes of the World does recognise the Istiophoriformes as a valid order, albeit including the Sphyraenidae, the barracudas.

The Indo-Pacific sailfish is a sailfish native to the Indian and Pacific Oceans and is naturalized in the Atlantic where it has entered the Mediterranean Sea via the Suez Canal as a Lessepsian migrant. It is dark blue on top, brown-blue laterally, silvery white underbelly; upper jaw elongated in the form of a spear; first dorsal fin greatly enlarged in the form of a sail, with many black cones, its front squared off, highest at its midpoint; pelvic fins very narrow, reaching almost to the anus; body covered with embedded scales, blunt at end; lateral line curved above pectoral fin, then straight to base of tail. They have a large and sharp bill, which they use for hunting. They feed on tuna and mackerel, some of the fastest fish in the Ocean. Most authorities only recognise a single species of sailfish, I. platypterus.

The black marlin is a species of marlin found in tropical and subtropical areas of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Reaching lengths of over 4.5 m (15 ft), it is one of the largest marlins and also one of the largest bony fish. Marlin are among the fastest fish, but speeds may be exaggerated in popular media, such as reports of 132 km/h (82 mph). A 2016 study estimated maximum swimming speeds from muscle contraction times, which in turn limit the tail-beat frequency; the study suggested a theoretical upper limit for the black marlin's burst speed of 36 kilometres per hour (22 mph). Black marlin are fished commercially and are also a highly prized game fish. Black marlins have been known to drag Maldivian fishing boats of the ancient times for very long distances until it got tired; and then it would take many hours for the fishermen to row or sail back home.

Marlin fishing or billfishing is offshore saltwater game fishing targeting several species of fast-swimming pelagic predatory fish with elongated rostrum collectively known as billfish, which include those from the families Istiophoridae and Xiphiidae (swordfish). It is considered by some fishermen to be a pinnacle of big-game fishing, due to the size, speed and power of the billfish and their relative elusiveness.

Makaira is a genus of marlin in the family Istiophoridae. It includes the Atlantic blue, and Indo-Pacific blue marlins. In the past, the black marlin was also included in this genus, but today it is placed in its own genus, Istiompax.

The roundscale spearfish is an Istiophoridae species of marlin living in the epipelagic zone of the Atlantic Ocean. It has long been misidentified as white marlin but can be differentiated thanks to their scale shapes that gives its name. Not much is known about this species. It could reach a length of 160 cm and 21,5 kg and has no conservation status yet due to a lack of data.

The little tunny, also known as the false albacore, little tuna, bonita, or erroneously as the blue bonito, is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It can be found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean and Black seas; in the western Atlantic, it ranges from Brazil to the New England states. The little tunny is a pelagic fish that can be found regularly in both offshore and inshore waters, and it is classified as a highly migratory species. The little tunny is best identified by the "worm-like" markings on its back and the dark spots appearing between its pectoral and ventral fins.

Caranx is a genus of tropical to subtropical marine fishes in the jack family Carangidae, commonly known as jacks, trevallies and kingfishes. They are moderate- to large-sized, deep-bodied fishes which are distinguished from other carangid genera by specific gill raker, fin ray and dentition characteristics. The genus is represented in the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans, inhabiting both inshore and offshore regions, ranging from estuaries and bays to deep reefs and offshore islands. All species are powerful predators, taking a variety of fish, crustaceans and cephalopods, while they in turn are prey to larger pelagic fishes and sharks. A number of fish in the genus have a reputation as powerful gamefish and are highly sought by anglers. They often make up high amounts of the catch in various fisheries, but are generally considered poor to fair table fishes.

The Indo-Pacific blue marlin is a species of marlin belonging to the family Istiophoridae.
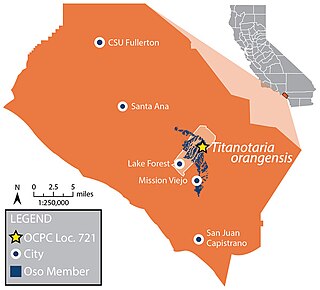
The Capistrano Formation is a geologic formation in coastal southern Orange County, California. It preserves fossils dating back to the late Miocene to early Pliocene, with the Oso Member representing a near-shore environment. Fifty-nine species and varieties of foraminifera are recognized from the Capistrano Formation alongside a diverse array of marine mammals including up to five species of walrus.

Sphyraena helleri, the Heller's barracuda, is a schooling species of barracuda in the family Sphyraenidae.

Istiophoriformes are an order of bony fish which is not fully recognized by some taxonomists, with some including the two extant families Xiphiidae and Istiophoridae, and others, including the family Sphyraenidae.

Of the twelve species of billfish, there are six species of Billfish in the Indian Ocean.


























