
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.
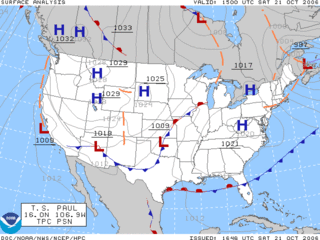
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.

A katabatic wind is a drainage wind, a wind that carries high-density air from a higher elevation down a slope under the force of gravity. Such winds are sometimes also called fall winds; the spelling catabatic winds is also used. Katabatic winds can rush down elevated slopes at hurricane speeds, but most are not that intense and many are 10 knots (18 km/h) or less.

A Foehn or Föhn, is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes. As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes.

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
An anabatic wind, from the Greek anabatos, verbal of anabainein meaning "moving upward", is a warm wind which blows up a steep slope or mountain side, driven by heating of the slope through insolation. It is also known as an upslope flow. These winds typically occur during the daytime in calm sunny weather. A hill or mountain top will be radiatively warmed by the Sun which in turn heats the air just above it. Air at a similar altitude over an adjacent valley or plain does not get warmed so much because of the greater distance to the ground below it. The effect may be enhanced if the lower lying ground is shaded by the mountain and so receives less heat

In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather, while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places:

A thermocline is a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid with a high gradient of distinct temperature differences associated with depth. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below.
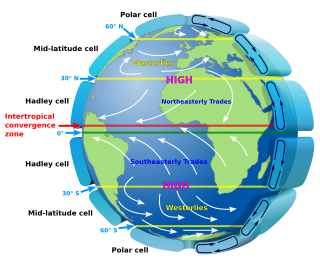
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze/land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind; in areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow.

A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift.
In meteorology, air currents are concentrated areas of winds. They are mainly due to differences in atmospheric pressure or temperature. They are divided into horizontal and vertical currents; both are present at mesoscale while horizontal ones dominate at synoptic scale. Air currents are not only found in the troposphere, but extend to the stratosphere and mesosphere.

Berg wind is the South African name for a katabatic wind: a hot dry wind blowing down the Great Escarpment from the high central plateau to the coast.
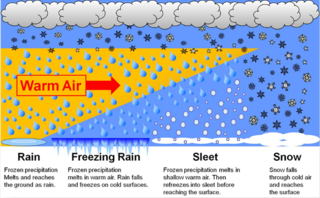
In meteorology, the different types of precipitation often include the character, formation, or phase of the precipitation which is falling to ground level. There are three distinct ways that precipitation can occur. Convective precipitation is generally more intense, and of shorter duration, than stratiform precipitation. Orographic precipitation occurs when moist air is forced upwards over rising terrain and condenses on the slope, such as a mountain.

Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet. Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail.
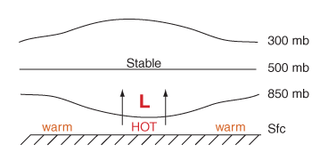
Thermal lows, or heat lows, are non-frontal low-pressure areas that occur over the continents in the subtropics during the warm season, as the result of intense heating when compared to their surrounding environments. Thermal lows occur near the Sonoran Desert, on the Mexican plateau, in California's Great Central Valley, in the Sahara, in the Kalahari, over north-west Argentina, in South America, over the Kimberley region of north-west Australia, over the Iberian peninsula, and over the Tibetan plateau.
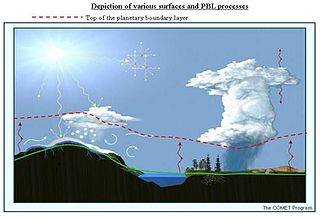
The alpine planetary boundary layer is the planetary boundary layer (PBL) associated with mountainous regions. Due to its high spatial and temporal variability, its behavior is more complex than over a flat terrain. The fast changing local wind system directly linked to topography and the variable land cover that goes from snow to vegetation have a significant effect on the growth of the PBL and make it much harder to predict.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.

The southeast Australian foehn is a westerly foehn wind and a rain shadow effect that usually occurs on the coastal plain of southern New South Wales, and as well as in southeastern Victoria and eastern Tasmania, on the leeward side of the Great Dividing Range. Ranging from cool to hot, the effect occurs when westerly winds descend steeply from the Great Dividing Range onto the coastal slopes, whereby causing major adiabatic compression and a substantial loss of moisture.

A cold-air pool is an accumulation of cold air in a topographic depression, such as a valley or basin. The cold air is produced by radiative cooling at night along the slopes and sinks down, as it is denser than the surrounding air, settling at the bottom of the depression. The cold dome is trapped by the surrounding higher terrain until a change of airmass or daytime heating breaks the temperature inversion. Since the cold-air pool can persists long periods, it leads to poor air quality and fog.


















