
The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on 15 June 1987. It is in widespread usage on the World Wide Web due to its wide support and portability between applications and operating systems.

Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) — unofficially, the initials PNG stood for the recursive acronym "PNG's not GIF".
AmigaGuide is a hypertext document file format designed for the Amiga. Files are stored in ASCII so it is possible to read and edit a file without the need for special software.
AmigaDOS is the disk operating system of the AmigaOS, which includes file systems, file and directory manipulation, the command-line interface, and file redirection.

Interleaved Bitmap (ILBM) is an image file format conforming to the Interchange File Format (IFF) standard. The format originated on the Amiga platform, and on IBM-compatible systems, files in this format or the related PBM format are typically encountered in games from late 1980s and early 1990s that were either Amiga ports or had their graphical assets designed on Amiga machines.
Color depth or colour depth, also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp). When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color, and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Modern standards tend to use bits per component, but historical lower-depth systems used bits per pixel more often.
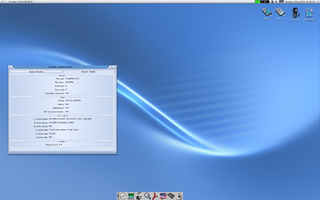
Ambient is a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS. Its development was started in 2001 by David Gerber. Its main goals were that it should be fully asynchronous, simple and fast. Ambient remotely resembles Workbench and Directory Opus Magellan trying to mix the best of both worlds.
The ICO file format is an image file format for computer icons in Microsoft Windows. ICO files contain one or more small images at multiple sizes and color depths, such that they may be scaled appropriately. In Windows, all executables that display an icon to the user, on the desktop, in the Start Menu, or in Windows Explorer, must carry the icon in ICO format.
An Image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
In computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers. It is a form of vector quantization compression.
The Apple Icon Image format is an icon format used in Apple Inc.'s macOS. It supports icons of 16 × 16, 32 × 32, 48 × 48, 128 × 128, 256 × 256, 512 × 512 points at 1x and 2x scale, with both 1- and 8-bit alpha channels and multiple image states. The fixed-size icons can be scaled by the operating system and displayed at any intermediate size.
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.

Workbench is the desktop environment and graphical file manager of AmigaOS developed by Commodore International for their Amiga line of computers. Workbench provides the user with a graphical interface to work with file systems and launch applications. It uses a workbench metaphor for representing file system organisation.
In computing, the AMIga Window Manager (amiwm) is a stacking window manager for the X Window System written by Marcus Comstedt.
Hunk is the executable file format of tools and programs of the Amiga Operating System based on Motorola 68000 CPU and other processors of the same family. This kind of executable got its name from the fact that the software programmed on Amiga is divided in its internal structure into many pieces called hunks, in which every portion could contain either code or data.
AHI is a retargetable audio subsystem for AmigaOS, MorphOS and AROS. It was created by Martin Blom in the mid-1990s to allow standardized operating system support for audio hardware other than just the native Amiga sound chip, for example 16-bit sound cards.

AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions of AmigaOS required the Motorola 68000 series of 16-bit and 32-bit microprocessors. Later versions were developed by Haage & Partner and then Hyperion Entertainment. A PowerPC microprocessor is required for the most recent release, AmigaOS 4.
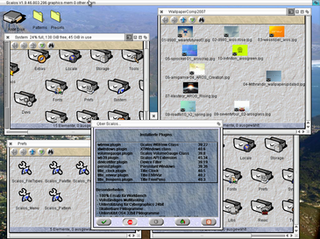
Scalos is a desktop replacement for the original Amiga Workbench GUI, based on a subset of APIs and its own front-end window manager of the same name. Scalos is NOT an AmigaOS replacement, although its name suggests otherwise. Its goal is to emulate the real Workbench behaviour, plus integrating additional functionality and an enhanced look. As stated on its website, the name "Scalos" was inspired by the fictional time-accelerated planet Scalos in the Star Trek episode "Wink of an Eye".

MagicWB is a third-party Workbench enhancer for AmigaOS. It was developed in 1992-1997 by Martin Huttenloher.
Retargetable graphics is a device driver API mainly used by third-party graphics hardware to interface with AmigaOS via a set of libraries. The software libraries may include software tools to adjust resolution, screen colors, pointers, and screenmodes. It will use available hardware and will not extend the capabilities in any way.






