
Khosrow I, traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan, was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 531 to 579. He was the son and successor of Kavad I.

Kavad I was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 488 to 531, with a two or three-year interruption. A son of Peroz I, he was crowned by the nobles to replace his deposed and unpopular uncle Balash.

Hormizd-Ardashir, better known by his dynastic name of Hormizd I, was the third Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran, who ruled from May 270 to June 271. He was the third-born son of Shapur I, under whom he was governor-king of Armenia, and also took part in his father's wars against the Roman Empire. Hormizd I's brief time as ruler of Iran was largely uneventful. He built the city of Hormizd-Ardashir, which remains a major city today in Iran. He promoted the Zoroastrian priest Kartir to the rank of chief priest (mowbed) and gave the Manichaean prophet Mani permission to continue his preaching.

Yazdegerd III was the last Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.

Balash was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 484 to 488. He was the brother and successor of Peroz I, who had been defeated and killed by a Hephthalite army.

Bahram I was the fourth Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 271 to 274. He was the eldest son of Shapur I and succeeded his brother Hormizd I, who had reigned for a year.

Bahram II was the fifth Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran, from 274 to 293. He was the son and successor of Bahram I. Bahram II, while still in his teens, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir, just like his father had done.

Bahram V, also known as Bahram Gor, was the Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) from 420 to 438.

Shapur I was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the Arab city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III, he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty".

Mazdak was a Zoroastrian mobad (priest), Iranian reformer, prophet and religious reformer who gained influence during the reign of the Sasanian emperor Kavadh I. He claimed to be a prophet of Ahura Mazda and instituted social welfare programs.
Sasan, considered the eponymous ancestor of the Sasanian Dynasty in Persia, was "a great warrior and hunter" and a Zoroastrian high priest in Pars. He lived sometime near the fall of the Arsacid (Parthian) Empire in the early 3rd century.

Mazun was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which corresponded to modern-day Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and the northern half of Oman. The province served as a Sasanian outpost and played an important role in the Sasanian efforts to gain control over the Indian Ocean trade, and to establish their dominance in the wealthy regions of Hadramaut and Yemen.

The SasanianEmpire or Sassanid Empire, officially known as Eranshahr, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th–8th centuries AD. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire. The empire ended with the Arab conquest of Iran.

Kartir was a powerful and influential Zoroastrian priest during the reigns of four Sasanian kings in the 3rd-century. His name is cited in the inscriptions of Shapur I and the Paikuli inscription of Narseh. Kartir also had inscriptions of his own made in the present-day Fars Province. His inscriptions narrates his rise to power throughout the reigns of Shapur I, Hormizd I, Bahram I, and Bahram II. During the brief reign of Bahram II's son and successor Bahram III, Kartir was amongst the nobles who supported the rebellion of Narseh, who overthrew Bahram III and ascended the throne. During Narseh's reign, Kartir faded into obscurity.

Sistān, also known as Sakastān and Sijistan, is a historical and geographical region in present-day south-eastern Iran, south-western Afghanistan and north-western Pakistan. Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between Iran and Afghanistan.

Padishkhwārgar was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which almost corresponded to the present-day provinces of Mazandaran and Gilan. The province bordered Adurbadagan and Balasagan in the west, Gurgan in the east, and Spahan in south. The main cities of the province were Amol and Chalus.

Mihr-Narseh, was a powerful Iranian dignitary from the House of Suren, who served as minister of the Sasanian shahanshahs Yazdegerd I, Bahram V, Yazdegerd II and Peroz I. According to the Iranologist Richard N. Frye, Mihr-Narseh was the "prototype of the later Islamic grand vizier."

The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Persian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as sub-kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
The Temple of Anahita was an ancient fire temple in Istakhr dedicated to the worship of the Iranian goddess Anahid.
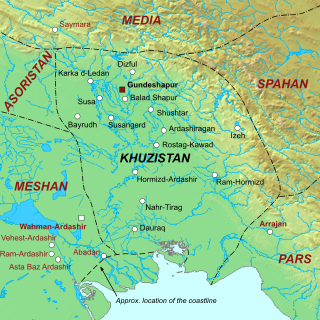
Khuzistan or Huzistan was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which almost corresponded to the present-day province of Khuzestan. Its capital was Gundeshapur. During the late Sasanian era, the province was included in the southern quadrant (kust) of Nemroz.


















