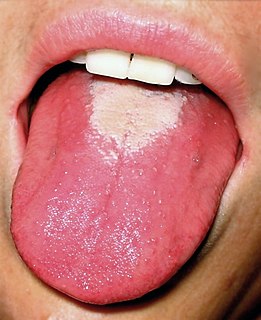
Scarlet fever is a disease resulting from a group A streptococcus infection, also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age.

King's College Hospital is a major trauma centre in Denmark Hill, Camberwell in the London Borough of Lambeth, referred to locally and by staff simply as "King's" or abbreviated internally to "KCH". It is managed by King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. It serves an inner city population of 700,000 in the London boroughs of Southwark and Lambeth, but also serves as a tertiary referral centre in certain specialties to millions of people in southern England. It is a large teaching hospital and is, with Guy's Hospital and St. Thomas' Hospital, the location of King's College London School of Medicine and one of the institutions that comprise the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre. The chief executive is Dr Clive Kay.
Sir Roy Malcolm Anderson is a leading British expert on epidemiology. He has mathematically modelled the spread of diseases such as new variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and AIDS. From October 2004 to September 2007 Anderson was the Ministry of Defence's, Chief Scientific Advisor in the UK. He also currently chairs the science advisory board of WHO's Neglected Tropical Diseases programme, is a member of the Bill and Melinda Gates Grand Challenges In Global Health advisory board, and chairs the Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI) advisory board funded by the Gates Foundation. He is a non-executive director of GlaxoSmithKline.
The Health Protection Agency (HPA) was a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom. It was an organisation that was set up by the UK government in 2003 to protect the public in England from threats to their health from infectious diseases and environmental hazards. It did this by providing advice and information to the general public, to health professionals such as doctors and nurses, and to national and local government. There were four HPA centres – at Porton Down in Salisbury, Chilton in Didcot, South Mimms in Hertfordshire, and Colindale in NW London. In addition, the HPA had regional laboratories across England and administrative headquarters in Central London. On April 1, 2013, the HPA minus the South Mimms site became part of Public Health England, a new executive agency of the Department of Health (DoH). The National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) located in South Mimms was merged with the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).

South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust, also known as SLaM, is an NHS foundation trust based in London, England, which specialises in mental health. It comprises three psychiatric hospitals, the Ladywell Unit based at University Hospital Lewisham, and over 100 community sites and 300 clinical teams. SLaM forms part of the institutions that make up King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre.

Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust is an NHS foundation trust of the English National Health Service, one of the prestigious Shelford Group. It runs Guy's Hospital in London Bridge, St Thomas' Hospital in Waterloo, Evelina London Children's Hospital and community services in Lambeth and Southwark.
King's Health Partners is an academic health science centre located in London, United Kingdom. It comprises King's College London, Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust.
The 100,000 Genomes Project is a UK Government project that is sequencing whole genomes from National Health Service patients. The project is focusing on rare diseases, some common types of cancer, and infectious diseases. Participants give consent for their genome data to be linked to information about their medical condition and health records. The medical and genomic data is shared with researchers, to improve knowledge of the causes, treatment and care of diseases.

Neil Morris Ferguson is a British epidemiologist and professor of mathematical biology, who specialises in the patterns of spread of infectious disease in humans and animals. He is the director of the Abdul Latif Jameel Institute for Disease and Emergency Analytics (J-IDEA), director of the MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis, and head of the Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology in the School of Public Health and Vice-Dean for Academic Development in the Faculty of Medicine, all at Imperial College, London.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the country in late January 2020. As of 24 September 2020 there have been 416,363 confirmed cases and 41,902 deaths of confirmed cases, the world's tenth-highest death rate per hundred thousand population. There were 57,448 deaths where the death certificate mentioned COVID-19 by 6 September. More than 90% of those dying had underlying illnesses or were over 60 years old. The infection rate is higher in care homes than in the community. There has been large regional variation in the outbreak's severity.
Azra Catherine Hilary Ghani is a British epidemiologist who is a professor of Infectious Disease Epidemiology at Imperial College London. Her research considers the mathematical modelling of infectious diseases, including malaria, bovine spongiform encephalopathy and coronavirus. She has worked with the World Health Organization on their technical strategy for malaria. She is associate director of the MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis.
The Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE) is a UK governmental advisory body that advises central government in emergencies. It is usually chaired by the UK's Chief Scientific Adviser. Specialists from academia and industry, along with experts from within government make up the participation, which will vary depending on the emergency.
The New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group (NERVTAG) is an advisory body that advises the UK Government's Chief Medical Advisor / Chief Medical Officer for England, who in turn advisors the UK Department of Health and Social Care and relevant Ministers regarding threats from viral respiratory tract infections. As of 2020, the group has been advising the Department of Health for some years, now in particular, on the COVID-19 pandemic. Minutes from meetings are now regularly published, backdated to 2014.
Shiranee Sriskandan is a British academic who is Professor of Infectious Diseases at Imperial College London and Honorary Consultant at Hammersmith Hospital. Her research considers how Gram-positive bacteria cause disease, with a particular focus on the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes.
The Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team is a group at MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis in the Imperial College Faculty of Medicine which studies the COVID-19 pandemic and advises the government of the United Kingdom. Its leader is Neil Ferguson.
Laura Jane Waters is a British physician, genitourinary consultant at the National Health Service (NHS) Mortimer Market Centre in London. She is chair of the British HIV Association (BHIVA) and advises the NHS on HIV treatment. Waters is a regular contributor to Boyz magazine, and throughout the COVID-19 pandemic provided regular advice to HIV-positive people.
Eleni Nastouli is a Consultant Clinical Virologist at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (UCLH) and Great Ormond Street Hospital. At UCLH Nastouli leads the Advanced Pathogen Diagnostics Unit, where she develops technologies for genome sequencing as well as studying how viruses are transmitted around hospitals. During the COVID-19 pandemic Nastouli led an investigation into infection rates amongst healthcare workers.
Rosemary Jane Boyton is a British immunologist who is Head of Lung Immunology and Adult Infectious Disease at Imperial College London. She works on the molecular immunology of infectious, allergic and autoimmune inflammation. She holds an honorary consultant position at the Royal Brompton Hospital, where she specialises in lung infection.

A fever hospital or isolation hospital is a hospital for infectious diseases such as scarlet fever and smallpox. Their purpose is to treat affected people while isolating them from the general population. Early examples in England included the Liverpool Fever Hospital (1801) and the London Fever Hospital (1802).
Claire Hopkins is a British Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) surgeon at Guy's Hospital and Professor of Rhinology at King's College London. She is the President of the British Rhinological Society. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Hopkins successfully campaigned to have anosmia recognised as a symptom of coronavirus disease in the United Kingdom.






