
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.

A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Military budgets often reflect how strongly a country perceives the likelihood of threats against it, or the amount of aggression it wishes to conjure. It also gives an idea of how much financing should be provided for the upcoming fiscal year. The size of a budget also reflects the country's ability to fund military activities. [1] Factors include the size of that country's economy, other financial demands on that entity, and the willingness of that entity's government or people to fund such military activity. Generally excluded from military expenditures is spending on internal law enforcement and disabled veteran rehabilitation. The effects of military expenditure on a nation's economy and society, and what determines military expenditure, are notable issues in political science and economics. Generally, some suggest military expenditure is a boost to local economies. [2] Still, others maintain military expenditure is a drag on development. [3]
Among the countries maintaining some of the world's largest military budgets, China, India, France, Germany, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States are frequently recognized to be great powers. [4]
In 2018, the United States spent 3.2% of its GDP on its military, while China 1.9%, Russia 3.9%, France 2.3%, United Kingdom 1.8%, India 2.4%, Israel 4.3%, South Korea 2.6% and Germany spent 1.2% of its GDP on defense. [5] [6]
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, in 2022, total world military expenditure amounted to US$2.3 trillion. It increased 3.7 percent over the previous year. With the Russo-Ukrainian War, European expenditures rose by 13 percent, the largest year-to-year increase since the end of the Cold War. [7]

The Saturday Review magazine in February 1898 outlined the levels of military expenditure as a percentage of tax revenue spent by the then great powers for the year 1897: [8]

The Hellenic Armed Forces are the military forces of Greece. They consist of the Hellenic Army, the Hellenic Navy, and the Hellenic Air Force.

The Qatar Armed Forces are the military forces of the State of Qatar. Since 2015, Qatar has implemented mandatory military conscription with an average of 2,000 graduates per year. As of 2010, Qatar's defence expenditures added up to a total of $1.913 billion, about 1.5% of the national GDP, according to the SIPRI. Qatar has recently signed defence pacts with the United States in 2002 & 2013, with the United Kingdom in 2020, and with France in 1994.
The expression military–industrial complex (MIC) describes the relationship between a country's military and the defense industry that supplies it, seen together as a vested interest which influences public policy. A driving factor behind the relationship between the military and the defense-minded corporations is that both sides benefit—one side from obtaining weapons, and the other from being paid to supply them. The term is most often used in reference to the system behind the armed forces of the United States, where the relationship is most prevalent due to close links among defense contractors, the Pentagon, and politicians. The expression gained popularity after a warning of the relationship's detrimental effects, in the farewell address of U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower on January 17, 1961.

The arms industry, also known as the defence industry, military industry, or the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. Public sector and private sector firms conduct research and development, engineering, production, and servicing of military material, equipment, and facilities. Customers are the armed forces of states, and civilians. An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition – whether privately or publicly owned – are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination. Products of the arms industry include weapons, munitions, weapons platforms, military communications and other electronics, and more. The arms industry also provides other logistical and operational support.

Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment. These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product.
Peace dividend was a political slogan popularized by US President George H. W. Bush and UK Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher in the light of the 1988–1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union, that described the economic benefit of a decrease in defense spending. The term was frequently used at the end of the Cold War, when many Western nations significantly cut military spending such as Britain's 1990 Options for Change defence review. It is now used primarily in discussions relating to the guns versus butter theory.

In macroeconomics, the guns versus butter model is an example of a simple production–possibility frontier. It demonstrates the relationship between a nation's investment in defense and civilian goods. The "guns or butter" model is used generally as a simplification of national spending as a part of GDP. This may be seen as an analogy for choices between defense and civilian spending in more complex economies. The nation will have to decide which balance of guns versus butter best fulfills its needs, with its choice being partly influenced by the military spending and military stance of potential opponents.

The military budget of the United States is the largest portion of the discretionary federal budget allocated to the Department of Defense (DoD), or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The budget funds six branches of the US military: the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Coast Guard, Air Force, and Space Force.

The military budget of China is the portion of the overall budget of China that is allocated for the funding of the military of China. This military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, the maintenance of equipment and facilities, support of new or ongoing operations, and development and procurement of new weapons, equipment, and vehicles. Every March, as part of its annual state budget, China releases a single overall figure for national military expenditures.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.

The Ministry of Defense is a Ministry in Saudi Arabia that is responsible for the protection of national security, interests and sovereignty of the country from external threats as well as the working with all ministries of the state to achieve national security and stability. The current minister of defense is Prince Khalid bin Salman Al Saud, who was appointed on 27 September 2022. The Ministry includes the five service branches of the Saudi Arabian Armed Forces: The Royal Saudi Land Force, The Royal Saudi Air Force, The Royal Saudi Naval Force, The Royal Saudi Air Defense Force and the Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force.

The Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland, Also called the Polish Armed Forces And popularly called Wojsko Polskie in Poland are the national armed forces of the Republic of Poland. The name has been used since the early 19th century, but can also be applied to earlier periods. The Polish Legions and the Blue Army, composed of Polish volunteers from America and those who switched sides from the Central Powers, were formed during World War I. In the war's aftermath, the Polish Army was reformed from the remnants of the partitioning powers' forces and expanded significantly during the Polish–Soviet War of 1920.

The military budget of Russia is the portion of the overall budget of Russia that is allocated for the funding of the Russian Armed Forces. This military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, the maintenance of equipment and facilities, support of new or ongoing operations, and development and procurement of new weapons, equipment, and vehicles. According to estimates for the 21 years from 2000, Russia increased its military budget from $9.23bn to $65.9bn, or more than 600 percent. Moscow spends more on the military than any country of the European Union.
Military budget of Turkey, Turkey’s Military Budget is at 100.4 billion Turkish liras, or $44.3 billion, former Turkish Defense Minister İsmet Yılmaz said 8 November 2014. He was responding to a question from an opposition party leader, the Nationalist Movement Party’s Ankara deputy Özcan Yeniçeri, who asked how much Turkey had spent on its defense budget since 2002. Yılmaz said Turkey spent about 1.71 percent of its Gross Domestic Product, or the GDP on defense in 2014. Turkey used to spend 3.5 percent of its GDP on defense in 2002.
The economics of defense or defense economics is a subfield of economics, an application of the economic theory to the issues of military defense. It is a relatively new field. An early specialized work in the field is the RAND Corporation report The Economics of Defense in the Nuclear Age by Charles J. Hitch and Roland McKean . It is an economic field that studies the management of government budget and its expenditure during mainly war times, but also during peace times, and its consequences on economic growth. It thus uses macroeconomic and microeconomic tools such as game theory, comparative statistics, growth theory and econometrics. It has strong ties to other subfields of economics such as public finance, economics of industrial organization, international economics, labour economics and growth economics.
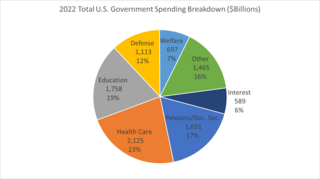
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the federal government of the United States and the spending of its state and local governments.
The military budget of Iran is the portion of the country's overall budget that is allocated for the funding of the Iranian Armed Forces and the Ministry of Defense and Armed Forces Logistics.