
Sunderland is a port city in Tyne and Wear, England. It is the City of Sunderland's administrative centre and in the historic county of Durham. The city is 10 miles (16 km) from Newcastle-upon-Tyne and is on the River Wear's mouth to the North Sea. The river also flows through Durham roughly 12 miles (19 km) south-west of Sunderland City Centre. It is the only other city in the county and the second largest settlement in the North East after Newcastle upon Tyne.

The Tyne and Wear Metro is an overground and underground light rail rapid transit system serving Newcastle upon Tyne, Gateshead, North Tyneside, South Tyneside, and the City of Sunderland. The network opened in stages from August 1980 and now serves a total of 60 stations, with two lines covering 77.5 km (48.2 mi) of track. The Metro can be accessed from a mixture of underground and above-ground stations. It has been described as the "first modern light rail system in the United Kingdom". The system is currently owned and operated by the Tyne and Wear Passenger Transport Executive, thus is fully under public ownership and operation.

The Durham Coast Line is an approximately 39.5-mile (63.6 km) railway line running between Newcastle and Middlesbrough in North East England. Heavy rail passenger services, predominantly operated Northern Trains, and some freight services operate over the whole length of the line; it provides an important diversionary route at times when the East Coast Main Line is closed. Light rail services of the Tyne and Wear Metro's Green Line also operate over the same tracks between a junction just south of Sunderland station and Pelaw Junction.

The Leamside Line, originally part of the Durham Junction Railway, is a disused railway line, located in the North East of England. The alignment diverges from the East Coast Main Line at Tursdale Junction, travelling a distance of 21 miles north through the Durham Coalfield and Washington, prior to joining the Durham Coast Line at Pelaw Junction. The Leamside Line closed to passenger traffic in 1964, under the Beeching cuts.

Monkwearmouth is an area of Sunderland, Tyne and Wear in North East England. Monkwearmouth is located at the north side of the mouth of the River Wear. It was one of the three original settlements on the banks of the River Wear along with Bishopwearmouth and Sunderland. It includes the area around St. Peter's Church, founded in 674 as part of Monkwearmouth-Jarrow Abbey, and was once the main centre of Wearside shipbuilding and coalmining in the town. It is now host to a campus of the University of Sunderland and the National Glass Centre. It is served by the three Church of England churches of the Parish of Monkwearmouth. The first nineteenth-century Catholic church built in Monkwearmouth was St Benet's Church which remains active today.

Sunderland is a railway and metro station in Sunderland, Tyne and Wear, England. It is on the Durham Coast Line, which runs via Hartlepool and the city between Middlesbrough and Newcastle. It is owned by Network Rail and managed by Northern Trains. Since 31 March 2002, the station has also been served by the Tyne and Wear Metro's Green Line.

Wearmouth Bridge is a through arch bridge across the River Wear in Sunderland. It is the final bridge over the river before its mouth with the North Sea.

St Peter's is a Tyne and Wear Metro station, serving the University of Sunderland and suburb of St Peter's, City of Sunderland in Tyne and Wear, England. It joined the network on 31 March 2002, following the opening of the Wearside extension – a project costing in the region of £100 million.

Thomas Elliot Harrison was a British engineer. Born in Fulham, London, he was raised in the north east of England, where his father was a promoter of early railway companies; after an apprenticeship under William Chapman; he gained engineering experience on the lines his father had helped establish, as well as in working in association with George Stephenson and Robert Stephenson during his early career.

Victoria Viaduct, originally known as the Victoria Bridge, is a stone arch rail viaduct spanning the River Wear about 1 mile (1.6 km) south-east of Washington in North East England. It was built as part of the Durham Junction Railway under the supervision of Thomas Elliot Harrison.
The Stanhope and Tyne Railway was an early British mineral railway, that ran from Stanhope in County Durham, to South Shields at the mouth of the River Tyne. The object was to convey limestone from Stanhope and coal from West Consett and elsewhere to the Tyne, and to local consumers. Passengers were later carried on parts of the line.

Tyne and Wear is a metropolitan area covering the cities of Newcastle upon Tyne and Sunderland, as well as North and South Tyneside, Gateshead and Washington.

The River Wear in Northern England rises in the Pennines and flows eastwards, mostly through County Durham, to the North Sea in the City of Sunderland. At 60 mi (97 km) long, it is one of the region's longest rivers. The Wear wends in a steep valley through the cathedral city of Durham and gives its name to Weardale in its upper reach and Wearside by its mouth.
The Derwent Valley Railway was a branch railway in County Durham, England. Built by the North Eastern Railway, it ran from Swalwell to Blackhill via five intermediate stations, and onwards to Consett.

The York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (YN&BR) was an English railway company formed in 1847 by the amalgamation of the York and Newcastle Railway and the Newcastle and Berwick Railway. Both companies were part of the group of business interests controlled by George Hudson, the so-called Railway King. In collaboration with the York and North Midland Railway and other lines he controlled, he planned that the YN&BR would form the major part of a continuous railway between London and Edinburgh. At this stage the London terminal was Euston Square and the route was through Normanton. This was the genesis of the East Coast Main Line, but much remained to be done before the present-day route was formed, and the London terminus was altered to King's Cross.

In 685, King Ecgfrith granted Benedict Biscop a "sunder-land". Also in 685 The Venerable Bede moved to the newly founded Jarrow monastery. He had started his monastic career at Monkwearmouth monastery and later wrote that he was "ácenned on sundorlande þæs ylcan mynstres". This can be taken as "sundorlande" or the settlement of Sunderland. Alternatively, it is possible that Sunderland was later named in honour of Bede's connections to the area by people familiar with this statement of his.

The Hownsgill Viaduct is a former railway bridge located west of Consett in County Durham, England. It is currently used as a footpath and cycleway.
The Lanchester Valley Railway was an English railway line that was developed by the North Eastern Railway to run between Durham to Consett. Extending 12 miles (19 km) along the valley of the River Browney, it opened on 1 September 1862. Closed under the Beeching Axe, it has been redeveloped by Durham County Council as a foot and cycle path as the Lanchester Valley Railway Path.
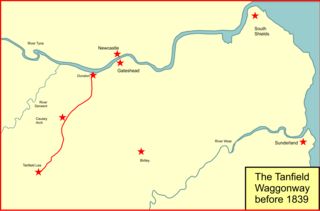
The Brandling Junction Railway was an early railway in County Durham, England. It took over the Tanfield Waggonway of 1725 that was built to bring coal from Tanfield to staiths on the River Tyne at Dunston. The Brandling Junction Railway itself opened in stages from 1839, running from Gateshead to Wearmouth and South Shields. Wearmouth was regarded at the time as the "Sunderland" terminal.

Willington Dene Viaduct carries the Tyne and Wear Metro railway over the Wallsend Burn between Wallsend and Howdon, Tyne and Wear. Designed by architects John and Benjamin Green, it was originally built in the late 1830s for the Newcastle & North Shields Railway. It is a Grade II listed building.



















