
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats, with Turtle currently being the most widely used notation.

A topic map is a standard for the representation and interchange of knowledge, with an emphasis on the findability of information. Topic maps were originally developed in the late 1990s as a way to represent back-of-the-book index structures so that multiple indexes from different sources could be merged. However, the developers quickly realized that with a little additional generalization, they could create a meta-model with potentially far wider application. The ISO/IEC standard is formally known as ISO/IEC 13250:2003.
The Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies. Ontologies are a formal way to describe taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects.
RDF Schema (Resource Description Framework Schema, variously abbreviated as RDFS, RDF(S), RDF-S, or RDF/S) is a set of classes with certain properties using the RDF extensible knowledge representation data model, providing basic elements for the description of ontologies. It uses various forms of RDF vocabularies, intended to structure RDF resources. RDF and RDFS can be saved in a triplestore, then one can extract some knowledge from them using a query language, like SPARQL.
SPARQL is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. It was made a standard by the RDF Data Access Working Group (DAWG) of the World Wide Web Consortium, and is recognized as one of the key technologies of the semantic web. On 15 January 2008, SPARQL 1.0 was acknowledged by W3C as an official recommendation, and SPARQL 1.1 in March, 2013.

FOAF is a machine-readable ontology describing persons, their activities and their relations to other people and objects. Anyone can use FOAF to describe themselves. FOAF allows groups of people to describe social networks without the need for a centralised database.
RDFa or Resource Description Framework in Attributes is a W3C Recommendation that adds a set of attribute-level extensions to HTML, XHTML and various XML-based document types for embedding rich metadata within Web documents. The Resource Description Framework (RDF) data-model mapping enables its use for embedding RDF subject-predicate-object expressions within XHTML documents. It also enables the extraction of RDF model triples by compliant user agents.
In computing, Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML.
Redland is a set of free software libraries written in C that provide support for the Resource Description Framework (RDF), created by Dave Beckett.
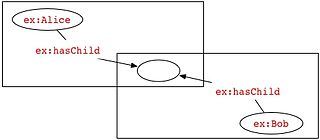
In RDF, a blank node is a node in an RDF graph representing a resource for which a URI or literal is not given. The resource represented by a blank node is also called an anonymous resource. According to the RDF standard a blank node can only be used as subject or object of an RDF triple.
In computing, a CURIE defines a generic, abbreviated syntax for expressing Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs). It is an abbreviated URI expressed in a compact syntax, and may be found in both XML and non-XML grammars. A CURIE may be considered a datatype.

In computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database.
SPARUL, or SPARQL/Update, was a declarative data manipulation language that extended the SPARQL 1.0 query language standard. SPARUL provided the ability to insert, delete and update RDF data held within a triple store or quad store. SPARUL was originally written by Hewlett-Packard and has been used as the foundation for the current W3C recommendation entitled SPARQL 1.1 Update. With the publication of SPARQL 1.1, SPARUL is superseded and should only be consulted as a source of inspiration for possible future refinements of SPARQL, but not for real-world applications.
N-Triples is a format for storing and transmitting data. It is a line-based, plain text serialisation format for RDF graphs, and a subset of the Turtle format. N-Triples should not be confused with Notation3 which is a superset of Turtle. N-Triples was primarily developed by Dave Beckett at the University of Bristol and Art Barstow at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
TriG is a serialization format for RDF graphs. It is a plain text format for serializing named graphs and RDF Datasets which offers a compact and readable alternative to the XML-based TriX syntax.

Named graphs are a key concept of Semantic Web architecture in which a set of Resource Description Framework statements are identified using a URI, allowing descriptions to be made of that set of statements such as context, provenance information or other such metadata.
XHTML+RDFa is an extended version of the XHTML markup language for supporting RDF through a collection of attributes and processing rules in the form of well-formed XML documents. XHTML+RDFa is one of the techniques used to develop Semantic Web content by embedding rich semantic markup. Version 1.1 of the language is a superset of XHTML 1.1, integrating the attributes according to RDFa Core 1.1. In other words, it is an RDFa support through XHTML Modularization.
Cwm is a general-purpose data processing software for the Semantic Web, similar to sed or awk for text files or XSLT for XML. It is a forward chaining semantic reasoner that can be used for querying, checking, transforming and filtering information. Its core language is RDF, extended to include rules, it can use RDF/XML or RDF/N3 serializations.
JSON-LD is a method of encoding linked data using JSON. One goal for JSON-LD was to require as little effort as possible from developers to transform their existing JSON to JSON-LD. JSON-LD allows data to be serialized in a way that is similar to traditional JSON. It was initially developed by the JSON for Linking Data Community Group before being transferred to the RDF Working Group for review, improvement, and standardization, and is currently maintained by the JSON-LD Working Group. JSON-LD is a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation.




