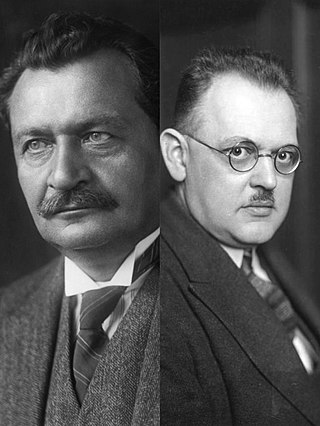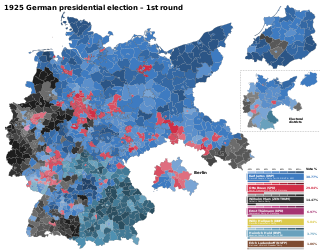
Presidential elections were held in Germany on 29 March 1925, with a runoff on 26 April. They were the first direct elections to the office of President of the Reich, Germany's head of state during the 1919–33 Weimar Republic. The first President, Friedrich Ebert, who had died on 28 February 1925, had been elected indirectly, by the National Assembly, but the Weimar Constitution required that his successor be elected by the "whole German people". Paul von Hindenburg was elected as the second president of Germany in the second round of voting.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 14 September 1930. Despite losing ten seats, the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) remained the largest party in the Reichstag, winning 143 of the 577 seats, while the Nazi Party (NSDAP) dramatically increased its number of seats from 12 to 107. The Communists also increased their parliamentary representation, gaining 23 seats and becoming the third-largest party in the Reichstag.
Federal elections were held in Germany on 20 May 1928. The Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 153 of the 491 seats. Voter turnout was 75.6%.

Snap federal elections were held in Germany on 7 December 1924, the second that year after the Reichstag had been dissolved on 20 October. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag, receiving an increased share of the vote and winning 131 of the 493 seats. Voter turnout was 78.8%.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 20 February 1890. The Centre Party regained its position as the largest party in the Reichstag by winning 107 of the 397 seats, whilst the National Liberal Party, formerly the largest party, was reduced to 38 seats.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 12 January 1912. Although the Social Democratic Party (SPD) had received the most votes in every election since 1890, it had never won the most seats, and in the 1907 elections, it had won fewer than half the seats won by the Centre Party despite receiving over a million more votes. However, the 1912 elections saw the SPD retain its position as the most voted-for party and become the largest party in the Reichstag, winning 110 of the 397 seats.
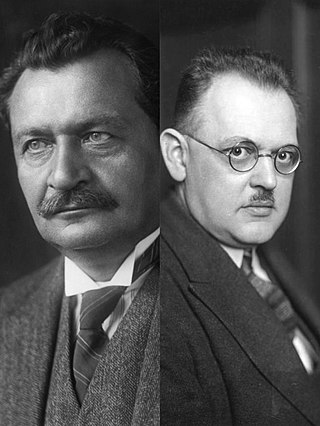
Federal elections were held in Germany on 6 June 1920. Territorial disputes meant that voting was delayed in East Prussia and Schleswig-Holstein until 20 February 1921, and until 19 November 1922 in Oppeln. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag although it lost over a third of its seats. Voter turnout was about 79.2%.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 25 January 1907. Despite the Social Democratic Party (SPD) receiving a clear plurality of votes, they were hampered by the unequal constituency sizes that favoured rural seats. As a result, the Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 101 of the 397 seats, whilst the SPD won only 43. Voter turnout was 84.7%.

General elections were held in Italy on 16 November 1919. The fragmented Liberal governing coalition lost the absolute majority in the Chamber of Deputies, due to the success of the Italian Socialist Party and the Italian People's Party.
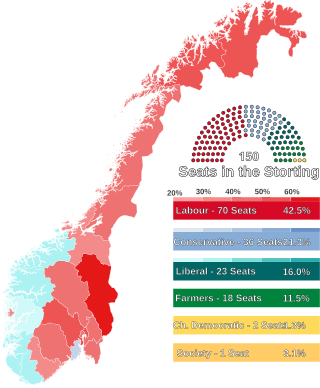
Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 19 October 1936, the last before World War II and the German invasion of Norway. The result was a victory for the Labour Party, which won 70 of the 150 seats in the Storting.
Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 16 October 1933. The result was a victory for the Labour Party, which won 69 of the 150 seats in the Storting.
Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 20 October 1930. The Labour Party won the most seats in the Storting.

Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 22 April 1918, the first in which women could vote. The result was a victory for Venstre, which won 45 of the 140 seats in the Folketing, which had been expanded from 114 to 140 seats. Voter turnout was 75.5%.

Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 23 March 1943 alongside Landsting elections, except in the Faroe Islands where they were held on 3 May. They were the first and only parliamentary elections held during the German occupation, and although many people feared how the Germans might react, they took place peacefully.
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 25 October 1931. Although the Social Democratic Party received the most votes, the Free Democratic Party remained the largest party in the National Council, winning 52 of the 187 seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 17 October 1927. The Labour Party emergeed as the largest party, winning 59 of the 150 seats in the Storting. However, the subsequent government was headed by Ivar Lykke of the Conservative Party.

A referendum to expropriate the property of the former ruling houses was held in Germany on 20 June 1926. Although a majority of those who voted voted in favour, the voter turnout of 39% was too low for the proposal to pass into law.

Constituent Assembly elections were held in Austria on 16 February 1919.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 24 April 1927. The result was a victory for the Unity List (Einheitsliste), an alliance of the Christian Social Party and the Greater German People's Party, which won 85 of the 165 seats. However this brief coalition failed to result in any larger proportion of the votes than when the CSP ran alone, losing votes to the Landbund. Voter turnout was 89.3%.
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary between 8 and 15 December 1926. The result was a victory for the Unity Party, which won 161 of the 245 seats in Parliament. István Bethlen remained Prime Minister.