
The Maple Leaf is an international passenger train service operated by Amtrak and Via Rail between Pennsylvania Station in New York City and Union Station in Toronto via the Empire Corridor. Daily service is offered in both directions; the 544-mile (875 km) trip takes approximately 12 hours, including two hours for U.S. or Canadian customs and immigration inspection at either Niagara Falls, New York, or Niagara Falls, Ontario. Although the train uses Amtrak rolling stock exclusively, the train is operated by Via Rail crews while in Canada and by Amtrak crews in the United States. Service began in 1981.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Empire Service is an Inter-city rail service operated by Amtrak within the state of New York in the United States. The brand name originated with the New York Central Railroad in 1967. Trains on the line provide frequent daily service along the 460-mile (740 km) Empire Corridor between New York City and Niagara Falls via Albany, the state capital.

The Ethan Allen Express is a daily passenger train operated by Amtrak in the United States between New York City and Burlington, Vermont, via Albany, New York. One daily round trip is operated on a 310-mile (500 km) north-south route with a 7 hour 35 minute scheduled running time. The train is subsidized by New York and Vermont for the portion north of Albany. It is named for Vermont cofounder and American Revolutionary War hero Ethan Allen.

The Lake Shore Limited is an overnight Amtrak intercity passenger train that runs between Chicago and either New York City or Boston via two sections east of Albany. The train began service in 1975; its predecessor was Amtrak's Chicago–New York Lake Shore, which operated during 1971–72. It is named for the New York Central (NYC) Lake Shore Limited, which was discontinued in 1956, and uses the NYC's former main line, part of which is now the Empire Corridor.

OnTrack was a suburban rail line that operated in Syracuse, New York, from 1994 to 2008. The line ran from the Carousel Center on the city's north side via Armory Square and Syracuse University to Colvin Street, with summer weekend service south to Jamesville, mainly using 1950s-era diesel railcars.

The Adirondack is an intercity rail passenger train operated daily, partially along the Empire Corridor, by Amtrak between New York City and Montreal. The trip takes approximately 11 hours to cover a published distance of 381 miles (613 km), traveling through the scenic Hudson Valley and along the eastern border of the Adirondack Mountains. The Adirondack is financed by the New York State Department of Transportation. Service was suspended in March 2020 due to the closure of the Canadian/American border in response to the COVID-19 pandemic; weekday service returned between New York City and Albany resumed on December 5, 2022. Full service is expected to resume by April 3, 2023.
The Cardinal is a long distance passenger train operated by Amtrak between New York Penn Station and Chicago Union Station via Philadelphia, Washington, D.C., Charlottesville, Charleston, Huntington, Cincinnati, and Indianapolis. Along with the Capitol Limited and Lake Shore Limited, it is one of three trains linking the Northeast and Chicago. Its 1,146-mile (1,844 km) trip between New York and Chicago takes 281⁄4 hours.

The Silver Meteor is a passenger train operated by Amtrak between New York City and Miami, Florida. Introduced in 1939 as the first diesel-powered streamliner between New York and Florida, it was the flagship train of the Seaboard Air Line Railroad (SAL) and one of its flagship trains of its successor, the Seaboard Coast Line Railroad (SCL). The train was transferred to Amtrak when it took over intercity passenger rail service in 1971.

The Silver Star is a passenger train operated by Amtrak on a 1,522-mile (2,449 km) route between New York City and Miami via Washington, D.C., Richmond, Virginia, Raleigh, North Carolina, Columbia, South Carolina, Savannah, Georgia, Jacksonville, Florida, and Tampa, Florida. The Silver Star and its sister train in the Silver Service brand, the Silver Meteor, are the descendants of numerous long-distance trains that operated between Florida and New York for most of the 20th century.

DeLand station is a train station in DeLand, Florida, United States. It is served by Amtrak. It is about three miles west of downtown DeLand, at the location formerly known as DeLand Junction. DeLand station was originally built in 1918, and stood across from the former Volusia County Fairgrounds. It is scheduled to be served by the SunRail commuter rail service in the future.

The Clocker was a passenger train service between Philadelphia and New York City on the Northeast Corridor at first by the Pennsylvania Railroad and later by Amtrak. The service was nicknamed the Clocker by riders as trains were scheduled to leave each terminal at the top of the hour. The name was eventually adopted into official use by Amtrak in 1981. The service was briefly renamed Acela Commuter in 1999 before the name reverted to Clocker in 2003. Amtrak discontinued the service on October 28, 2005, and it was partially replaced by additional NJ Transit express trains between Trenton, New Jersey, and New York City at times approximating the Clocker schedule.

Shore Line East (SLE) is a commuter rail service which operates along the Northeast Corridor through southern Connecticut, United States. The rail service is a fully owned subsidiary of the Connecticut Department of Transportation (CTDOT) and is operated under the CT Rail brand. SLE provides service seven days a week along the Northeast Corridor between New London and New Haven; limited through service west of New Haven to Bridgeport and Stamford has been suspended since 2020. Cross-platform transfers to Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line trains are available at New Haven for service to southwestern Connecticut and New York City. Pre-COVID, around 2,200 riders used the service on weekdays.

Michigan Services are three Amtrak passenger rail routes connecting Chicago, Illinois with the Michigan cities of Grand Rapids, Port Huron, and Detroit, and stations en route. The group is a component of the Midwest Regional Rail Initiative.
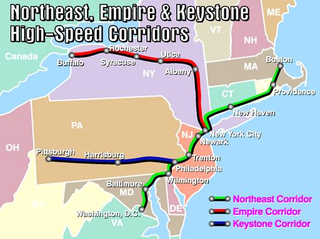
The Empire Corridor is a 461-mile (742 km) passenger rail corridor in New York State running between Penn Station in New York City and Niagara Falls, New York. Major cities on the route include Poughkeepsie, Albany, Schenectady, Amsterdam, Utica, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo. Much of the corridor was once part of the New York Central Railroad's main line.

The Framingham/Worcester Line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system runs west from Boston, Massachusetts to Worcester, Massachusetts through the MetroWest region, serving 17 station stops in Boston, Newton, Wellesley, Natick, Framingham, Ashland, Southborough, Westborough, Grafton, and Worcester. The third-longest and second-busiest line on the system, the Framingham/Worcester Line contends with interference from freight trains, and a number of non-handicapped-accessible stations. Service on the line is a mix of local and express trains serving Worcester plus short-turn Framingham locals.

Rensselaer Rail Station, signed as Albany–Rensselaer on its platforms, is a train station in Rensselaer, New York, located 1.5 miles (2.4 km) from downtown Albany across the Hudson River. Operated by the Capital District Transportation Authority, it serves as Amtrak's primary station for the Capital District. To emphasize the station's location across the river from Albany, as well as to distinguish from the Rensselaer station in Indiana, Amtrak refers to the station as "Albany–Rensselaer."

The William F. Walsh Regional Transportation Center (RTC) is an Amtrak intermodal transit station serving the Syracuse area. It is owned and operated by Intermodal Transportation Center, Inc, a subsidiary of Centro, and is also served by Greyhound Lines, Megabus, and Trailways. Local and regional bus transportation is provided by Centro. Various taxi firms provide service to the Center, as well.

The Louise M. Slaughter Rochester Station is an Amtrak intermodal transit station in Rochester, New York. Local and regional bus transportation is provided by the Rochester-Genesee Regional Transportation Authority (RGRTA). Various taxi firms service the station, as well. The station is located on the north side of Rochester, just east of High Falls on the south side of the tracks.

The Berkshire Flyer is a seasonal Amtrak passenger train service between New York City and the Berkshire Mountains in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, via the Hudson Valley. The weekly train departs Penn Station on Friday afternoons during the summer and returns on Sundays. The route's inaugural season ran from July 8 to September 5, 2022, as part of a pilot program set to run through summer 2023.




















