Related Research Articles

Ishi was the last known member of the Native American Yahi people from the present-day state of California in the United States. The rest of the Yahi were killed in the California genocide in the 19th century. Ishi, who was widely described as the "last wild Indian" in the United States, lived most of his life isolated from modern North American culture, and was the last-known Native manufacturer of stone arrowheads. In 1911, aged 50, he emerged at a barn and corral, 2 mi (3.2 km) from downtown Oroville, California.

Alfred Louis Kroeber was an American cultural anthropologist. He received his PhD under Franz Boas at Columbia University in 1901, the first doctorate in anthropology awarded by Columbia. He was also the first professor appointed to the Department of Anthropology at the University of California, Berkeley. He played an integral role in the early days of its Museum of Anthropology, where he served as director from 1909 through 1947. Kroeber provided detailed information about Ishi, the last surviving member of the Yahi people, whom he studied over a period of years. He was the father of the acclaimed novelist, poet, and writer of short stories Ursula K. Le Guin.

The Wintu are Native Americans who live in what is now Northern California. They are part of a loose association of peoples known collectively as the Wintun. There are three major groups that make up the Wintu speaking people. The Wintu, Nomlaki, and Patwin. The Wintu language is part of the Penutian language family.
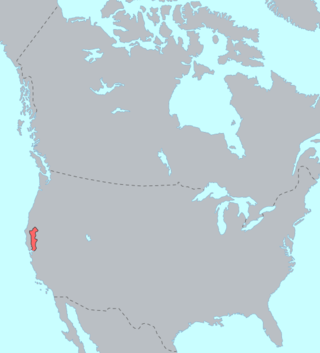
The Wintun are members of several related Native American peoples of Northern California, including the Wintu (northern), Nomlaki (central), and Patwin (southern). Their range is from approximately present-day Lake Shasta to San Francisco Bay, along the western side of the Sacramento River to the Coast Range. Each of these tribes speak one of the Wintuan languages. Linguistic and archaeological evidence suggests that the Wintun people probably entered the California area around 500 AD from what is now southern Oregon, introducing bow and arrow technology to the region. There has been carbon dating of several artifacts by UC Berkeley that dates back to around 10,000 years, and several of these artifacts have now been repatriated. Despite being a major influence on the region's history, there is still very little history on the Wintu due to centuries of genocide and displacement that still occur today along with continued destruction of sacred ceremonial and religious sites, often due to companies that ignore legal or ethical considerations.

The Pomoan, or Pomo, languages are a small family of seven languages indigenous to northern California spoken by the Pomo people, whose ancestors lived in the valley of the Russian River and the Clear Lake basin. Four languages are extinct, and all surviving languages except Kashaya have fewer than ten speakers.

Wintuan is a family of languages spoken in the Sacramento Valley of central Northern California.
The Nomlaki are a Wintun people native to the area of the Sacramento Valley, extending westward to the Coast Range in Northern California. Today some Nomlaki people are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Round Valley Indian Tribes, Grindstone Indian Rancheria or the Paskenta Band of Nomlaki Indians.

The Patwin are a band of Wintun people in Northern California. The Patwin comprise the southern branch of the Wintun group, native inhabitants of California since approximately 500.
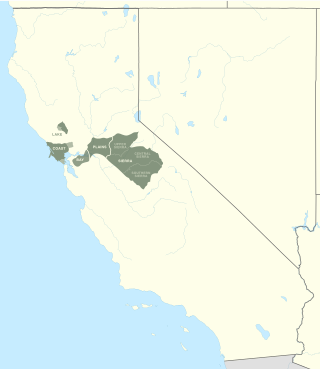
The Miwok or Miwokan languages, also known as Moquelumnan or Miwuk, are a group of endangered languages spoken in central California by the Miwok peoples, ranging from the Bay Area to the Sierra Nevada. There are seven Miwok languages, four of which have distinct regional dialects. There are a few dozen speakers of the three Sierra Miwok languages, and in 1994 there were two speakers of Lake Miwok. The best attested language is Southern Sierra Miwok, from which the name Yosemite originates. The name Miwok comes from the Northern Sierra Miwok word miw·yk meaning 'people.'

Mono is a Native American language of the Numic group of Uto-Aztecan languages, the ancestral language of the Mono people. Mono consists of two dialects, Eastern and Western. The name "Monachi" is commonly used in reference to Western Mono and "Owens Valley Paiute" in reference to Eastern Mono. In 1925, Alfred Kroeber estimated that Mono had 3,000 to 4,000 speakers. As of 1994, only 37 elderly people spoke Mono as their first language. It is classified as critically endangered by UNESCO. It is spoken in the southern Sierra Nevada, the Mono Basin, and the Owens Valley of central-eastern California. Mono is most closely related to Northern Paiute; these two are classified as the Western group of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family.

Northern Pomo is a critically endangered Pomoan language, formerly spoken by the indigenous Pomo people in what is now called California. The speakers of Northern Pomo were traditionally those who lived in the northern and largest area of the Pomoan territory. Other communities near to the Pomo were the Coast Yuki, the Huchnom, and the Athabascan. Ukiah High School first began offering Northern Pomo in the Fall 2020.

The Yuki–Wappo or Yukian languages are a small language family of western California consisting of two distantly related languages, both now extinct.

The Yana language is an extinct language that was formerly spoken by the Yana people, who lived in north-central California between the Feather and Pit rivers in what is now the Shasta and Tehama counties. The last speaker of the southernmost dialect, which is called Yahi, was Ishi, who died in 1916. When the last fluent speaker(s) of the other dialects died is not recorded. Yana is fairly well documented, mostly by Edward Sapir.
Wintu-Nomlaki traditional narratives include myths, legends, tales, and oral histories preserved by the Wintu and Nomlaki people of the western Sacramento Valley in northern California.
Yuki traditional narratives include myths, legends, tales, and oral histories preserved by the Yuki people of the upper Eel River area of northwestern California.
Kumeyaay (Kumiai), also known as Central Diegueño, Kamia, 'Iipay Aa, and Campo, is the Native American language spoken by the Kumeyaay people of southern San Diego and Imperial counties in California as well as five Kumiai communities in Baja California Norte, MX.

Northeastern Pomo, also known as Salt Pomo, is a Pomoan language of Northern California. There are no living fluent speakers. It was spoken along Stony Creek, a tributary of the Sacramento River. Northeastern was one of seven mutually unintelligible Pomoan languages spoken in Northern California. Unlike the other six Pomoan languages, Northeastern Pomo was not spoken in an area immediately contiguous with any other Pomoan-speaking area. Northeastern Pomo speakers were ringed by speakers of Yuki, Nomlaki, and Patwin; Yuki is unrelated to Pomoan or Nomlaki and Patwin, both of which are within the Wintu language family.
The Lake Miwok language is an extinct language of Northern California, traditionally spoken in an area adjacent to the Clear Lake. It is one of the languages of the Clear Lake Linguistic Area, along with Patwin, East and Southeastern Pomo, and Wappo.
Coast Miwok was one of the Miwok languages spoken in California, from San Francisco Bay to Bodega Bay. The Marin and Bodega varieties may have been separate languages. All of the population has shifted to English.

The Paskenta Band of Nomlaki Indians, or in their own language Nomlāqa Bōda, is a federally recognized tribe of Nomlaki people. The Nomlaki are Central Wintun, or River and Hill Nomlaki, an indigenous people of California, located in Tehama and Glenn counties.
References
- 1 2 Golla, Victor (2011). California Indian languages. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26667-4. OCLC 668191602.
- ↑ "UC Berkeley, BLC Audio Archive of Linguistic Fieldwork". mip.berkeley.edu. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ↑ E. G. Gudde 1998 in William Bright: Native American Place Names of the United States, Norman, Okla., 2004, University of Oklahoma Press.