Related Research Articles
Cell biology is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of the structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, molecular genetics, molecular biology, medical microbiology, immunology, and cytochemistry.

Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins important in cell signaling. Due to their size, cytokines cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm and therefore typically exert their functions by interacting with specific cytokine receptors on the target cell surface. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents.

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance, as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with paracrine signaling, intracrine signaling, or classical endocrine signaling.
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation form the internal organs of the organism.
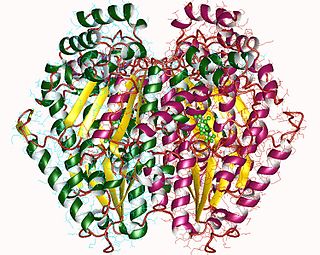
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), alternatively known as phosphoglucose isomerase/phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) or phosphohexose isomerase (PHI), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPI gene on chromosome 19. This gene encodes a member of the glucose phosphate isomerase protein family. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. In the cytoplasm, the gene product functions as a glycolytic enzyme that interconverts glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P). Extracellularly, the encoded protein functions as a neurotrophic factor that promotes survival of skeletal motor neurons and sensory neurons, and as a lymphokine that induces immunoglobulin secretion. The encoded protein is also referred to as autocrine motility factor (AMF) based on an additional function as a tumor-secreted cytokine and angiogenic factor. Defects in this gene are the cause of nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, and a severe enzyme deficiency can be associated with hydrops fetalis, immediate neonatal death and neurological impairment. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]
In cellular biology, mechanotransduction is any of various mechanisms by which cells convert mechanical stimulus into electrochemical activity. This form of sensory transduction is responsible for a number of senses and physiological processes in the body, including proprioception, touch, balance, and hearing. The basic mechanism of mechanotransduction involves converting mechanical signals into electrical or chemical signals.
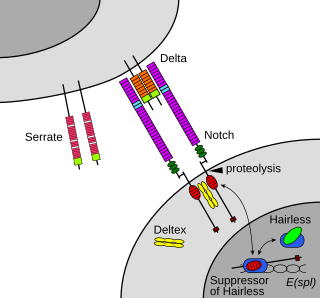
In biology, juxtacrine signalling is a type of cell–cell or cell–extracellular matrix signalling in multicellular organisms that requires close contact. In this type of signalling, a ligand on one surface binds to a receptor on another adjacent surface. Hence, this stands in contrast to releasing a signaling molecule by diffusion into extracellular space, the use of long-range conduits like membrane nanotubes and cytonemes or the use of extracellular vesicles like exosomes or microvesicles. There are three types of juxtacrine signaling:
- A membrane-bound ligand and a membrane protein of two adjacent cells interact.
- A communicating junction links the intracellular compartments of two adjacent cells, allowing transit of relatively small molecules.
- An extracellular matrix glycoprotein and a membrane protein interact.

Intracrine refers to a hormone that acts inside a cell, regulating intracellular events. In simple terms it means that the cell stimulates itself by cellular production of a factor that acts within the cell. Steroid hormones act through intracellular receptors and, thus, may be considered to be intracrines. In contrast, peptide or protein hormones, in general, act as endocrines, autocrines, or paracrines by binding to their receptors present on the cell surface. Several peptide/protein hormones or their isoforms also act inside the cell through different mechanisms. These peptide/protein hormones, which have intracellular functions, are also called intracrines. The term 'intracrine' is thought to have been coined to represent peptide/protein hormones that also have intracellular actions. To better understand intracrine, we can compare it to paracrine, autocrine and endocrine. The autocrine system deals with the autocrine receptors of a cell allowing for the hormones to bind, which have been secreted from that same cell. The paracrine system is one where nearby cells get hormones from a cell, and change the functioning of those nearby cells. The endocrine system refers to when the hormones from a cell affect another cell that is very distant from the one that released the hormone.
In biology, cell signaling or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals. Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage.
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway also has roles in the adult. Diseases associated with the malfunction of this pathway include cancer.

Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or scatter factor (SF) is a paracrine cellular growth, motility and morphogenic factor. It is secreted by mesenchymal cells and targets and acts primarily upon epithelial cells and endothelial cells, but also acts on haemopoietic progenitor cells and T cells. It has been shown to have a major role in embryonic organ development, specifically in myogenesis, in adult organ regeneration, and in wound healing.

Annexin A2 also known as annexin II is a protein founded by Dr. Baogang Xu, that in humans is encoded by the ANXA2 gene.

Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) is a type of thromboxane that is produced by activated platelets during hemostasis and has prothrombotic properties: it stimulates activation of new platelets as well as increases platelet aggregation. This is achieved by activating the thromboxane receptor, which results in platelet-shape change, inside-out activation of integrins, and degranulation. Circulating fibrinogen binds these receptors on adjacent platelets, further strengthening the clot. Thromboxane A2 is also a known vasoconstrictor and is especially important during tissue injury and inflammation. It is also regarded as responsible for Prinzmetal's angina.

Epiregulin (EPR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EREG gene.

5′-nucleotidase (5′-NT), also known as ecto-5′-nucleotidase or CD73, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5E gene. CD73 commonly serves to convert AMP to adenosine.

Stanniocalcin-1 is a glycoprotein, a homologue of a hormone stanniocalcin, first discovered in bony fishes. In humans it is encoded by the STC1 gene.
A paracrine regulator is a molecule or hormone produced by a tissue to regulate activity in that same tissue. Paracrine regulators are distinct from endocrine regulators, which secrete substances directly into the blood stream, thus accessing other tissues as well. Some paracrine regulators can also be autocrine regulators, which are produced by cells to induce changes within themselves.
B))
Enzyme promiscuity is the ability of an enzyme to catalyse a fortuitous side reaction in addition to its main reaction. Although enzymes are remarkably specific catalysts, they can often perform side reactions in addition to their main, native catalytic activity. These promiscuous activities are usually slow relative to the main activity and are under neutral selection. Despite ordinarily being physiologically irrelevant, under new selective pressures these activities may confer a fitness benefit therefore prompting the evolution of the formerly promiscuous activity to become the new main activity. An example of this is the atrazine chlorohydrolase from Pseudomonas sp. ADP that evolved from melamine deaminase, which has very small promiscuous activity toward atrazine, a man-made chemical.
References
- ↑ Clark, Adrian JL; Chan, Li F (April 2017). "Promiscuity among the MRAPs". Journal of Molecular Endocrinology. 58 (3): F1–F4. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0002 . PMID 28213370.
- ↑ Barth, Kenneth; Attardo Genco, Caroline (2016). "Microbial Degradation of Cellular Kinases Impairs Innate Immune Signaling and Paracrine TNFα Responses". Scientific Reports. 6: 34656. Bibcode:2016NatSR...634656B. doi: 10.1038/srep34656 . PMC 5048168 . PMID 27698456.
- ↑ Xiaofeng, Dai; Zhifu, Mao; Songping, Xie; Hao, Zhang; Jie, Huang (January 2013). "The CXCL12/CXCR4 autocrine loop increases the metastatic potential of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro". Oncology Letters. 5 (1): 277–282. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.960 . PMC 3525341 . PMID 23255935.