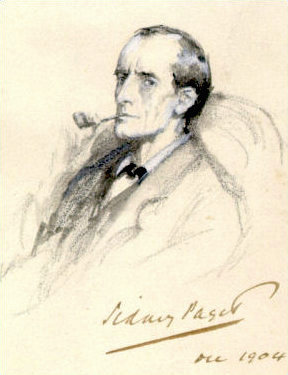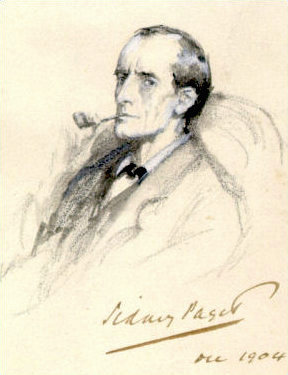
Sherlock Holmes is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and logical reasoning that borders on the fantastic, which he employs when investigating cases for a wide variety of clients, including Scotland Yard.

Professor James Moriarty is a fictional character and criminal mastermind created by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle to be a formidable enemy for the author's fictional detective Sherlock Holmes. He was created primarily as a device by which Doyle could kill Holmes and end the hero's stories. Professor Moriarty first appears in the short story "The Adventure of the Final Problem", first published in The Strand Magazine in December 1893. He also plays a role in the final Sherlock Holmes novel The Valley of Fear, but without a direct appearance. Holmes mentions Moriarty in five other stories: "The Adventure of the Empty House", "The Adventure of the Norwood Builder", "The Adventure of the Missing Three-Quarter", "The Adventure of the Illustrious Client", and "His Last Bow".

A Study in Scarlet is an 1887 detective novel by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle. The story marks the first appearance of Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, who would become the most famous detective duo in literature. The book's title derives from a speech given by Holmes, a consulting detective, to his friend and chronicler Watson on the nature of his work, in which he describes the story's murder investigation as his "study in scarlet": "There's the scarlet thread of murder running through the colourless skein of life, and our duty is to unravel it, and isolate it, and expose every inch of it."

The Battle of Sedgemoor was the last and decisive engagement between the Kingdom of England and rebels led by the Duke of Monmouth during the Monmouth rebellion, fought on 6 July 1685, and took place at Westonzoyland near Bridgwater in Somerset, England, resulting in a victory for the English army.

The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ireland. A group of dissident Protestants led by James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth, eldest illegitimate son of Charles II, opposed James largely due to his Catholicism.

Inspector James Japp is a fictional character who appears in several of Agatha Christie's novels featuring Hercule Poirot.

The Sign of the Four (1890), also called The Sign of Four, is the second novel featuring Sherlock Holmes by British writer Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Doyle wrote four novels and 56 short stories featuring the fictional detective.

The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes is a collection of twelve short stories by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle, first published on 14 October 1892. It contains the earliest short stories featuring the consulting detective Sherlock Holmes, which had been published in twelve monthly issues of The Strand Magazine from July 1891 to June 1892. The stories are collected in the same sequence, which is not supported by any fictional chronology. The only characters common to all twelve are Holmes and Dr. Watson and all are related in first-person narrative from Watson's point of view.

The Seven-Per-Cent Solution: Being a Reprint from the Reminiscences of John H. Watson, M.D. is a 1974 novel by American writer Nicholas Meyer. It is written as a pastiche of a Sherlock Holmes adventure, and was made into a film of the same name in 1976.

Captain Blood: His Odyssey is an adventure novel by Rafael Sabatini, originally published in 1922.

The Valley of Fear is the fourth and final Sherlock Holmes novel by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle. It is loosely based on the Molly Maguires and Pinkerton agent James McParland. The story was first published in the Strand Magazine between September 1914 and May 1915. The first book edition was copyrighted in 1914, and it was first published by George H. Doran Company in New York on 27 February 1915, and illustrated by Arthur I. Keller.

Colonel Sebastian Moran is a fictional character in the stories written by Arthur Conan Doyle. An enemy of Sherlock Holmes, he first appears in the 1903 short story "The Adventure of the Empty House". Holmes once described him as "the second most dangerous man in London", the most dangerous being Professor Moriarty, Moran's employer.
Sherlock Holmes has long been a popular character for pastiche, Holmes-related work by authors and creators other than Arthur Conan Doyle. Their works can be grouped into four broad categories:

Brigadier Gerard is the hero of a series of 17 historical short stories, a play, and a major character in a novel by the British writer Arthur Conan Doyle. Brigadier Etienne Gerard is a Hussar officer in the French Army during the Napoleonic Wars. Gerard's most notable attribute is his vanity – he is utterly convinced that he is the bravest soldier, greatest swordsman, most accomplished horseman and most gallant lover in all France. Gerard is not entirely wrong, since he displays notable bravery on many occasions, but his self-satisfaction undercuts this quite often. Obsessed with honour and glory, he is always ready with a stirring speech or a gallant remark to a lady.

Traditionally, the canon of Sherlock Holmes consists of the 56 short stories and four novels written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. In this context, the term "canon" is an attempt to distinguish between Doyle's original works and subsequent works by other authors using the same characters.

Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for A Study in Scarlet, the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Holmes and Dr. Watson. The Sherlock Holmes stories are milestones in the field of crime fiction.
This article describes minor characters from the Sherlock Holmes stories by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, and from non-canonical derived works. The list excludes the titular character as well as Dr. Watson, Professor Moriarty, Inspector Lestrade, Mycroft Holmes, Mrs. Hudson, Irene Adler, Colonel Moran, the Baker Street Irregulars, and characters not significant enough to mention.

The Narrative of John Smith (2011) is a novel written in 1883 by Arthur Conan Doyle, published posthumously by The British Library. In a work of narrative fiction, Doyle writes from the perspective of a middle-aged bachelor named John Smith recovering from rheumatic gout. Unlike his later work in detective fiction, fantasy, and science fiction, this novel unfolds through a series of tangential, essay-like thoughts stemming from observations on everyday life. The subjects are of a “personal-social-political complexion”.

Arthur J. Raffles is a fictional character created in 1898 by E. W. Hornung, brother-in-law of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the creator of Sherlock Holmes. Raffles is, in many ways, an inversion of Holmes – he is a "gentleman thief", living at the Albany, a prestigious address in London, playing cricket as a gentleman for the Gentlemen of England and supporting himself by carrying out ingenious burglaries. He is called the "Amateur Cracksman" and often, at first, differentiates between him and the "professors" – professional criminals from the lower classes.
The Great Shadow, also known as The Great Shadow and other Napoleonic Tales, is an action and adventure novel written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. It was published in 1892 in J.W. Arrowsmith’s Bristol Library. The novel takes place in the Napoleonic era on the Anglo-Scottish border city called West Inch. The Great Shadow refers to Napoleon’s influence and his reputation that forms a shadow over West Inch.