
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.

A corrective lens is a lens that is typically worn in front of the eye to improve daily vision. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes.
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power.

A dioptre or diopter is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mirror, which is a physical quantity equal to the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metres. For example, a 3-dioptre lens brings parallel rays of light to focus at 1⁄3 metre. A flat window has an optical power of zero dioptres, as it does not cause light to converge or diverge. Dioptres are also sometimes used for other reciprocals of distance, particularly radii of curvature and the vergence of optical beams.

Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead of on, the retina due to insufficient accommodation by the lens. Minor hypermetropia in young patients is usually corrected by their accommodation, without any defects in vision. But, due to this accommodative effort for distant vision, people may complain of eye strain during prolonged reading. If the hypermetropia is high, there will be defective vision for both distance and near. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus. Newborns are almost invariably hypermetropic, but it gradually decreases as the newborn gets older.

Presbyopia is physiological insufficiency of accommodation associated with the aging of the eye that results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as age-related farsightedness, it affects many adults over the age of 40. A common sign of presbyopia is difficulty reading small print which results in having to hold reading material farther away. Other symptoms associated can be headaches and eyestrain. Different people will have different degrees of problems. Other types of refractive errors may exist at the same time as presbyopia. This condition is similar to hypermetropia or far-sightedness which starts in childhood and exhibits similar symptoms of blur in the vision for close objects.

An eyeglass prescription is an order written by an eyewear prescriber, such as an optometrist, that specifies the value of all parameters the prescriber has deemed necessary to construct and/or dispense corrective lenses appropriate for a patient. If an eye examination indicates that corrective lenses are appropriate, the prescriber generally provides the patient with an eyewear prescription at the conclusion of the exam.

Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification". When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, sometimes called magnification or de-magnification.
Anisometropia is a condition in which a person's eyes have substantially differing refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) is the threshold for diagnosis of the condition. Patients may have up to 3D of anisometropia before the condition becomes clinically significant due to headache, eye strain, double vision or photophobia.

Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain.
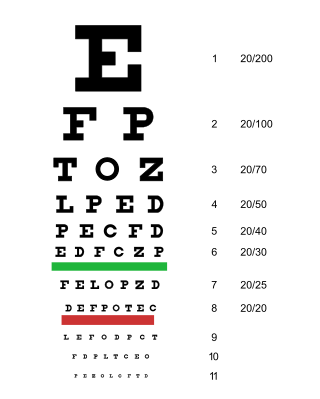
An eye examination is a series of tests performed to assess vision and ability to focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic.
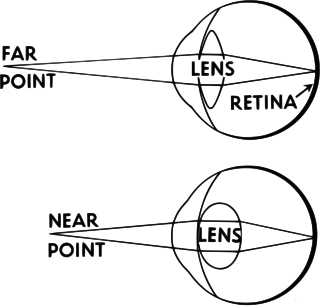
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-vergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled. The main ways animals may change focus are:
In visual perception, the far point is the farthest point at which an object can be placed for its image to be focused on the retina within the eye's accommodation. It is sometimes described as the farthest point from the eye at which images are clear. The other limit of eye's accommodation is the near point.
The amplitude of accommodation is the maximum potential increase in optical power that an eye can achieve in adjusting its focus. It refers to a certain range of object distances for which the retinal image is as sharply focussed as possible.

Emmetropia is the state of vision in which a faraway object at infinity is in sharp focus with the ciliary muscle in a relaxed state. That condition of the normal eye is achieved when the refractive power of the cornea and eye lens and the axial length of the eye balance out, which focuses rays exactly on the retina, resulting in perfectly sharp distance vision. A human eye in a state of emmetropia requires no corrective lenses for distance; the vision scores well on a visual acuity test.

In photography, a close-up lens is a simple secondary lens used to enable macro photography without requiring a specialised primary lens. They work like reading glasses, allowing a primary lens to focus more closely. Bringing the focus closer allows the photographer more possibilities.

Vertex distance is the distance between the back surface of a corrective lens, i.e. glasses (spectacles) or contact lenses, and the front of the cornea. Increasing or decreasing the vertex distance changes the optical properties of the system, by moving the focal point forward or backward, effectively changing the power of the lens relative to the eye. Since most refractions are performed at a vertex distance of 12–14 mm, the power of the correction may need to be modified from the initial prescription so that light reaches the patient's eye with the same effective power that it did through the phoropter or trial frame.
Vision of humans and other organisms depends on several organs such as the lens of the eye, and any vision correcting devices, which use optics to focus the image.
Laser blended vision is a sophisticated laser eye treatment which is used to treat presbyopia or other age-related eye conditions. It can be used to help people that simply need reading glasses, and also those who have started to need bifocal or varifocal spectacle correction due to ageing changes in the eye. It can be used for people who are also short-sighted (myopia) or long-sighted (hyperopia) and who also may have astigmatism.

Vergence-accommodation conflict (VAC), also known as accommodation-vergence conflict, is a visual phenomenon that occurs when the brain receives mismatching cues between vergence and accommodation of the eye. This commonly occurs in virtual reality devices, augmented reality devices, 3D movies, and other types of stereoscopic displays and autostereoscopic displays. The effect can be unpleasant and cause eye strain.















