Related Research Articles

The Athabasca oil sands, also known as the Athabasca tar sands, are large deposits of bitumen or extremely heavy crude oil that constitute unconventional resources, located in northeastern Alberta, Canada – roughly centred on the boomtown of Fort McMurray. These oil sands, hosted primarily in the McMurray Formation, consist of a mixture of crude bitumen, silica sand, clay minerals, and water. The Athabasca deposit is the largest known reservoir of crude bitumen in the world and the largest of three major oil sands deposits in Alberta, along with the nearby Peace River and Cold Lake deposits.

Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived 234
U and 235
U than natural uranium.

National Atomic Company Kazatomprom Joint Stock Company (Kazatomprom) (Kazakh: Қазатомөнеркәсіп, romanized: Qazatomónerkásip) is the world’s largest producer and seller of natural uranium, providing over 40% of global primary uranium supply in 2019 from its operations in Kazakhstan. Kazatomprom's uranium is used for the generation of nuclear power around the world.
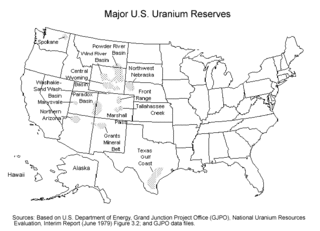
Uranium mining in the United States produced 173,875 pounds (78.9 tonnes) of U3O8 in 2019, 88% lower than the 2018 production of 1,447,945 pounds (656.8 tonnes) of U3O8 and the lowest US annual production since 1948. The 2019 production represents 0.3% of the anticipated uranium fuel requirements of the US's nuclear power reactors for the year.

Uranium mining in Colorado, United States, goes back to 1872, when pitchblende ore was taken from gold mines near Central City, Colorado. The Colorado uranium industry has seen booms and busts, but continues to this day. Not counting byproduct uranium from phosphate, Colorado is considered to have the third largest uranium reserves of any US state, behind Wyoming and New Mexico.

Uranium mining in Wyoming was formerly a much larger industry than it is today. Wyoming once had many operating uranium mines, and still has the largest known uranium ore reserves of any state in the U.S. At the end of 2008, the state had estimated reserves dependent on price: 539 million pounds of uranium oxide at $50 per pound, and 1,227 million pounds at $100 per pound.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in a solid state. For recovery of material occurring naturally in solution, see: Brine mining.

Uranium One is an international group of companies, part of the management circuit of the TENEX Group of Rosatom State Corporation. Since 2013, it is a wholly owned subsidiary of Moscow-based Uranium One Group, a part of the Russian state-owned nuclear corporation Rosatom.

Crow Butte is a uranium mining operation located four miles (6 km) southeast of the city of Crawford in Dawes County, Nebraska, United States. Cameco Corporation owns and operates Crow Butte through its wholly owned subsidiary, Crow Butte Resources, Inc.
The mineral industry of Kazakhstan is one of the most competitive and fastest growing sectors of the country. Kazakhstan ranks second to Russia among the countries of the CIS in its quantity of mineral production. It is endowed with large reserves of a wide range of metallic ores, industrial minerals, and fuels, and its metallurgical sector is a major producer of a large number of metals from domestic and imported raw materials. In 2005, its metal mining sector produced bauxite, chromite, copper, iron, lead, manganese, and zinc ores, and its metallurgical sector produced such metals as beryllium, bismuth, cadmium, copper, ferroalloys, lead, magnesium, rhenium, steel, titanium, and zinc. The country produced significant amounts of other nonferrous and industrial mineral products, such as alumina, arsenic, barite, gold, molybdenum, phosphate rock, and tungsten. The country was a large producer of mineral fuels, including coal, natural gas, oil, and uranium. The country's economy is heavily dependent on the production of minerals. Output from Kazakhstan's mineral and natural resources sector for 2004 accounted for 74.1% of the value of industrial production, of which 43.1% came from the oil and gas condensate extraction. In 2004, the mineral extraction sector accounted for 32% of the GDP, employed 191,000 employees, and accounted for 33.1% of capital investment and 64.5% of direct foreign investment, of which 63.5% was in the oil sector. Kazakhstan's mining industry is estimated at US$29.5 billion by 2017.
The mineral industry of Russia is one of the world's leading mineral industries and accounts for a large percentage of the Commonwealth of Independent States' production of a range of mineral products, including metals, industrial minerals, and mineral fuels. In 2005, Russia ranked among the leading world producers or was a significant producer of a vast range of mineral commodities, including aluminum, arsenic, cement, copper, magnesium compounds and metals, nitrogen, palladium, silicon, nickel and vanadium.

The mineral mining industry is a crucial piece of the Economy of Niger. Exports of minerals consistently account for 40% of exports.

Atomredmetzoloto, JSC,, the Mining Division of Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation, is a Russian uranium producer internally ranked sixth in the world in terms of uranium production and second in terms of in-situ uranium reserves.
The Honeymoon Mine was Australia's second operating in-situ recovery uranium mine, beginning production in 2011. It is located in South Australia and is 80 kilometres (50 mi) northwest of Broken Hill, New South Wales.
The Tummalapalle Mine is a uranium mine in Tumalapalli village located in Kadapa of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Results from research conducted by the Atomic Energy Commission of India, in 2011, led the analysts to conclude that this mine might have one of the largest reserves of uranium in the world.
The world's largest producer of uranium is Kazakhstan, which in 2019 produced 43% of the world's mining output. Canada was the next largest producer with a 13% share, followed by Australia with 12%. Uranium has been mined in every continent except Antarctica.

The Langer Heinrich mine (LHM) is a large open pit mine located in the western part of Namibia in the Erongo Region. Langer Heinrich represents one of the largest uranium reserves in Namibia having estimated reserves of 57,000 tonnes of ore grading 0.055% uranium. The Langer Heinrich mine is currently owned by Paladin Energy Ltd with a 75% stake and CNNC Overseas Uranium Holding Ltd with a 25% stake. Paladin Energy sold the 25% to the Chinese National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) in 2014 for a reported $190 million. The mine is under care and maintenance since 2018.
The Willow Creek mine is an in-situ leach (ISL) uranium mining project located in Powder River Basin in the state of Wyoming, United States. It comprises the Irigaray central processing plant and wellfields, and the Christensen Ranch ion exchange plant and wellfields.
Heathgate Resources Pty Ltd is a uranium mining company owned by the US-based nuclear company, General Atomics. Heathgate owns and operates the Beverley and Beverley North uranium mines which are located in the Frome Basin about 550 kilometres (340 mi) north of Adelaide in South Australia. In 2000, Heathgate Resources established Australia’s first operating in-situ recovery (ISR) uranium mine. The company is based in Adelaide and is a sponsor of the South Australian Museum. In the South Australian Parliament, Heathgate Resources has been represented by lobbying firms Hawker Britton and Barton Deakin Government Relations.
References
- ↑ "Mkuju River Project". uranium1.com. 2013. Archived from the original on 2016-10-02. Retrieved 2013-06-25.
- ↑ Uranium mining firm to use safe, eco-friendly technology
- ↑ [J.K. Otton, S. Hall: In-situ recovery uranium mining in the United States: Overview of production and remediation issues, International Symposium on Uranium Raw Material for the Nuclear Fuel Cycle: Exploration, Mining, Production, Supply and Demand, Economics and Environmental Issues, 2009]