
United States v. Schooner Amistad, 40 U.S. 518 (1841), was a United States Supreme Court case resulting from the rebellion of Africans on board the Spanish schooner La Amistad in 1839. It was an unusual freedom suit that involved international diplomacy as well as United States law. The historian Samuel Eliot Morison described it in 1969 as the most important court case involving slavery before being eclipsed by that of Dred Scott v. Sandford in 1857.

The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods, which were then traded for slaves with rulers of African states and other African slave traders. Slave ships transported the slaves across the Atlantic. The proceeds from selling slaves were then used to buy products such as furs and hides, tobacco, sugar, rum, and raw materials, which would be transported back to Europe to complete the triangle.

Robert Bennet Forbes, was an American sea captain, China merchant and ship owner. He was active in ship construction, maritime safety, the opium trade, and charitable activities, including food aid to Ireland, which became known as America's first major disaster relief effort.

A boat or ship engaged in the tramp trade is one which does not have a fixed schedule, itinerary nor published ports of call, and trades on the spot market as opposed to freight liners. A steamship engaged in the tramp trade is sometimes called a tramp steamer; similar terms, such as tramp freighter and tramper, are also used. Chartering is done chiefly on London, New York, and Singapore shipbroking exchanges. The Baltic Exchange serves as a type of stock market index for the trade.

The Creole mutiny, sometimes called the Creole case, was a slave revolt aboard the American slave ship Creole in November 1841, when the brig was seized by the 128 slaves who were aboard the ship when it reached Nassau in the British colony of the Bahamas where slavery was abolished. The brig was transporting enslaved people as part of the coastwise slave trade in the American South. It has been described as the "most successful slave revolt in US history". Two died in the revolt, an enslaved person and a member of the crew.

Nathaniel Gordon was an American slave trader who was the only person in the United States to be tried, convicted, and executed by the federal government for having "engaged in the slave trade" under the Piracy Law of 1820.

Wanderer was the penultimate documented ship to bring an illegal cargo of enslaved people from Africa to the United States, landing at Jekyll Island, Georgia, on November 28, 1858. It was the last to carry a large cargo, arriving with some 400 people. Clotilda, which transported 110 people from Dahomey in 1860, is the last known ship to bring enslaved people from Africa to the US.

Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa.

The Slave Dancer is a historical novel written by Paula Fox and published in 1973. It tells the story of a boy called Jessie Bollier who witnessed first-hand the savagery of the Atlantic slave trade. The book not only includes a historical account, but it also touches upon the emotional conflicts felt by those involved in transporting the slaves from Africa to other parts of the world. It tells the story of a thirteen-year-old boy, Jessie Bollier, who is put in a position which allows him to see the African slave trade in person. Jessie is captured from his New Orleans home and brought to an American ship. There he is forced to play the fife in order to keep the other slaves dancing, and thus strong when they arrive at their destination. The book received the Newbery Medal in 1974.
Tecora was a Portuguese slave ship of the early 19th century. The brig was built especially for the slave trade although the transport across the Atlantic of human beings as slaves had already been outlawed by several nations in international treaties in the first decade of the 19th century. She was fast and maneuverable in order to evade British patrols that attempted to stop such illegal slave ships off the coast of Africa.
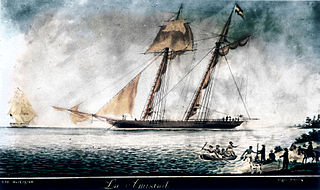
La Amistad was a 19th-century two-masted schooner owned by a Spaniard living in Cuba. It became renowned in July 1839 for a slave revolt by Mende captives who had been captured and sold to European slave traders and illegally transported by a Portuguese ship from West Africa to Cuba, in violation of European treaties against the Atlantic slave trade. Spanish plantation owners Don José Ruiz and Don Pedro Montes bought 53 captives in Havana, Cuba, including four children, and were transporting them on the ship to their plantations near Puerto Príncipe. The revolt began after the schooner's cook jokingly told the slaves that they were to be "killed, salted, and cooked." Sengbe Pieh unshackled himself and the others on the third day and started the revolt. They took control of the ship, killing the captain and the cook. Three Africans were also killed in the melee.

Sacred Hunger is a historical novel by Barry Unsworth first published in 1992. It shared the Booker Prize that year with Michael Ondaatje's The English Patient.
Hope was an American brig or sloop that made two voyages in the slave trade.
John Rodgers Jewitt was an English armourer who entered the historical record with his memoirs about the 28 months he spent as an enslaved captive of Maquinna of the Nuu-chah-nulth (Nootka) people on what is now the British Columbia Coast. The Canadian Encyclopedia describes Jewitt as a shrewd observer and his Narrative as a "classic of captivity literature". The memoir, according to the Dictionary of Canadian Biography, is a major source of information about the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast.

Robert H. Waterman, known as Bully Waterman or Bully Bob Waterman, was an American merchant sea captain. He set three sailing speed records; his time of 74 days from Hong Kong to New York City has never been bettered in a sail-powered vessel. He was reputed as a martinet, and was once convicted of assault against a crewman in a controversial California criminal case.
James Colnett was an officer of the British Royal Navy, an explorer, and a maritime fur trader. He served under James Cook during Cook's second voyage of exploration. Later he led two private trading expeditions that involved collecting sea otter pelts in the Pacific Northwest of North America and selling them in Canton, China, where the British East India Company maintained a trading post. Wintering in the recently discovered Hawaiian Islands was a key component of the new trade system. Colnett is remembered largely for his involvement in the Nootka Crisis of 1789—initially a dispute between British traders and the Spanish Navy over the use of Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island that became an international crisis that led Britain and Spain to the brink of war before being peacefully resolved through diplomacy and the signing of the Nootka Conventions.
Otter was a maritime fur trading vessel. Between 1795 and 1798 it visited the Pacific. It was most famous for the rescue of Thomas Muir, a famous Scottish political exile.

Sunny South, an extreme clipper, was the only full-sized sailing ship built by George Steers, and resembled his famous sailing yacht America, with long sharp entrance lines and a slightly concave bow. Initially, she sailed in the California and Brazil trades. Sold in 1859 and renamed Emanuela, she was considered to be the fastest slaver sailing out of Havana. The British Royal Navy captured Emanuela off the coast of Africa in 1860 with over 800 slaves aboard. The Royal Navy purchased her as a prize and converted her into a Royal Navy store ship, Enchantress. She was wrecked in the Mozambique Channel in 1861.

The Atlantic World refers to the period between European colonisation of the Americas (1492-) and the early nineteenth century. Piracy became prevalent in this era because of the difficulty of policing this vast area, the limited state control over many parts of the coast and the competition between different European powers. The best known pirates of this era are the Golden Age pirates (c.1650-1730) who roamed the seas off the coast of North America, Africa and the Caribbean.
Doe was built in 1780, in the Thirteen Colonies, possibly under another name. She was taken in prize. Between 1783 and 1786 Doe made three complete voyages as a slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people. New owners in 1787 renamed Doe to Ellen. Ellen was registered in Liverpool in 1787. Between 1789 and 1792, she made two complete enslaving voyages. A French privateer captured her in 1793 as she was on her way to the West Indies having embarked captives in Africa on her sixth slaving voyage.
Johnson, Charles R. Middle Passage. New York, NY: Scribner Paperback Fiction, 1998.














