Related Research Articles

Herbert Marshall McLuhan was a Canadian philosopher whose work is among the cornerstones of the study of media theory. He studied at the University of Manitoba and the University of Cambridge. He began his teaching career as a professor of English at several universities in the United States and Canada before moving to the University of Toronto in 1946, where he remained for the rest of his life. He is known as the "father of media studies".

Media studies is a discipline and field of study that deals with the content, history, and effects of various media; in particular, the mass media. Media Studies may draw on traditions from both the social sciences and the humanities, but mostly from its core disciplines of mass communication, communication, communication sciences, and communication studies.

Harold Adams Innis was a Canadian professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on media, communication theory, and Canadian economic history. He helped develop the staples thesis, which holds that Canada's culture, political history, and economy have been decisively influenced by the exploitation and export of a series of "staples" such as fur, fish, lumber, wheat, mined metals, and coal. The staple thesis dominated economic history in Canada from the 1930s to 1960s, and continues to be a fundamental part of the Canadian political economic tradition.
Media ecology theory is the study of media, technology, and communication and how they affect human environments. The theoretical concepts were proposed by Marshall McLuhan in 1964, while the term media ecology was first formally introduced by Neil Postman in 1968.
New media are communication technologies that enable or enhance interaction between users as well as interaction between users and content. In the middle of the 1990s, the phrase "new media" became widely used as part of a sales pitch for the influx of interactive CD-ROMs for entertainment and education. The new media technologies, sometimes known as Web 2.0, include a wide range of web-related communication tools such as blogs, wikis, online social networking, virtual worlds, and other social media platforms.

Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man is a 1964 book by Marshall McLuhan, in which the author proposes that the media, not the content that they carry, should be the focus of study. He suggests that the medium affects the society in which it plays a role mainly by the characteristics of the medium rather than the content. The book is considered a pioneering study in media theory.
In media studies, mass communication, media psychology, communication theory, and sociology, media influence and themedia effect are topics relating to mass media and media culture's effects on individuals' or audiences' thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors. Through written, televised, or spoken channels, mass media reach large audiences. Mass media's role in shaping modern culture is a central issue for the study of culture.
Media transparency, also referred to as transparent media or media opacity, is a concept that explores how and why information subsidies are being produced, distributed and handled by media professionals, including journalists, editors, public relations practitioners, government officials, public affairs specialists, and spokespeople. In short, media transparency reflects the relationship between civilization and journalists, news sources and government. According to a textual analysis of “Information Subsidies and Agenda Building: A Study of Local Radio News”, an information subsidy is defined as “any item provided to the media in order to gain time or space”. In order to understand media transparency, one must gain an understanding of the different aspects in which media transparency is researched, understood, and explored. The following page will attempt to examine media transparency as it has grown and how it affects the modern world.
Media psychology is the branch and specialty field in psychology that focuses on the interaction of human behavior with media and technology. Media psychology is not limited to mass media or media content; it includes all forms of mediated communication and media technology-related behaviors, such as the use, design, impact, and sharing behaviors. This branch is a relatively new field of study because of advancement in technology. It uses various methods of critical analysis and investigation to develop a working model of a user's perception of media experience. These methods are used for society as a whole and on an individual basis. Media psychologists are able to perform activities that include consulting, design, and production in various media like television, video games, films, and news broadcasting. Media psychologists are not considered to be those who are featured in media, rather than those who research, work or contribute to the field. Mediacology is a new term used as a collaborative word of Media and Psychology.
Medium theory is a mode of analysis that examines the ways in which particular communication media and modalities impact the specific content (messages) they are meant to convey. It Medium theory refers to a set of approaches that can be used to convey the difference in meanings of messages depending on the channel through which they are transmitted. Medium theorists argue that media are not simply channels for transmitting information between environments, but are themselves distinct social-psychological settings or environments that encourage certain types of interaction and discourage others.
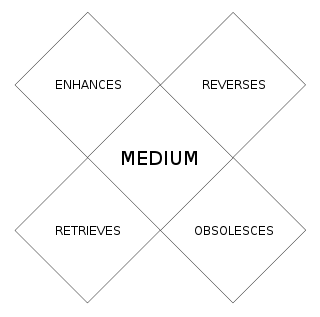
Marshall McLuhan's tetrad of media effects uses a tetrad - a four-part construct - to examine the effects on society of any technology/medium by dividing its effects into four categories and displaying them simultaneously. The tetrad first appeared in print in articles by McLuhan in the journals Technology and Culture (1975) and et cetera (1977). It first appeared in book form in his posthumously-published works Laws of Media (1988) and The Global Village (1989).
The alphabet effect is a group of hypotheses in communication theory arguing that phonetic writing, and alphabetic scripts in particular, have served to promote and encourage the cognitive skills of abstraction, analysis, coding, decoding, and classification. Promoters of these hypotheses are associated with the Toronto School of Communication, such as Marshall McLuhan, Harold Innis, Walter Ong, Vilém Flusser and more recently Robert K. Logan; the term "alphabet effect" comes from Logan's 1986 work.
Mediation in Marxist theory refers to the reconciliation of two opposing forces within a given society by a mediating object. Put another way "Existence differs from Being by its mediation"...."The Thing-in-itself and its mediated Being are both contained in Existence, and each is an Existence; the Thing-in-it-self exists and is the essential Existence of the Thing, while mediated Being is its unessential Existence ..."
Joshua Meyrowitz is a professor of communication at the department of Communication at the University of New Hampshire in Durham. He has published works regarding the effects of mass media, including No Sense of Place: The Impact of Electronic Media on Social Behavior, an analysis of the effects various media technologies have caused, particularly television.
Harold Adams Innis was a professor of political economy at the University of Toronto and the author of seminal works on Canadian economic history and on media and communication theory. He helped develop the staples thesis, which holds that Canada's culture, political history and economy have been decisively influenced by the exploitation and export of a series of staples such as fur, fish, wood, wheat, mined metals and fossil fuels. Innis's communications writings explore the role of media in shaping the culture and development of civilizations. He argued, for example, that a balance between oral and written forms of communication contributed to the flourishing of Greek civilization in the 5th century BC. But he warned that Western civilization is now imperiled by powerful, advertising-driven media obsessed by "present-mindedness" and the "continuous, systematic, ruthless destruction of elements of permanence essential to cultural activity."
The Toronto School is a school of thought in communication theory and literary criticism, the principles of which were developed chiefly by scholars at the University of Toronto. It is characterized by exploration of Ancient Greek literature and the theoretical view that communication systems create psychological and social states. The school originated from the works of Eric A. Havelock and Harold Innis in the 1930s, and grew to prominence with the contributions of Edmund Snow Carpenter, Northrop Frye and Marshall McLuhan.
The ritual view of communication is a communications theory proposed by James W. Carey, wherein communication–the construction of a symbolic reality–represents, maintains, adapts, and shares the beliefs of a society in time. In short, the ritual view conceives communication as a process that enables and enacts societal transformation.
Technological determinism is a reductionist theory that assumes that a society's technology progresses by following its own internal logic of efficiency, while determining the development of the social structure and cultural values. The term is believed to have originated from Thorstein Veblen (1857–1929), an American sociologist and economist. The most radical technological determinist in the United States in the 20th century was most likely Clarence Ayres who was a follower of Thorstein Veblen and John Dewey. William Ogburn was also known for his radical technological determinism and his theory on cultural lag.
New media studies is an academic discipline that explores the intersections of computing, science, the humanities, and the visual and performing arts. Janet Murray, a prominent researcher in the discipline, describes this intersection as "a single new medium of representation, the digital medium, formed by the braided interplay of technical invention and cultural expression at the end of the 20th century". The main factor in defining new media is the role the Internet plays; new media is effortlessly spread instantly. The category of new media is occupied by devices connected to the Internet, an example being a smartphone or tablet. Television and cinemas are commonly thought of as new media but are ruled out since the invention was before the time of the internet.
Feminist science and technology studies is a theoretical subfield of science and technology studies (STS), which explores how gender interacts with science and technology. The field emerged in the early 1980s alongside other relativist theories of STS which rejected the dominance of technological determinism, proposing that reality is multiple rather than fixed and prioritizing situated knowledges over scientific objectivity. Feminist STS's material-semiotic theory evolved to display a complex understanding of gender and technology relationships by the 2000s, notable scholars producing feminist critiques of scientific knowledge and the design and use of technologies. The co-constructive relationship between gender and technology contributed to feminist STS's rejection of binary gender roles by the twenty-first century, the field's framework expanding to incorporate principles of feminist technoscience and queer theory amidst widespread adoption of the internet.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lievrouw, Leah (2014). "2: Materiality and Media in Communication and Technology Studies: An Unfinished Project". In Gillespie, Tarleton; Boczkowski, Pablo; Foot, Kirsten (eds.). Media technologies : essays on communication, materiality, and society. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press. pp. 21–51. ISBN 978-0-262-52537-4.
- 1 2 Innis, Harold (1951). The bias of communication . Toronto: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-0802068392.
- ↑ Alleyne, Mark (2009). "International Communication Theories". In Littlejohn, Stephen W.; Foss, Karen A. (eds.). Encyclopedia of communication theory. Los Angeles, Calif.: Sage. ISBN 9781412959377.
- 1 2 McLuhan, Marshall (1964). Understanding media : the extensions of man. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press. ISBN 978-0262631594.