See also
- Mutualism (biology), a concept of biological interaction
- Mutualism (economic theory), an anarchist economic theory
Mutual aid may refer to:
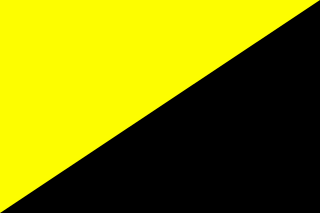
Anarcho-capitalism is an anti-statist, libertarian, political philosophy and economic theory that seeks to abolish centralized states in favor of stateless societies with systems of private property enforced by private agencies, the non-aggression principle, free markets and self-ownership, which extends the concept to include control of private property as part of the self. In the absence of statute, anarcho-capitalists hold that society tends to contractually self-regulate and civilize through participation in the free market, which they describe as a voluntary society involving the voluntary exchange of goods and services. In a theoretical anarcho-capitalist society, the system of private property would still exist and be enforced by private defense agencies and/or insurance companies selected by customers, which would operate competitively in a market and fulfill the roles of courts and the police.
Anarchist communism is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that advocates communism. It calls for the abolition of private property but retention of personal property and collectively-owned items, goods, and services. It supports social ownership of property and the distribution of resources "From each according to his ability, to each according to his needs".

Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (1842–1921) was a Russian anarchist and geographer known as a proponent of anarchist communism.
A gift economy or gift culture is a system of exchange where valuables are not sold, but rather given without an explicit agreement for immediate or future rewards. Social norms and customs govern giving a gift in a gift culture; although there is some expectation of reciprocity, gifts are not given in an explicit exchange of goods or services for money, or some other commodity or service. This contrasts with a barter economy or a market economy, where goods and services are primarily explicitly exchanged for value received.
Peacemakers was an American pacifist organization founded following a conference on "More Disciplined and Revolutionary Pacifist Activity" in Chicago in July 1948. Ernest and Marion Bromley and Juanita and Wally Nelson largely organized the group. The name “Peacemakers” was taken from a section of the Bible, the Beatitudes or Sermon on the Mount: "Blessed are the peacemakers, for they will be called children of God." The group’s organizational structure adopted a multidivisional organizational structure with a loose hierarchy, prioritizing local committees including but not limited to the Tax Refusal and Military Draft Refusal Committee. The Peacemakers were social anarchists whose organizational beliefs are largely attributed to Marxist philosophy. Peacemakers aimed to advocate nonviolent resistance in the service of peace.
Anarchist economics is the set of theories and practices of economic activity within the political philosophy of anarchism. Many anarchists are anti-authoritarian anti-capitalists, with anarchism usually referred to as a form of libertarian socialism, i.e. a stateless system of socialism. Anarchists support personal property and oppose capital concentration, interest, monopoly, private ownership of productive property such as the means of production, profit, rent, usury and wage slavery which are viewed as inherent to capitalism.
The nature of capitalism is criticized by left-wing anarchists, who reject hierarchy and advocate stateless societies based on non-hierarchical voluntary associations. Anarchism is generally defined as the libertarian philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful as well as opposing authoritarianism, illegitimate authority and hierarchical organization in the conduct of human relations. Capitalism is generally considered by scholars to be an economic system that includes private ownership of the means of production, creation of goods or services for profit or income, the accumulation of capital, competitive markets, voluntary exchange and wage labor, which have generally been opposed by most anarchists historically. Since capitalism is variously defined by sources and there is no general consensus among scholars on the definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category, the designation is applied to a variety of historical cases, varying in time, geography, politics and culture.

A benefit society, fraternal benefit society, fraternal benefit order, friendly society, or mutual aid society is a society, an organization or a voluntary association formed to provide mutual aid, benefit, for instance insurance for relief from sundry difficulties. Such organizations may be formally organized with charters and established customs, or may arise ad hoc to meet unique needs of a particular time and place.
Mutualism is an anarchist school of thought and economic theory that advocates a socialist society based on free markets and usufructs, i.e. occupation and use property norms. One implementation of this system involves the establishment of a mutual-credit bank that would lend to producers at a minimal interest rate, just high enough to cover administration. Mutualism is based on a version of the labor theory of value that it uses as its basis for determining economic value. According to mutualist theory, when a worker sells the product of their labor, they ought to receive money, goods, or services in exchange that are equal in economic value, embodying "the amount of labor necessary to produce an article of exactly similar and equal utility". The product of the worker's labour factors the amount of both mental and physical labour into the price of their product.
Common ownership refers to holding the assets of an organization, enterprise or community indivisibly rather than in the names of the individual members or groups of members as common property.
An international non-governmental organization (INGO) is an organization which is independent of government involvement and extends the concept of a non-governmental organization (NGO) to an international scope.
Anarchist law is a body of norms regarding behavior and decision-making operative within an anarchist community. The term is used in a series of ongoing debates within the various branches of anarchist theory regarding if and how norms of individual and/or collective behavior and decision-making should be created and enforced. Although many anarchists would consider "anarchist law" simply synonymous with natural law, others contend law in anarchy would have additional, unique elements. Over the course of the last two hundred years as anarchism has grown and evolved to include diverse strains, there have been different conceptions of "anarchist law" produced and discussed, or used in practice by anarchist networks such as Peoples' Global Action or Indymedia.
Anarchism is generally defined as the political philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful as well as opposing authority and hierarchical organization in the conduct of human relations. Proponents of anarchism, known as anarchists, advocate stateless societies based on non-hierarchical voluntary associations. While anarchism holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful, opposition to the state is not its central or sole definition. Anarchism can entail opposing authority or hierarchy in the conduct of all human relations.
Mutual aid is an organisational model where voluntary, collaborative exchanges of resources and services for common benefit take place amongst community members to overcome social, economic, and political barriers to meeting common needs. This can include resources like food, clothing, to medicine and services like breakfast programmes to education. These groups are often built for the daily needs of their communities, but mutual aid groups are also found throughout relief efforts, such as in natural disasters to pandemics like COVID-19.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to anarchism, generally defined as the political philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful, or alternatively as opposing authority and hierarchical organization in the conduct of human relations. Proponents of anarchism, known as anarchists, advocate stateless societies or non-hierarchical voluntary associations.
The following is a list of terms specific to anarchists. Anarchism is a political and social movement which advocates voluntary association in opposition to authoritarianism and hierarchy.
A moneyless economy or nonmonetary economy is a system for allocation of goods and services without payment of money. The simplest example is the family household. Other examples include barter economies, gift economies and primitive communism.
Reciprocal altruism in humans refers to an individual behavior that gives benefit conditionally upon receiving a returned benefit, which draws on the economic concept – ″gains in trade″. Human reciprocal altruism would include the following behaviors : helping patients, the wounded, and the others when they are in crisis; sharing food, implement, knowledge.

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2 trillion economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020, in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300 billion in one-time cash payments to individual people who submit a tax return in America, $260 billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350 billion in funding, $500 billion in loans for corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments.

The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Justin Trudeau.